HeatmapDensityBasedAlgorithm Class
The algorithm that allows the Map Control to plot a heatmap based on the density of heatmap points.
Namespace: DevExpress.XtraMap
Assembly: DevExpress.XtraMap.v25.2.dll
NuGet Package: DevExpress.Win.Map
Declaration
public class HeatmapDensityBasedAlgorithm :
HeatmapAlgorithmBase,
IDensityBasedAlgorithm,
IHeatmapAlgorithmRemarks
When you use the HeatmapDensityBasedAlgorithm to create a heatmap, the Map Control aggregates points into areas of different colors. An area with high point density is painted red. A green area indicates that this region contains a low number of points. The Map Control re-aggregates heatmap points when you zoom in/out a map. For this reason, areas of aggregated points can change their colors.

To change the predefined color scheme, specify the HeatmapProvider.Colorizer property. The first item in the ChoroplethColorizer.ColorItems collection defines a color for areas with low point density, the last item specifies the color of areas with high point density.
Example
This example shows how to create a heatmap layer for the Map Control.
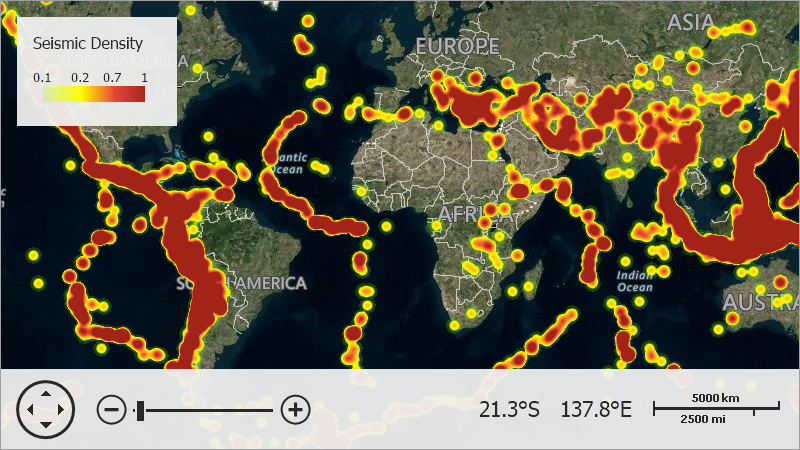
- Create an ImageLayer object and add it to the MapControl.Layers collection.
- Assign a HeatmapProvider object to the ImageLayer.DataProvider property.
using DevExpress.XtraMap;
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace HeatMapSample {
public partial class Form1 : Form {
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) {
ImageLayer bingLayer = new ImageLayer();
bingLayer.DataProvider = new BingMapDataProvider { BingKey = "Your Bing Maps key here." };
mapControl1.Layers.Add(bingLayer);
ChoroplethColorizer colorizer = new ChoroplethColorizer();
colorizer.RangeStops.AddRange(new double[] { 0.1, 0.2, 0.7, 1 });
colorizer.ColorItems.Add(new ColorizerColorItem(Color.FromArgb(50, 128, 255, 0)));
colorizer.ColorItems.Add(new ColorizerColorItem(Color.FromArgb(255, 255, 255, 0)));
colorizer.ColorItems.Add(new ColorizerColorItem(Color.FromArgb(255, 234, 72, 58)));
colorizer.ColorItems.Add(new ColorizerColorItem(Color.FromArgb(255, 162, 36, 25)));
colorizer.ApproximateColors = true;
HeatmapDataSourceAdapter adapter = new HeatmapDataSourceAdapter();
adapter.Mappings.XCoordinate = "glon"; // The data source field name that provides x-coordinates.
adapter.Mappings.YCoordinate = "glat"; // The data source field name that provides y-coordinates.
adapter.DataSource = LoadData("../../Data/Earthquakes.xml", "Row");
HeatmapProvider provider = new HeatmapProvider();
provider.PointSource = adapter;
provider.Algorithm = new HeatmapDensityBasedAlgorithm { PointRadius = 8 };
provider.Colorizer = colorizer;
ImageLayer heatmapLayer = new ImageLayer();
heatmapLayer.DataProvider = provider;
mapControl1.Layers.Add(heatmapLayer);
ColorScaleLegend legend = new ColorScaleLegend();
legend.Header = "Seismic Density";
legend.EnableGradientScale = true;
legend.Layer = heatmapLayer;
legend.HeaderStyle.Font = new Font("Tahoma", 12F);
mapControl1.Legends.Add(legend);
}
DataTable LoadData(string filePath, string tableName) {
DataSet xmlDataSet = new DataSet("XML DataSet");
xmlDataSet.ReadXml(filePath);
return xmlDataSet.Tables[tableName];
}
}
}