Advanced Filtering, Custom Filtering, Search
- 24 minutes to read
Filter Expressions
A filter expression is a formula (or a set of formulas) that specifies how data should be filtered. Each expression contains three parts:
- A data field whose values should be filtered.
- A filter value that should be compared to records stored in the data field.
- An operator that compares data field values with a filter value.
For example, the following expression selects all “Count” data field values that are greater than 5 but less than 20:
[Count] Between ('5', '20')
Filter Expression Syntax
The table below enumerates most frequently used operators. To learn more, see the following topic: Criteria Language Syntax.
Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
= | Equals — Selects data field values that equal the filter value. | [OrderDate] = #2016-01-01# |
<> | Does not equal — Selects data field values that are not equal to the filter value. | [OrderDate] <> #2016-01-01# |
> | Is greater than — Selects data field values that are greater than the filter value. | [OrderDate] > #2016-01-01# |
>= | Is greater than or equal to — Selects data field values that are greater than or equal to the filter value. | [OrderDate] >= #2016-01-01# |
<= | Is less than or equal to — Selects data field values that are less than or equal to the filter value. | [OrderDate] >= #2016-01-01# |
< | Is less than — Selects data field values that are less than the filter value. | [OrderDate] >= #2016-01-01# |
Between | Is between — Selects data field values that belong to the specific value interval. | [CustomerID] Between (‘1’, ‘100’) |
Not Between | Is not between — Selects data field values that are outside the specific value interval. | Not [CustomerID] Between (‘1’, ‘100’) |
Contains | Contains — Selects data field values that contain the filter value. | Contains([ShipCountry], ‘land’) |
Not Contains | Does not contain — Selects data field values that do not contain the filter value. | Not Contains([ShipCountry], ‘land’) |
Starts with | Begins with — Selects data field values that start with the filter value. | StartsWith([ShipCountry], ‘G’) |
Ends with | Ends with — Selects data field values that end with the filter value. | Ends with([ShipCountry], ‘ia’) |
In | Is any of — Selects data field values that equal any of the entered filter values. | [ShipCountry] In (‘Germany’, ‘Italy’, ‘USA’) |
Not In | Is none of — Selects data field values that do not equal any of the entered filter values. | Not [ShipCountry] In (‘Germany’, ‘Italy’, ‘USA’) |
Like | Is like — Selects data field values that contain the filter value. Accepts wildcards: ‘_’ to replace a single character, ‘%’ to replace any number of characters. | [OrderDate] Like ‘%2011’ same as Contains ([OrderDate], ‘2011’) |
Not Like | Is not like — Selects data field values that do not contain the filter value. Accepts wildcards: ‘_’ to replace a single character, ‘%’ to replace any number of characters. | Not [OrderID] Like ‘103__’ same as Not [OrderID] Between (‘10300’, ‘10399’) |
Is Null | Is null — Selects null values. | [ShipRegion] Is Null |
Is Not Null | Is not null — Excludes null values. | [ShipRegion] Is Not Null |
- String values must be enclosed within single quote characters. If a single quote character needs to be included as a literal to a filter, it must be doubled (for example, [ProductID] LIKE ‘Uncle Bob’’s%’).
Date-time values must be wrapped with the ‘#’ characters and displayed using a culture-independent (invariant) format. The invariant culture is based on the English culture, but some of the idiosyncratic English formats have been replaced by more globally-accepted formats. Below are some of the culture-independent date-time formats.
MM/dd/yyyy — 07/30/2008
dd MMM yyyy — 30 JUL 2008
yyyy-MM-dd — 2008-07-30
yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss — 2008-07-30T22:59:59
yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ssZ — 2008-07-30 15:59:59Z
- DateOnly and TimeOnly values must meet requirements for Date-time values and also be enclosed within ‘!’ characters (for example,
[Date] = #!2024-02-27!#).
Filter Data in Code
ColumnView.ActiveFilterString and ColumnView.ActiveFilter
These properties allow you to pass a filter expression as a string to apply a data filter to the entire View. The following sample filters data by the “Order Date” and “Ship Region” fields.
gridView1.ActiveFilterString = "[OrderDate] Between (#01 JAN 2010#, #01 DEC 2010#) And [ShipRegion] Is not null";
Call this method to remove any filter conditions applied to the View’s columns.
This property allows you to filter data by specific columns. The FilterInfo property accepts objects of the ColumnFilterInfo type.
string filterString = "[UnitPrice] > 20 AND [UnitPrice] < 30 AND [InStock] = true";
gridView.Columns["UnitPrice"].FilterInfo = new ColumnFilterInfo(filterString);
A ColumnFilterInfo object can hold any valid filter expression, including an expression that filters another column’s data.
string filterString = "[ShipCountry] = 'Canada'";
gridView1.Columns["ShipCity"].FilterInfo = new ColumnFilterInfo(filterString);
ColumnView.ActiveFilter.NonColumnFilter
Utilize this property to apply a filter expression that is not associated with one specific Grid column. As a result, end users cannot use the column’s drop-down filter to clear or modify this filter.
Allows you to hide/show specific rows (that exist in the data source) based on a condition regardless of the grid’s filter.
Note
Filtering the data displayed in the Grid Control does not filter the data in the data source. To obtain data source records that correspond to rows displayed in the Grid Control, you need to manually iterate over visible data rows. Use GetDataRow and GetFocusedDataRow() methods.
Read the following topic for additional information: Traversing Rows.
Override Current Grid Filters
Handle the ColumnView.CustomRowFilter event to manually show or hide Data Grid rows, even if they do not match active Grid filters. The following sample makes rows with the “USA” value in the “Country” column always visible:
using DevExpress.XtraGrid.Views.Base;
private void gridView1_CustomRowFilter(object sender, RowFilterEventArgs e) {
ColumnView view = sender as ColumnView;
string country = view.GetListSourceRowCellValue(e.ListSourceRow, "Country").ToString();
// Check whether the current row contains "USA" in the "Country" field.
if (country == "USA") {
// Make the current row visible.
e.Visible = true;
// Prevent default processing, so that the row is visible
// regardless of the view's filter.
e.Handled = true;
}
}
Handle the ColumnView.SubstituteFilter event to update or replace the filter that is about to be applied with a custom filter.
The code below shows how to handle the SubstituteFilter event to update the filter applied in the grid with a filter selected in a combo box.
using DevExpress.Data.Filtering;
using DevExpress.Data;
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) {
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
ds.ReadXml("nwind.xml");
this.GridControl.DataSource = ds;
this.GridControl.DataMember = "Orders";
this.GridView.ActiveFilterCriteria = CriteriaOperator.Parse("Freight > 0");
}
private void GridView_SubstituteFilter(object sender, SubstituteFilterEventArgs e) {
e.Filter &= CriteriaOperator.Parse("getyear(OrderDate) = ?", Convert.ToInt32(this.beiShowByYear.EditValue));
}
private void beiShowByYear_EditValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) {
CriteriaOperator filter = this.GridView.ActiveFilterCriteria;
this.GridView.BeginDataUpdate();
try {
this.GridView.ActiveFilterCriteria = null;
this.GridView.ActiveFilterCriteria = filter;
} finally {
this.GridView.EndDataUpdate();
}
}
Filter Modes: Display Text vs Value
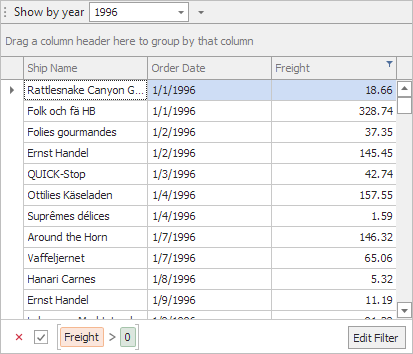
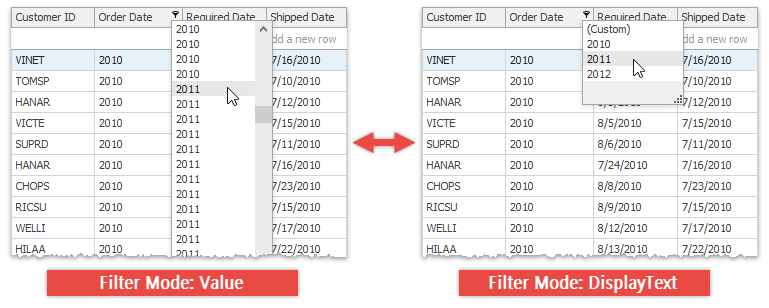
The figure below illustrates a classic drop-down menu invoked for a DateTime “Order Date” column. This column has a custom ‘yyyy’ display format, which leaves only years visible. Since Data Grid filters data by values, and all underlying cell values are unique, the pop-up filter menu displays multiple identical items (left figure).
Utilize the GridColumn.FilterMode property to switch to the DisplayText filter mode. In this mode, the Data Grid filter menus are populated with display text strings of records (right figure).
An automatic filter row has its own dedicated property to change the filter mode: WindowsFormsSettings.ColumnAutoFilterMode.
To filter non-string column values with string operators (“Contains”, “Starts With”, and others), set the FilterMode property to DisplayText. This technique is applicable to other DevExpress data-aware controls that support the filter feature (Gantt Control, Vertical Grid, TreeList).
Customize Filter Drop-down Menus
ColumnView.ShowFilterPopupExcel, ExcelFilterOptions
Allow you to customize Excel-style menus. The sample below demonstrates how to remove the “Is Null” and “Is Not Null” items.
// Customizes the drop-down menu for one specific Data Grid
void gridView1_ShowFilterPopupExcel(object sender, FilterPopupExcelEventArgs e) {
e.ShowNulls = false;
}
// Customizes the drop-down menu for all Data Grid controls within an application
DevExpress.Utils.Filtering.ExcelFilterOptions.Default.ShowNulls = false;
ColumnView.FilterPopupExcelData
Allows you to modify and remove items within Excel-styled filter drop-downs, as well as add custom items that apply specific filter conditions. The code snippet below adds custom filter options to the “Modification” and “MPG City” columns.
void gridView_FilterPopupExcelData(object sender, Views.Grid.FilterPopupExcelDataEventArgs e) {
if(e.Column == bcModification) {
e.AddFilter("Automatic Transmission (6-speed)", "Contains([" + e.Column.FieldName + "], '6A')");
e.AddFilter("Automatic Transmission (8-speed)", "Contains([" + e.Column.FieldName + "], '8A')");
e.AddFilter("Manual Transmission (6-speed)", "Contains([" + e.Column.FieldName + "], '6M')");
e.AddFilter("Manual Transmission (7-speed)", "Contains([" + e.Column.FieldName + "], '7M')");
e.AddFilter("Variomatic Transmission", "Contains([" + e.Column.FieldName + "], 'VA')");
e.AddFilter("Limited Edition", "Contains([" + e.Column.FieldName + "], 'Limited')");
}
if(e.Column == bcMPGCity) {
e.AddFilter("Fuel Economy (High)", "[" + e.Column.FieldName + "]<=15");
e.AddFilter("Fuel Economy (Medium)", "[" + e.Column.FieldName + "]>15 AND [" + e.Column.FieldName + "]<25");
e.AddFilter("Fuel Economy (Low)", "[" + e.Column.FieldName + "]>=25");
}
}
ColumnView.QueryCustomFunctions
Do the following to create a custom filter function (for example, ‘discount is more than 15%’) and add this function to Excel-style pop-up filter menus and the filter editor:
- Implement a custom function.
- Register the function.
- Add the function to pop-up filter menus and the filter editor in a QueryCustomFunctions event handler.
using DevExpress.Data.Filtering;
IsBlackFridayDiscountFunction.Register();
gridView1.QueryCustomFunctions += OnQueryCustomFunctions;
void OnQueryCustomFunctions(object sender, CustomFunctionEventArgs e) {
if(e.PropertyName == "Discount")
e.Add(IsBlackFridayDiscountFunction.FunctionName);
}
public class IsBlackFridayDiscountFunction : ICustomFunctionDisplayAttributes {
// See the QueryCustomFunctions event for the complete implementation.
}
Tip
To add custom functions to filter menus and filter editors of all DevExpress controls in the application, use the static (Shared in VB) QueryCustomFunctions event.
Regular filter menus display the “(Custom)” item. When users click this item, a Filter Dialog is invoked that allows them to build filter criteria from multiple simple expressions. The CustomFilterDialog event allows you to customize this dialog or change the “(Custom)” item’s action. The code sample below suppresses the Filter Dialog and applies a $10 to $30 price filter when users click “(Custom)” for the “Unit Price” column.
private void gridView_CustomFilterDialog(object sender, DevExpress.XtraGrid.Views.Grid.CustomFilterDialogEventArgs e) {
if (e.Column.FieldName != "UnitPrice") return;
string filterSting = "[UnitPrice] > 10 AND [UnitPrice] < 30";
string displayText = "[UnitPrice] > $10.00 AND [UnitPrice] < $30.00";
ColumnFilterInfo columnFilter = new ColumnFilterInfo(filterSting, displayText);
e.FilterInfo = columnFilter;
e.Handled = true;
}
ColumnView.ShowFilterPopupListBox
Handle this event to modify regular drop-down list menus. The sample below demonstrates how to add the “Important” item to a filter menu invoked for the “Priority” column. This custom filter selects records with Medium and High priorities.
private void gridView_ShowFilterPopupListBox(object sender, FilterPopupListBoxEventArgs e) {
if (e.Column.FieldName != "Priority") return;
// Get the first value item's index.
int index;
for (index = 0; index < e.ComboBox.Items.Count; index++) {
object item = e.ComboBox.Items[index];
if (item is FilterItem) {
object itemValue = ((FilterItem)item).Value;
if (itemValue is FilterItem || itemValue is ColumnFilterInfo) continue;
break;
}
}
// Create a filter criterion to select records with the "High" and "Medium" priorities.
string filterString = "([Priority] == 3 OR [Priority] == 2)";
string filterDisplayText = "[Priority] == High OR [Priority] == Medium";
ColumnFilterInfo filterInfo = new ColumnFilterInfo(filterString, filterDisplayText);
e.ComboBox.Items.Insert(index, new FilterItem("Important", filterInfo));
}
ColumnView.ShowFilterPopupCheckedListBox
This event allows you to customize checked list box menus. The code below removes items that start with “Help” and disables items that start with “Data”.
private void gridView_ShowFilterPopupCheckedListBox(object sender, FilterPopupCheckedListBoxEventArgs e) {
if (e.Column.FieldName != "Name") return;
for (int i = 0; i < e.CheckedComboBox.Items.Count; i++) {
CheckedListBoxItem item = e.CheckedComboBox.Items[i];
string itemValue = (string)(item.Value as FilterItem).Value;
// Disable checked items that start with "Data".
if (itemValue.StartsWith("Data"))
e.CheckedComboBox.Items[i].Enabled = false;
// Remove checked items that start with "Help".
if (itemValue.StartsWith("Help")) {
e.CheckedComboBox.Items.Remove(item);
i--;
}
}
}
ColumnView.ShowFilterPopupDate
This event allows you to customize calendar filters. The code sample below adds a custom “Last Year” filter item to calendar menus.
private void gridView1_ShowFilterPopupDate(object sender, FilterPopupDateEventArgs e) {
if(e.Column.FieldName != "Date") return;
e.List.Clear();
DateTime firstDayOfThisYear = new DateTime(DateTime.Today.Year, 1, 1);
DateTime firstDayOfLastYear = firstDayOfThisYear.AddYears(-1);
CriteriaOperator lastYear = new BinaryOperator(
e.Column.FieldName, firstDayOfLastYear, BinaryOperatorType.GreaterOrEqual);
CriteriaOperator thisYear = new BinaryOperator(
e.Column.FieldName, firstDayOfThisYear, BinaryOperatorType.Less);
CriteriaOperator crit = new GroupOperator(GroupOperatorType.And, lastYear, thisYear);
e.List.Add(new DevExpress.XtraEditors.FilterDateElement("Last Year", "", crit));
}
Automatic Filter Row API
GridOptionsFilter.AllowAutoFilterConditionChange
This property specifies whether the auto-filter row’s condition selector is visible.
OptionsColumnFilter.AutoFilterCondition
This property specifies the filter criteria operator for this column (“Equals”, “Like”, “Greater”, etc.).
OptionsColumnFilter.ImmediateUpdateAutoFilter
If this setting is enabled, the Data Grid filters its records immediately after a user modifies the filter condition. Otherwise, the filter will not be applied until a user presses the Enter key or moves focus to another cell.
GridView.ShowAutoFilterConditionsMenu
Call this method from code to invoke the automatic filter row popup menu for the specific column.
GridView.SetAutoFilterValue, GridView.GetAutoFilterValue
These methods allow you to retrieve the currently applied auto-filter row condition and apply a new one from code.
GridView.ResetAutoFilterConditions
This method clears all data filters applied through the automatic filter row.
Filter Attribute Support
In code-first data sources, you can mark specific properties with DevExpress filter attributes to change editors that appear inside Excel-style filter menus. For example, in the code sample below the integer “ID” property is recognized as a numeric property, and a corresponding Excel-style filter shows two text boxes and a range trackbar for this property. If you declare the FilterLookup attribute before this property, you can change these default editors with a check-list box control.
using DevExpress.Utils.Filtering;
public class Customer {
[FilterLookup]
public Int32 ID { get; set; }
//. . .
}
Record Search
This method allows you to manually start a search.
ColumnViewOptionsFind.FindFilterColumns
Initially, this property is set to “*”. In this instance, all visible columns/card fields are searched. To search specific columns/fields, assign the corresponding field names to the FindFilterColumns property, delimiting them with the “;” character. This property also allows you to limit the search columns to prevent text from being highlighted in specific columns.
ColumnView.LocateByValue, ColumnView.LocateByDisplayText
Utilize these methods to find rows by value and/or display text.
// Find rows by cell value
private void btn_LocateRow_ItemClick(object sender, ItemClickEventArgs e) {
int rowHandle = gridView.LocateByValue(gridView.FocusedRowHandle + 1, gridView.Columns["Category"], 1);
gridView.FocusedRowHandle = rowHandle;
}
// Find rows by cell display text
private void btn_LocateRow_ItemClick(object sender, ItemClickEventArgs e) {
int rowHandle = gridView.LocateByDisplayText(gridView.FocusedRowHandle + 1, gridView.Columns["Category"], "Beverages");
gridView.FocusedRowHandle = rowHandle;
}
Group Filters
OptionsColumnFilter.PopupExcelFilterGrouping
Allows you to group values in a column’s filter menu by values in another column. When this feature is enabled, users can use a filter menu to filter data by multiple columns.
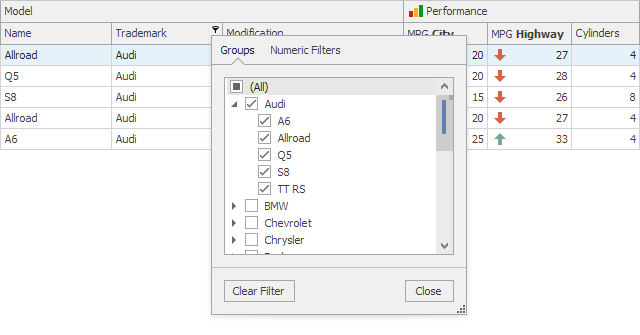
The OptionsColumnFilter.PopupExcelFilterGrouping property specifies data fields (columns) by which to group values in a specific column’s filter menu. Data fields (columns) should be specified by their names as strings separated by a comma, semicolon, space, or tab character. The code below shows how to display available models below each trademark as illustrated in the figure above.
// Customize the Trademark column's filter menu.
bcTrademark.OptionsFilter.PopupExcelFilterGrouping = "Trademark;Name";
// The customized column's values are displayed at the root level by default; you can omit its name ("Trademark").
// The code below has the same effect.
bcTrademark.OptionsFilter.PopupExcelFilterGrouping = "Name";
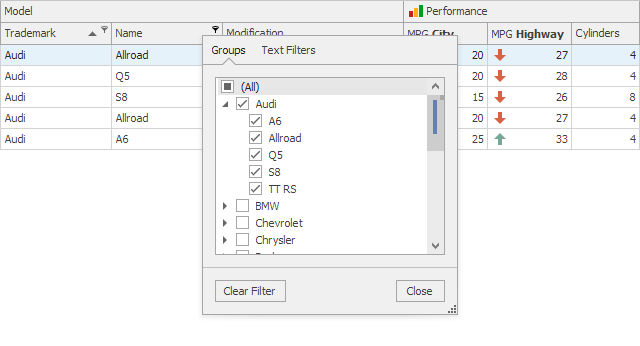
You can specify two or more data fields to group filter values by multiple columns. The order of the field names determines the group hierarchy. To show available models below each trademark in the Name column’s filter menu, use the following code to change the group hierarchy:
// Customize the Name column's filter menu.
// The customized column's values are displayed at the root level. You can omit its name ("Trademark").
bcName.OptionsFilter.PopupExcelFilterGrouping = "Trademark;Name";
As a result, values from the Trademark column are shown at the root level.
In the case of a Code First data source, you can annotate data fields with the FilterGroup attribute using the same syntax in the attribute parameter.
[Utils.Filtering.FilterGroup("Trademark;Name")]
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Trademark { get; set; }
Filter Glyphs
Filter menus can display glyphs against filter values.
Combo box editor images: If column values are edited in a combo box that displays an image for each item (see ImageComboBoxEdit), the images are also displayed in the filter menu.
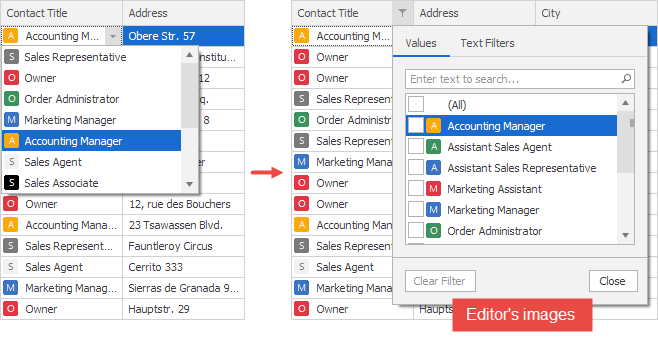
To edit column values using the image combo box:
- Create an editor (see RepositoryItemImageComboBox).
- Assign an image list to the editor (see RepositoryItemImageComboBox.SmallImages, RepositoryItemImageComboBox.LargeImages).
- Associate menu items with images in the image collection (see ImageComboBoxItem.ImageIndex).
- Specify the image alignment if required (see RepositoryItemImageComboBox.GlyphAlignment).
- Assign the editor to the column (see GridColumn.ColumnEdit).
private void gridControl1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { RepositoryItemImageComboBox combo = new RepositoryItemImageComboBox(); combo.Items.Add(new ImageComboBoxItem("Sales Agent", 0, 0)); combo.Items.Add(new ImageComboBoxItem("Owner", 1, 1)); // ... add your items here. combo.SmallImages = imageCollection1; combo.GlyphAlignment = HorzAlignment.Near; gridControl1.RepositoryItems.Add(combo); colContactTitle.ColumnEdit = combo; }Custom images: You can substitute editor images and/or change the image alignment. It is also possible to display custom images even if a column does not use the image combo box as an editor.
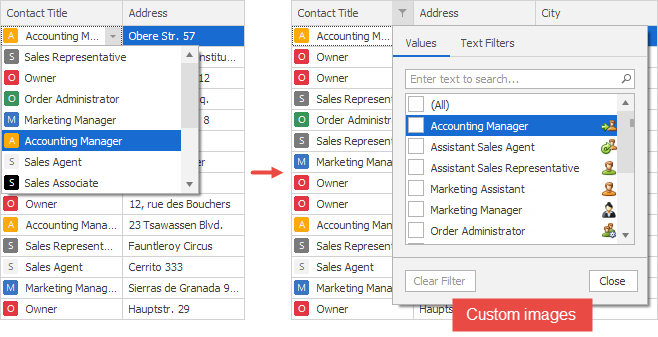
Do the following to replace an editor image:
- Handle the ColumnView.FilterPopupExcelData event.
- Use the Images event argument to supply an image list. This collection contains images fetched from the editor.
- Read the DataItems event argument to get access to filter items.
- Use an item’s ImageIndex property to associate the item with an image in the list.
- Use the ImageAlignment event argument to specify whether the images are aligned to the near or far edge or to the menu (the images are aligned in the same way as in the editor).
Customize Masks and Formatting of Filter Editors
Filter editors that are displayed in the grid’s Filter Control and Excel-inspired popup filters use the settings of cell editors assigned to the corresponding grid columns.
The following example binds the Grid to data created at runtime. The Grid uses a spin editor with default settings to display and edit numeric values in the Price column. The filter editors for the Price column use the same settings.
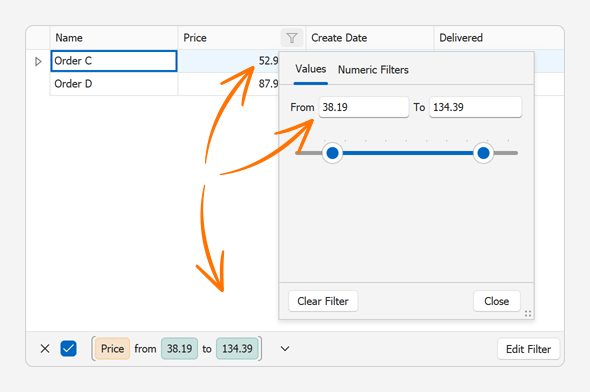
public partial class Form1 : DevExpress.XtraEditors.XtraForm {
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
gridControl1.DataSource = Order.InitData();
}
}
public class Order {
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Price { get; set; }
public DateTime CreateDate { get; set; }
public bool Delivered { get; set; }
static public List<Order> InitData() {
return new List<Order>() {
new Order(){ Name = "Order A", Price = 19.99, CreateDate = DateTime.Now, Delivered = false},
new Order(){ Name = "Order B", Price = 149.99, CreateDate = new DateTime(2022, 10, 10), Delivered = true},
new Order(){ Name = "Order C", Price = 52.99, CreateDate = DateTime.Now, Delivered = false},
new Order(){ Name = "Order D", Price = 87.99, CreateDate = new DateTime(2022, 5, 1), Delivered = true}
};
}
}
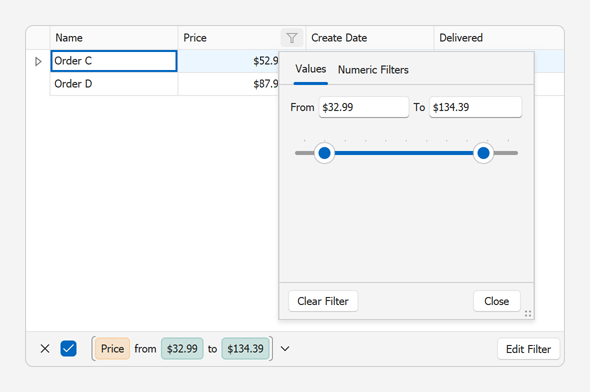
Create a repository item, customize its mask and formatting settings, and assign it to the Price column.
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
// Bind the Grid to data.
gridControl1.DataSource = Order.InitData();
// Forces the Grid to initialize its settings.
gridControl1.ForceInitialize();
// Create a repository item to display and edit numeric values.
RepositoryItemSpinEdit priceEdit = new RepositoryItemSpinEdit() { Name = "priceEdit" };
// Specifies the display format.
priceEdit.DisplayFormat.FormatType = DevExpress.Utils.FormatType.Numeric;
priceEdit.DisplayFormat.FormatString = "c2";
// Sets the mask expression.
priceEdit.MaskSettings.MaskExpression = "c2";
// Adds the repository item to the Grid's RepositoryItems collection.
gridControl1.RepositoryItems.Add(priceEdit);
// Assigns the repository item to the 'Price' column.
gridView1.Columns["Price"].ColumnEdit = priceEdit;
}
As you would expect, these changes are also applied to filter editors for the Price column.
Examples: Popular Filtering Scenarios
Apply a predefined filter on a button click:
private void showActiveCustomersBtn_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) {
gridView.ActiveFilterString = "IsActive = true";
}
Apply a filter that cannot be changed by a user:
private void GridView_CustomRowFilter(object sender, DevExpress.XtraGrid.Views.Base.RowFilterEventArgs e) {
GridView view = sender as GridView;
bool isCustomerActive = (bool)view.GetListSourceRowCellValue(e.ListSourceRow, "IsActive");
e.Visible = isCustomerActive;
e.Handled = true;
}
Get all currently visible rows when a filter is applied:
gridView.ActiveFilterString = "Contains([Name], 'Blue')";
btnObtainFilteredRows.Click += (s, e) => {
List<SampleData> filteredRows = new List<SampleData>();
// Traverse through all currently visible rows within GridView
for(int i = 0; i < gridView.RowCount; i++) {
// Obtain the processed row object
SampleData row = (SampleData)gridView.GetRow(i);
filteredRows.Add(row);
}
XtraMessageBox.Show(string.Format("Filtered rows: {0}", filteredRows.Count));
};