IRangeProvider.Parse(String) Method
Returns a cell range by its reference string in the A1 reference style.
Namespace: DevExpress.Spreadsheet
Assembly: DevExpress.Spreadsheet.v25.2.Core.dll
NuGet Package: DevExpress.Spreadsheet.Core
Declaration
Parameters
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| reference | String | A string that specifies the cell range reference in the A1 reference style. |
Returns
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| CellRange | A CellRange object. |
Exceptions
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| InvalidOperationException | Thrown if the specified reference is invalid. |
Remarks
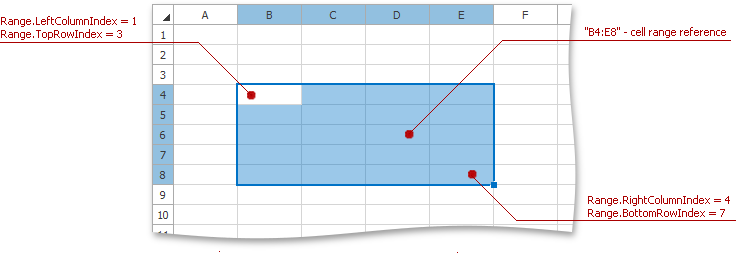
Get the IRangeProvider object via the Worksheet.Range property and use the Parse method to access a cell range object. The Parse method allows you to parse cell and table references, and defined names. Note that this method requires the cell range reference in the A1 reference style, regardless of which reference style is used in the workbook (DocumentSettings.R1C1ReferenceStyle). If you need to get a cell range by its R1C1 reference or by its reference in the style used in the workbook, pass the ReferenceStyle.R1C1 or ReferenceStyle.UseDocumentSettings value as the second parameter to the Parse method.
To get a cell range by the indexes of the bounding rows and columns, use the IRangeProvider.FromLTRB method.
Example
This example demonstrates how to access ranges of cells in a worksheet. There are several ways to accomplish this.
- The Worksheet.Item property obtains cell ranges defined by a cell reference (using A1 style) or a defined name.
- Ranges defined by a cell reference (using R1C1 or other reference styles), a defined name in a workbook, or by indexes of the bounding rows and columns - use the IRangeProvider.Item, IRangeProvider.Parse and IRangeProvider.FromLTRB members. Access the IRangeProvider object by the Worksheet.Range or IWorkbook.Range property.
// A range that includes cells from the top left cell (A1) to the bottom right cell (B5).
CellRange rangeA1B5 = worksheet["A1:B5"];
// A rectangular range that includes cells from the top left cell (C5) to the bottom right cell (E7).
CellRange rangeC5E7 = worksheet["C5:E7"];
// The C4:E7 cell range located in the "Sheet3" worksheet.
CellRange rangeSheet3C4E7 = workbook.Range["Sheet3!C4:E7"];
// A range that contains a single cell (E7).
CellRange rangeE7 = worksheet["E7"];
// A range that includes the entire column A.
CellRange rangeColumnA = worksheet["A:A"];
// A range that includes the entire row 5.
CellRange rangeRow5 = worksheet["5:5"];
// A minimal rectangular range that includes all listed cells: C6, D9 and E7.
CellRange rangeC6D9E7 = worksheet.Range.Parse("C6:D9:E7");
// A rectangular range whose left column index is 0, top row index is 0,
// right column index is 3 and bottom row index is 2. This is the A1:D3 cell range.
CellRange rangeA1D3 = worksheet.Range.FromLTRB(0, 0, 3, 2);
// A range that includes the intersection of two ranges: C5:E10 and E9:G13.
// This is the E9:E10 cell range.
CellRange rangeE9E10 = worksheet["C5:E10 E9:G13"];
// Create a defined name for the D20:G23 cell range.
worksheet.DefinedNames.Add("MyNamedRange", "Sheet1!$D$20:$G$23");
// Access a range by its defined name.
CellRange rangeD20G23 = worksheet["MyNamedRange"];
CellRange rangeA1D4 = worksheet["A1:D4"];
CellRange rangeD5E7 = worksheet["D5:E7"];
CellRange rangeRow11 = worksheet["11:11"];
CellRange rangeF7 = worksheet["F7"];
// Create a complex range using the Range.Union method.
CellRange complexRange1 = worksheet["A7:A9"].Union(rangeD5E7);
// Create a complex range using the IRangeProvider.Union method.
CellRange complexRange2 = worksheet.Range.Union(new CellRange[] { rangeRow11, rangeA1D4, rangeF7 });
// Fill the ranges with different colors.
complexRange1.FillColor = myColor1;
complexRange2.FillColor = myColor2;
// Use the Areas property to get access to a component of a complex range.
complexRange2.Areas[2].FillColor = Color.Beige;
Related GitHub Examples
The following code snippets (auto-collected from DevExpress Examples) contain references to the Parse(String) method.
Note
The algorithm used to collect these code examples remains a work in progress. Accordingly, the links and snippets below may produce inaccurate results. If you encounter an issue with code examples below, please use the feedback form on this page to report the issue.