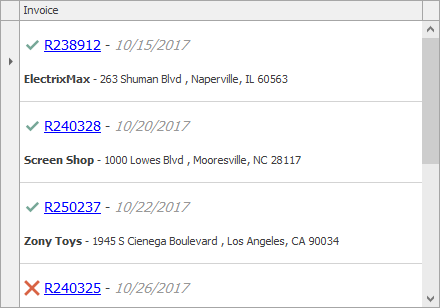
Format Cell Values
- 7 minutes to read
The WinForms Data Grid control supports multiple techniques to control the appearance of cell values:
- Display and input formatting
- Value substitution
- Dynamic text customization
Use these techniques to display values differently from underlying data without data source changes.
Choose the Right Formatting Technique
Use the simplest approach that meets the requirement:
- Display Formatting
- Format numeric and date-time values in display mode.
- Masks
- Restrict user input and optionally control display text.
- Dynamic Text Customization
- Replace or modify display text dynamically at runtime (event-based customization).
- Unbound Columns
- Replace values completely or compute display-only values.
- Display HTML Content
- Use HTML text for rich presentation.
Standard .NET Formatting
Use the standard .NET formatting mechanism for most usage scenarios. This technique formats values without changing data.
Formatting Levels
Level | Property | Description |
|---|---|---|
Column | Formats cell values in display mode. | |
Cell Editor (repository item) | Formats values in display mode and at edit start. Use input masks instead of |
Formatting at the repository item level is useful in the following cases:
- Shared Formatting
- Create and configure a repository item. Assign it to multiple columns or controls. See the following help topic for additional information: Editors and Simple Controls.
- Per-cell Formatting
- Create multiple repository items with different format settings. Assign them to individual cells within the GridView.CustomRowCellEdit or LayoutView.CustomRowCellEdit event handler.
Example 1 — Numeric and Date-Time Formatting
The following code snippet formats currency and date values in display mode.
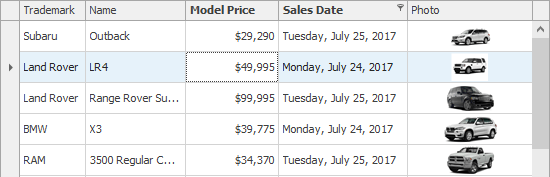
// Format a numeric column as currency with no decimals.
GridColumn colModelPrice = gridView1.Columns["ModelPrice"];
colModelPrice.DisplayFormat.FormatType = Utils.FormatType.Numeric;
colModelPrice.DisplayFormat.FormatString = "c0";
// Format a date column as a long date string.
GridColumn colSalesDate = gridView1.Columns["SalesDate"];
colSalesDate.DisplayFormat.FormatType = Utils.FormatType.DateTime;
colSalesDate.DisplayFormat.FormatString = "D";
Note
DisplayFormat does not apply in edit mode. Use masks to control runtime formatting.
Example 2 — Composite Format Patterns
Composite patterns combine formatted values with static text.
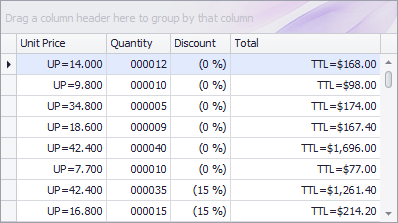
// Unit price with prefix and three decimals
colUnitPrice.DisplayFormat.FormatType = DevExpress.Utils.FormatType.Numeric;
colUnitPrice.DisplayFormat.FormatString = "UP={0:n3}";
// Quantity with fixed-width integer format
colQuantity.DisplayFormat.FormatType = DevExpress.Utils.FormatType.Numeric;
colQuantity.DisplayFormat.FormatString = "{0:d6}";
// Discount in percent format
colDiscount.DisplayFormat.FormatType = DevExpress.Utils.FormatType.Numeric;
colDiscount.DisplayFormat.FormatString = "({0:P0})";
// Calculated Total column
GridColumn columnTotal = new GridColumn();
columnTotal.Caption = "Total";
columnTotal.FieldName = "Total";
columnTotal.OptionsColumn.AllowEdit = false;
columnTotal.UnboundDataType = typeof(decimal);
columnTotal.UnboundExpression = "[UnitPrice]*[Quantity]*(1-[Discount])";
gridView1.Columns.Add(columnTotal);
columnTotal.VisibleIndex = gridView1.VisibleColumns.Count;
// Currency format with prefix
columnTotal.DisplayFormat.FormatType = DevExpress.Utils.FormatType.Numeric;
columnTotal.DisplayFormat.FormatString = "TTL={0:c2}";
Tip
Use custom formatters to apply complex formatting. See the following help topic for additional information and examples: Formatting Values.
Masks
Use masks to restrict user input or display formatting:
- Create a repository item (RepositoryItemTextEdit or its descendant).
- Configure the repository item’s mask settings. Use the MaskSettings property.
- Assign the repository item to a column. Use the column’s GridColumn.ColumnEdit property.
Masks are applied in edit mode by default. Enable the repository item’s UseMaskAsDisplayFormat setting to apply the mask in display mode.
Note
UseMaskAsDisplayFormat can reduce performance with large data sets.
The following image illustrates how to configure mask settings at design time:
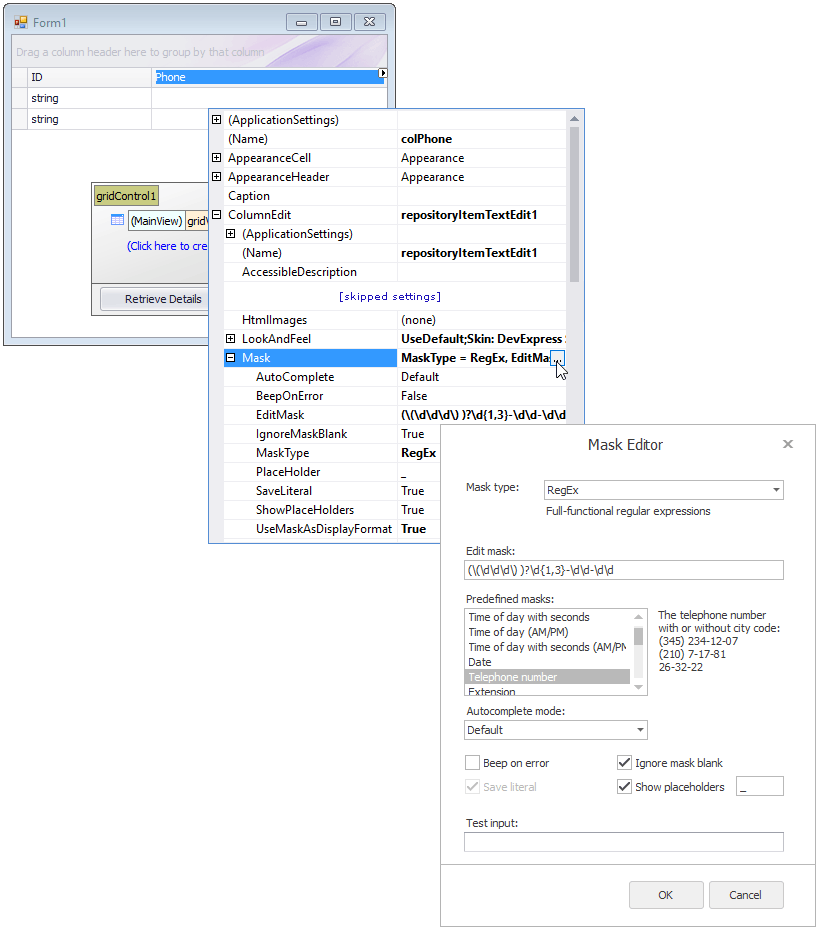
See the following help topic for additional information: Input Masks.
Example — Phone Number Mask
The following code snippet enforces a phone number format and applies it to display text:
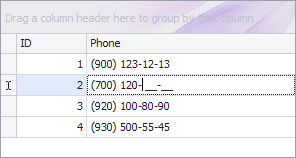
// Create a text editor with a RegEx mask.
RepositoryItemTextEdit textEdit = new RepositoryItemTextEdit();
textEdit.Mask.MaskType = DevExpress.XtraEditors.Mask.MaskType.RegEx;
textEdit.Mask.EditMask = "(\\(\\d\\d\\d\\) )?\\d{1,3}-\\d\\d-\\d\\d";
textEdit.Mask.UseMaskAsDisplayFormat = true;
// Register the editor and assign it to the column.
gridControl1.RepositoryItems.Add(textEdit);
gridView1.Columns["Phone"].ColumnEdit = textEdit;
Dynamic Text Customization
Handle the ColumnView.CustomColumnDisplayText event to display custom text within specific cells. This technique works when formatting depends on other cell values.
The following code snippet handles the CustomColumnDisplayText event to format prices based on a currency type column.
The currency type column contains only 0 and 1 values. If the currency type equals 0, the price is displayed in US dollars. If the currency type equals 1, the price is displayed in euros.
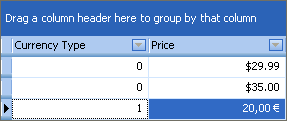
using DevExpress.XtraGrid.Views.Base;
using DevExpress.XtraGrid;
using System.Globalization;
// Culture settings for currency formatting
CultureInfo ciUSA = new CultureInfo("en-US");
CultureInfo ciEUR = new CultureInfo("fr-FR", false);
private void gridView1_CustomColumnDisplayText(object sender, CustomColumnDisplayTextEventArgs e) {
ColumnView view = sender as ColumnView;
// Process only valid data rows and the Price column.
if (e.Column.FieldName != "Price" || e.ListSourceRowIndex == GridControl.InvalidRowHandle)
return;
int currencyType = (int)view.GetListSourceRowCellValue(e.ListSourceRowIndex, "CurrencyType");
decimal price = Convert.ToDecimal(e.Value);
// Select format based on currency type.
e.DisplayText = currencyType == 0
? string.Format(ciUSA, "{0:c}", price)
: string.Format(ciEUR, "{0:c}", price);
}
Unbound Columns
Use an unbound column when display logic replaces source values completely (when lookup editors do not fit).
Typical use cases include:
- Hide zero values.
- Display calculated or conditional content.
Example — Replace Zero Values
The following code snippet handles the CustomUnboundColumnData event to hide zero prices and display empty cells instead.
This example assumes that the Grid Control and its columns are created at design time and are already bound to a data source.
public partial class Form1 : DevExpress.XtraEditors.XtraForm {
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
// Hide the original bound column.
gridView1.Columns["Price"].Visible = false;
// Create an unbound replacement column.
GridColumn customColPrice = new GridColumn();
customColPrice.FieldName = "CustomPrice";
customColPrice.Caption = "Custom Price";
customColPrice.UnboundDataType = typeof(string);
customColPrice.Visible = true;
gridView1.Columns.Add(customColPrice);
// Handle CustomUnboundColumnData
gridView1.CustomUnboundColumnData += GridView1_CustomUnboundColumnData;
}
}
void GridView1_CustomUnboundColumnData(object sender, DCustomColumnDataEventArgs e) {
GridView view = sender as GridView;
if (e.Column != view.Columns["CustomPrice"])
return;
// Read the original value from the hidden bound column.
decimal sourceValue = (decimal)view.GetRowCellValue(
view.GetRowHandle(e.ListSourceRowIndex),
view.Columns["Price"]);
// Replace zero with empty text.
e.Value = sourceValue == 0 ? String.Empty : sourceValue.ToString();
}
Display HTML Content
Use a simplified HTML syntax when cell content requires rich formatting. This technique allows you to do the following:
- Change font, size, and color.
- Display images.
- Add hyperlinks.
Use RepositoryItemHypertextLabel as an in-place editor.