TreeList.ParentFieldName Property
Gets or sets the data source field that identifies each record’s parent.
Namespace: DevExpress.XtraTreeList
Assembly: DevExpress.XtraTreeList.v25.2.dll
NuGet Packages: DevExpress.Win.Navigation, DevExpress.Win.TreeList
Declaration
[DefaultValue("ParentID")]
[XtraSerializableProperty]
public string ParentFieldName { get; set; }Property Value
| Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| String | "ParentID" | The parent identifier field name. |
Remarks
The TreeList.KeyFieldName and ParentFieldName properties specify Key and Parent fields in the bound data source that are used to set up a tree-like structure in a Tree List control.
See Tree Generation Algorithm in the Tree List to learn more.
The Tree List control does not automatically create columns specified in the TreeList.KeyFieldName and ParentFieldName fields. You need to activate the TreeListOptionsBehavior.PopulateServiceColumns option to create these columns.
A record is recognized as a root record if its ParentFieldName field satisfies any of the following conditions:
- equals TreeList.RootValue (the default is 0)
- equals null or DBNull.Value
- doesn’t match any of the nodes’ key field values, and is not equal to the
RootValue
Important
The RootValue property and values in the KeyFieldName and ParentFieldName fields must be of the same type.
Example
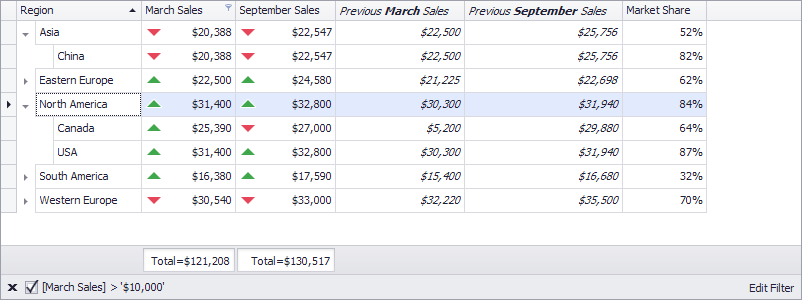
The following example creates a TreeList at runtime and shows how to perform basic customization tasks:
- Bind the treelist to a data source
- Specify the key fields that form a hierarchy
- Access automatically created columns
- Set a custom row height
- Customize column captions (using HTML tags) and cell appearance settings
- Create unbound columns and create Excel-style format conditions based on these column values
- Assign an in-place editor (a spin editor) to columns
- Sort data
- Calculate total summaries
- Filter nodes
- Hide columns and calculate column “best” widths
- Locate and expand nodes
- Focus a specific cell
- Specify DataAnnotation attributes at the data source level (the “p0” display format for the MarketShare field)
using DevExpress.XtraEditors;
using DevExpress.XtraEditors.Repository;
using DevExpress.XtraTreeList;
using DevExpress.XtraTreeList.Columns;
using DevExpress.XtraTreeList.Nodes;
using DevExpress.XtraTreeList.StyleFormatConditions;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace TreeList_example {
public partial class Form1 : Form {
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) {
TreeList treeList1 = new TreeList();
treeList1.Parent = this;
treeList1.Dock = DockStyle.Fill;
//Specify the fields that arrange underlying data as a hierarchy.
treeList1.KeyFieldName = "ID";
treeList1.ParentFieldName = "RegionID";
//Allow the treelist to create columns bound to the fields the KeyFieldName and ParentFieldName properties specify.
treeList1.OptionsBehavior.PopulateServiceColumns = true;
//Specify the data source.
treeList1.DataSource = SalesDataGenerator.CreateData();
//The treelist automatically creates columns for the public fields found in the data source.
//You do not need to call the TreeList.PopulateColumns method unless the treeList1.OptionsBehavior.AutoPopulateColumns option is disabled.
//Change the row height.
treeList1.RowHeight = 23;
//Access the automatically created columns.
TreeListColumn colRegion = treeList1.Columns["Region"];
TreeListColumn colMarchSales = treeList1.Columns["MarchSales"];
TreeListColumn colSeptemberSales = treeList1.Columns["SeptemberSales"];
TreeListColumn colMarchSalesPrev = treeList1.Columns["MarchSalesPrev"];
TreeListColumn colSeptemberSalesPrev = treeList1.Columns["SeptemberSalesPrev"];
TreeListColumn colMarketShare = treeList1.Columns["MarketShare"];
//Hide the key columns. An end user can access them from the Customization Form.
treeList1.Columns[treeList1.KeyFieldName].Visible = false;
treeList1.Columns[treeList1.ParentFieldName].Visible = false;
//Format column headers and cell values.
colMarchSalesPrev.Caption = "<i>Previous <b>March</b> Sales</i>";
colSeptemberSalesPrev.Caption = "<i>Previous <b>September</b> Sales</i>";
treeList1.OptionsView.AllowHtmlDrawHeaders = true;
colMarchSalesPrev.AppearanceCell.Font = new System.Drawing.Font(colMarchSalesPrev.AppearanceCell.Font, System.Drawing.FontStyle.Italic);
colSeptemberSalesPrev.AppearanceCell.Font = new System.Drawing.Font(colSeptemberSalesPrev.AppearanceCell.Font, System.Drawing.FontStyle.Italic);
//Create two hidden unbound columns that calculate their values from expressions.
TreeListColumn colUnboundMarchChange = treeList1.Columns.AddField("FromPrevMarchChange");
colUnboundMarchChange.Caption = "Change from prev March";
colUnboundMarchChange.UnboundDataType = typeof(decimal);
colUnboundMarchChange.UnboundExpression = "[MarchSales]-[MarchSalesPrev]";
TreeListColumn colUnboundSeptemberChange = treeList1.Columns.AddField("FromPrevSepChange");
colUnboundSeptemberChange.Caption = "Change from prev September";
colUnboundSeptemberChange.UnboundDataType = typeof(decimal);
colUnboundSeptemberChange.UnboundExpression = "[SeptemberSales]-[SeptemberSalesPrev]";
colUnboundMarchChange.OptionsColumn.ShowInCustomizationForm = false;
colUnboundSeptemberChange.OptionsColumn.ShowInCustomizationForm = false;
//Make the Region column read-only.
colRegion.OptionsColumn.ReadOnly = true;
//Sort data against the Region column.
colRegion.SortIndex = 0;
//Apply a filter.
treeList1.ActiveFilterString = "[MarchSales] > 10000";
//Calculate two total summaries against root nodes.
colMarchSales.SummaryFooter = DevExpress.XtraTreeList.SummaryItemType.Sum;
colMarchSales.SummaryFooterStrFormat = "Total={0:c0}";
colMarchSales.AllNodesSummary = false;
colSeptemberSales.SummaryFooter = DevExpress.XtraTreeList.SummaryItemType.Sum;
colSeptemberSales.SummaryFooterStrFormat = "Total={0:c0}";
colSeptemberSales.AllNodesSummary = false;
treeList1.OptionsView.ShowSummaryFooter = true;
//Use a 'SpinEdit' in-place editor for the 'sales' columns.
RepositoryItemSpinEdit riSpinEdit = new RepositoryItemSpinEdit();
riSpinEdit.DisplayFormat.FormatType = DevExpress.Utils.FormatType.Numeric;
riSpinEdit.DisplayFormat.FormatString = "c0";
treeList1.RepositoryItems.Add(riSpinEdit);
colMarchSales.ColumnEdit = riSpinEdit;
colMarchSalesPrev.ColumnEdit = riSpinEdit;
colSeptemberSales.ColumnEdit = riSpinEdit;
colSeptemberSalesPrev.ColumnEdit = riSpinEdit;
//Apply Excel-style formatting: display predefined 'Up Arrow' and 'Down Arrow' icons based on the unbound column values.
TreeListFormatRule rule1 = new TreeListFormatRule();
rule1.Rule = createThreeTrianglesIconSetRule();
rule1.Column = colUnboundMarchChange;
rule1.ColumnApplyTo = colMarchSales;
TreeListFormatRule rule2 = new TreeListFormatRule();
rule2.Rule = createThreeTrianglesIconSetRule();
rule2.Column = colUnboundSeptemberChange;
rule2.ColumnApplyTo = colSeptemberSales;
treeList1.FormatRules.Add(rule1);
treeList1.FormatRules.Add(rule2);
//Do not stretch columns to the treelist width.
treeList1.OptionsView.AutoWidth = false;
//Locate a node by a value it contains.
TreeListNode node1 = treeList1.FindNodeByFieldValue("Region", "North America");
//Focus and expand this node.
treeList1.FocusedNode = node1;
node1.Expanded = true;
//Locate a node by its key field value and expand it.
TreeListNode node2 = treeList1.FindNodeByKeyID(32);//Node 'Asia'
node2.Expand();
//Calculate the optimal column widths after the treelist is shown.
this.BeginInvoke(new MethodInvoker(delegate {
treeList1.BestFitColumns();
}));
}
FormatConditionRuleIconSet createThreeTrianglesIconSetRule() {
FormatConditionRuleIconSet ruleIconSet = new FormatConditionRuleIconSet();
FormatConditionIconSet iconSet = ruleIconSet.IconSet = new FormatConditionIconSet();
FormatConditionIconSetIcon icon1 = new FormatConditionIconSetIcon();
FormatConditionIconSetIcon icon2 = new FormatConditionIconSetIcon();
FormatConditionIconSetIcon icon3 = new FormatConditionIconSetIcon();
//Choose predefined icons.
icon1.PredefinedName = "Triangles3_3.png";
icon2.PredefinedName = "Triangles3_2.png";
icon3.PredefinedName = "Triangles3_1.png";
//Specify the type of threshold values.
iconSet.ValueType = FormatConditionValueType.Number;
//Define ranges to which icons are applied by setting threshold values.
icon1.Value = Decimal.MinValue;
icon1.ValueComparison = FormatConditionComparisonType.GreaterOrEqual;
icon2.Value = 0;
icon2.ValueComparison = FormatConditionComparisonType.GreaterOrEqual;
icon3.Value = 0;
icon3.ValueComparison = FormatConditionComparisonType.Greater;
//Add icons to the icon set.
iconSet.Icons.Add(icon1);
iconSet.Icons.Add(icon2);
iconSet.Icons.Add(icon3);
return ruleIconSet;
}
}
public class SalesData {
static int UniqueID = 37;
public SalesData() {
ID = UniqueID++;
}
public SalesData(int id, int regionId, string region, decimal marchSales, decimal septemberSales, decimal marchSalesPrev, decimal septermberSalesPrev, double marketShare) {
ID = id;
RegionID = regionId;
Region = region;
MarchSales = marchSales;
SeptemberSales = septemberSales;
MarchSalesPrev = marchSalesPrev;
SeptemberSalesPrev = septermberSalesPrev;
MarketShare = marketShare;
}
public int ID { get; set; }
public int RegionID { get; set; }
public string Region { get; set; }
public decimal MarchSales { get; set; }
public decimal SeptemberSales { get; set; }
public decimal MarchSalesPrev { get; set; }
public decimal SeptemberSalesPrev { get; set; }
[DisplayFormat(DataFormatString = "p0")]
public double MarketShare { get; set; }
}
public class SalesDataGenerator {
public static List<SalesData> CreateData() {
List<SalesData> sales = new List<SalesData>();
sales.Add(new SalesData(0, -1, "Western Europe", 30540, 33000, 32220, 35500, .70));
sales.Add(new SalesData(1, 0, "Austria", 22000, 28000, 26120, 28500, .92));
sales.Add(new SalesData(2, 0, "France", 23020, 27000, 20120, 29200, .51));
sales.Add(new SalesData(3, 0, "Germany", 30540, 33000, 32220, 35500, .93));
sales.Add(new SalesData(4, 0, "Spain", 12900, 10300, 14300, 9900, .82));
sales.Add(new SalesData(5, 0, "Switzerland", 9323, 10730, 7244, 9400, .14));
sales.Add(new SalesData(6, 0, "United Kingdom", 14580, 13967, 15200, 16900, .91));
sales.Add(new SalesData(17, -1, "Eastern Europe", 22500, 24580, 21225, 22698, .62));
sales.Add(new SalesData(18, 17, "Belarus", 7315, 18800, 8240, 17480, .34));
sales.Add(new SalesData(19, 17, "Bulgaria", 6300, 2821, 5200, 10880, .8));
sales.Add(new SalesData(20, 17, "Croatia", 4200, 3890, 3880, 4430, .29));
sales.Add(new SalesData(21, 17, "Russia", 22500, 24580, 21225, 22698, .85));
sales.Add(new SalesData(26, -1, "North America", 31400, 32800, 30300, 31940, .84));
sales.Add(new SalesData(27, 26, "USA", 31400, 32800, 30300, 31940, .87));
sales.Add(new SalesData(28, 26, "Canada", 25390, 27000, 5200, 29880, .64));
sales.Add(new SalesData(29, -1, "South America", 16380, 17590, 15400, 16680, .32));
sales.Add(new SalesData(30, 29, "Argentina", 16380, 17590, 15400, 16680, .88));
sales.Add(new SalesData(31, 29, "Brazil", 4560, 9480, 3900, 6100, .10));
sales.Add(new SalesData(32, -1, "Asia", 20388, 22547, 22500, 25756, .52));
sales.Add(new SalesData(34, 32, "India", 4642, 5320, 4200, 6470, .44));
sales.Add(new SalesData(35, 32, "Japan", 9457, 12859, 8300, 8733, .70));
sales.Add(new SalesData(36, 32, "China", 20388, 22547, 22500, 25756, .82));
return sales;
}
}
}
Related GitHub Examples
The following code snippets (auto-collected from DevExpress Examples) contain references to the ParentFieldName property.
Note
The algorithm used to collect these code examples remains a work in progress. Accordingly, the links and snippets below may produce inaccurate results. If you encounter an issue with code examples below, please use the feedback form on this page to report the issue.