ListSourceDataAdapter Class
The data adapter that provides the means to bind the Map control to data.
Namespace: DevExpress.XtraMap
Assembly: DevExpress.XtraMap.v25.2.dll
NuGet Package: DevExpress.Win.Map
Declaration
[ListSourceDataAdapter.ListSourceBindingProperties]
public class ListSourceDataAdapter :
DataSourceAdapterBase,
IListSourceDataAdapter,
IDataSourceDataAdapter,
IDataAdapter,
IDisposableExamples
Display Custom Elements on a Map
This example binds a Map control to data. This data is stored in an external XML file that contains information about wrecked ships, including ship coordinates.
In this example, the map control generates ship images based on data from the data source, along with a description for each image in a tooltip.
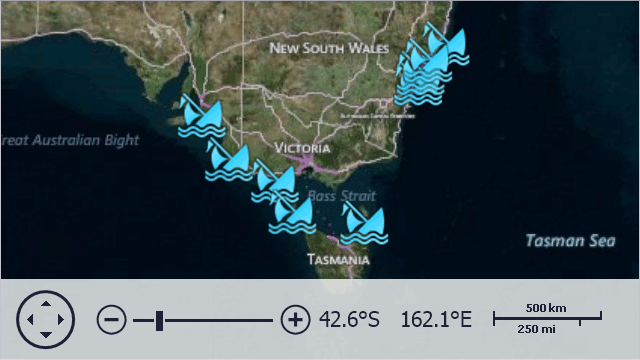
Follow the steps below to create a map as on the image above:
- Create a
ListSourceDataAdapterobject and assign it to the VectorItemsLayer.Data property. - Create a data source (in this example, the LoadData method generates a data table object to be used as a data source) and assign it to the data adapter’s DataSource property.
- To define names of data fields that contain information about latitude and longitude of vector items, specify appropriate values for MapItemMappingInfo.Latitude and MapItemMappingInfo.Longitude properties of the object, returned by the ListSourceDataAdapter.Mappings property.
- Once complete, define the names of other data fields that provide additional information for vector items. Note that these data fields values are accessible via attributes - and so you should specify attribute mapping via the DataSourceAdapterBase.AttributeMappings object.
Also, this sample illustrates how to customize tooltips using the MapItemsLayerBase.ToolTipPattern property.
Note
For more information on how to add images on the map, refer to the following help topic: Generate Vector Items Automatically.
// In the Form's constructor.
object data = LoadData(@"..\..\Data\Ships.xml");
// Create a vector layer.
map.Layers.Add(new VectorItemsLayer() {
Data = CreateAdapter(data),
ToolTipPattern = "<b>{Name} ({Year})</b> \r\n{Description}",
ItemImageIndex = 0
});
// Creates an adapter for the map's vector layer.
private IMapDataAdapter CreateAdapter(object source) {
ListSourceDataAdapter adapter = new ListSourceDataAdapter();
adapter.DataSource = source;
adapter.Mappings.Latitude = "Latitude";
adapter.Mappings.Longitude = "Longitude";
adapter.AttributeMappings.Add(new MapItemAttributeMapping() { Member = "Name", Name = "Name" });
adapter.AttributeMappings.Add(new MapItemAttributeMapping() { Member = "Year", Name = "Year" });
adapter.AttributeMappings.Add(new MapItemAttributeMapping() { Member = "Description", Name = "Description" });
return adapter;
}
// Loads data from a XML file.
private List<ShipwreckData> LoadData(string path) {
return XDocument.Load(path).Element("Ships").Elements("Ship")
.Select(e => new ShipwreckData(
year: Convert.ToInt32(e.Element("Year").Value, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture),
name: e.Element("Name").Value,
description: e.Element("Description").Value,
latitude: Convert.ToDouble(e.Element("Latitude").Value, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture),
longitude: Convert.ToDouble(e.Element("Longitude").Value, CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)
))
.ToList();
}
public class ShipwreckData {
public int Year { get; }
public string Name { get; }
public string Description { get; }
public double Latitude { get; }
public double Longitude { get; }
public ShipwreckData(int year, string name, string description, double latitude, double longitude) {
this.Year = year;
this.Name = name;
this.Description = description;
this.Latitude = latitude;
this.Longitude = longitude;
}
}
Create Polylines From a Collection of Points
The following example shows how to create map polylines based on a collection of coordinates, and configure the polyline color and thickness.

Follow the steps below to create a vector layer with polylines:
Create a VectorItemsLayer object and add it to the map’s Layers collection.
Create a
ListSourceDataAdapterobject and assign it to the vector layer’s Data property.Specify the adapter’s DataSource. The example below uses a list of objects that store information about lines, such as coordinate points.
Set the adapter’s DefaultMapItemType property to
MapItemType.Polylineto create polylines based on the data that the adapter loads.Add a MapPolylinePointCollectionMapping object to the adapter’s PropertyMappings. Specify the following mapping properties to define source fields from which the adapter should obtain polyline point data:
- PointSourceMember – Specifies the data member that stores polylines points.
- XCoordinateMember – Specifies the point source data member that contains x-coordinates of points (longitudes for geo points).
- YCoordinateMember – Specifies the point source data member that contains y-coordinates of points (latitudes for geo points).
To customize polyline appearance settings, use mappings that correspond to map item properties. For example, add the following mappings to the adapter’s PropertyMappings collection to specify the MapItem.Stroke and MapItem.StrokeWidth properties:
You can use a mapping’s DefaultValue property to explicitly specify a map item property value (for example,
MapItem.Stroke), or you can use the mapping’s Member property to map the property to a source data member.Call the MapControl.ZoomToFitLayerItems() method in the vector layer’s DataLoaded event handler to specify the map viewport boundaries so that they include all polylines.
The code below creates two polylines:
using DevExpress.XtraMap;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CreateMapLines {
public partial class Form1 : Form {
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
// Create a background image layer and add it to the map.
ImageLayer imageLayer = new ImageLayer();
imageLayer.DataProvider = new BingMapDataProvider {
BingKey = "Insert your Bing Maps key here.",
Kind = BingMapKind.RoadGray
};
mapControl1.Layers.Add(imageLayer);
// Create a vector layer and add it to the map.
VectorItemsLayer vectorLayer = new VectorItemsLayer();
mapControl1.Layers.Add(vectorLayer);
// Create a ListSourceDataAdapter.
// Specify its data source.
// Configure mappings.
// Assign the adapter to the vector layer.
ListSourceDataAdapter adapter = new ListSourceDataAdapter();
adapter.DataSource = GetLines();
adapter.DefaultMapItemType = MapItemType.Polyline;
adapter.PropertyMappings.Add(new MapPolylinePointCollectionMapping {
XCoordinateMember = "Longitude",
PointSourceMember = "PointSource",
YCoordinateMember= "Latitude"
});
adapter.PropertyMappings.Add(new MapItemStrokeMapping { Member = "Color" });
adapter.PropertyMappings.Add(new MapItemStrokeWidthMapping { DefaultValue = 4 });
vectorLayer.Data = adapter;
vectorLayer.DataLoaded += OnVectorLayerDataLoaded;
}
private void OnVectorLayerDataLoaded(object sender, DataLoadedEventArgs e) {
// Zooms the map to fit all created lines.
mapControl1.ZoomToFitLayerItems();
}
public List<Line> GetLines() {
List<Line> lines = new List<Line>();
Line line1 = new Line();
line1.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-5.93107, -35.112723));
line1.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-10.13507, -25.15696));
line1.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-5.183714, -8.911391));
line1.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(4.253438, 5.47072));
line1.Color = Color.Green;
lines.Add(line1);
Line line2 = new Line();
line2.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(1, 0.5));
line2.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-25, -15));
line2.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-15, -25));
line2.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-22.1531, -41.45984));
line2.Color = Color.Red;
lines.Add(line2);
return lines;
}
}
public struct Coordinate {
public double Latitude { get; }
public double Longitude { get; }
public Coordinate(double lat, double lon) {
Latitude = lat;
Longitude = lon;
}
}
public class Line {
public Color Color { get; set; }
public List<Coordinate> PointSource { get; } = new List<Coordinate>();
}
}
Create Polygons From a Collection of Points
The following example shows how to create map polygons based on a collection of coordinates, and configure the polygon stroke and fill colors.

Follow the steps below to create a vector layer with polygons:
Create a VectorItemsLayer object and add it to the map’s Layers collection.
Create a
ListSourceDataAdapterobject and assign it to the vector layer’s Data property.Specify the adapter’s DataSource. The example below uses a list of objects that store information about polygons, such as coordinate points.
Set the adapter’s DefaultMapItemType property to
MapItemType.Polygonto create polygon based on the data that the adapter loads.Add a MapPolygonPointCollectionMapping object to the adapter’s PropertyMappings. Specify the following mapping properties to define source fields from which the adapter should obtain polygon point data:
- PointSourceMember – Specifies the data member that stores polygon points.
- XCoordinateMember – Specifies the point source data member that contains x-coordinates of points (longitudes for geo points).
- YCoordinateMember – Specifies the point source data member that contains y-coordinates of points (latitudes for geo points).
To customize polygon appearance settings, use mappings that correspond to map item properties. For example, add the following mappings to the adapter’s PropertyMappings collection to specify the MapItem.Stroke, MapItem.Fill, and MapItem.StrokeWidth properties:
You can use a mapping’s DefaultValue property to explicitly specify a map item property value (for example,
MapItem.Stroke), or you can use the mapping’s Member property to map the property to a source data member.Call the MapControl.ZoomToFitLayerItems() method in the vector layer’s DataLoaded event handler to specify the map viewport boundaries so that they include all polygons.
The code below creates two polygons:
using DevExpress.XtraMap;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CreateMapPolygons {
public partial class Form1 : Form {
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
// Create a background image layer and add it to the map.
ImageLayer imageLayer = new ImageLayer();
imageLayer.DataProvider = new BingMapDataProvider {
BingKey = "Insert your Bing Maps key here.",
Kind = BingMapKind.RoadGray
};
mapControl1.Layers.Add(imageLayer);
// Create a vector layer and add it to the map.
VectorItemsLayer vectorLayer = new VectorItemsLayer();
mapControl1.Layers.Add(vectorLayer);
// Create a ListSourceDataAdapter.
// Specify its data source.
// Configure mappings.
// Assign the adapter to the vector layer.
ListSourceDataAdapter adapter = new ListSourceDataAdapter();
adapter.DataSource = GetPolygons();
adapter.DefaultMapItemType = MapItemType.Polygon;
adapter.PropertyMappings.Add(new MapPolygonPointCollectionMapping {
XCoordinateMember = "Longitude",
PointSourceMember = "PointSource",
YCoordinateMember = "Latitude"
});
adapter.PropertyMappings.Add(new MapItemStrokeMapping { Member = "StrokeColor" });
adapter.PropertyMappings.Add(new MapItemFillMapping { Member = "FillColor" });
adapter.PropertyMappings.Add(new MapItemStrokeWidthMapping { DefaultValue = 4 });
vectorLayer.Data = adapter;
vectorLayer.DataLoaded += OnVectorLayerDataLoaded;
}
private void OnVectorLayerDataLoaded(object sender, DataLoadedEventArgs e) {
// Zooms the map so that it displays all created polygons.
mapControl1.ZoomToFitLayerItems(paddingFactor: 0.5);
}
public List<Polygon> GetPolygons() {
List<Polygon> polygons = new List<Polygon>();
Polygon polygon1 = new Polygon();
polygon1.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-3.5, -30.3));
polygon1.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-2.4, -9.8));
polygon1.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-9.0, -19.4));
polygon1.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-12.9, -31.1));
polygon1.StrokeColor = Color.Green;
polygon1.FillColor = Color.White;
polygons.Add(polygon1);
Polygon polygon2 = new Polygon();
polygon2.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-13.5, -9.6));
polygon2.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-17.5, 0.3));
polygon2.PointSource.Add(new Coordinate(-21.8, -7.8));
polygon2.StrokeColor = Color.Red;
polygon2.FillColor = Color.DarkGray;
polygons.Add(polygon2);
return polygons;
}
}
public struct Coordinate {
public double Latitude { get; }
public double Longitude { get; }
public Coordinate(double lat, double lon) {
Latitude = lat;
Longitude = lon;
}
}
public class Polygon {
public Color StrokeColor { get; set; }
public Color FillColor { get; set; }
public List<Coordinate> PointSource { get; } = new List<Coordinate>();
}
}