Alignment.WrapText Property
Indicates whether the text contained in a cell is wrapped into multiple lines.
Namespace: DevExpress.Spreadsheet
Assembly: DevExpress.Spreadsheet.v25.2.Core.dll
NuGet Package: DevExpress.Spreadsheet.Core
Declaration
Property Value
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Boolean | true, if the cell text should be wrapped; otherwise, false. |
Remarks
Use the WrapText property to wrap the cell text into lines. This fits the cell content to the column width and prevents displaying it over adjacent cells. If the wrapped text is not completely visible within the cell, you can allow automatic adjustment of the row height to the cell content via the Row.AutoFit method.
To set other alignment characteristics for a cell or range of cells (for example, horizontal and vertical alignment type, indent, text rotation, a value indicating whether the text should be shrunk in a cell), use the corresponding properties of the Alignment object. Access this object via the Formatting.Alignment property.
- To specify the data alignment of an individual cell, access the Alignment object using the cell’s Formatting.Alignment property directly.
- To specify the data alignment of a cell range, modify the Alignment object within the CellRange.BeginUpdateFormatting - CellRange.EndUpdateFormatting method pair.
- To share the same alignment settings between multiple cells in one step, apply the style with the specified alignment to the required cells. To specify the alignment for a cell style, access the Style object from the IWorkbook.Styles collection and use this style’s Formatting.Alignment property within the Formatting.BeginUpdate-Formatting.EndUpdate paired methods to access and modify the Alignment object.
For examples on how to specify the format for an individual cell and cell range, or modify a style, refer to the How to: Format a Cell or Range of Cells or How to: Create or Modify a Style document, respectively.
Example
This example demonstrates how to specify the alignment of cell content so the cells appear as on the image below:
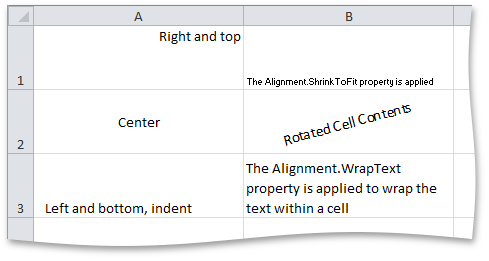
Cell cellA1 = worksheet.Cells["A1"];
cellA1.Value = "Right and top";
cellA1.Alignment.Horizontal = SpreadsheetHorizontalAlignment.Right;
cellA1.Alignment.Vertical = SpreadsheetVerticalAlignment.Top;
Cell cellA2 = worksheet.Cells["A2"];
cellA2.Value = "Center";
cellA2.Alignment.Horizontal = SpreadsheetHorizontalAlignment.Center;
cellA2.Alignment.Vertical = SpreadsheetVerticalAlignment.Center;
Cell cellA3 = worksheet.Cells["A3"];
cellA3.Value = "Left and bottom, indent";
cellA3.Alignment.Indent = 1;
Cell cellB1 = worksheet.Cells["B1"];
cellB1.Value = "The Alignment.ShrinkToFit property is applied";
cellB1.Alignment.ShrinkToFit = true;
Cell cellB2 = worksheet.Cells["B2"];
cellB2.Value = "Rotated Cell Contents";
cellB2.Alignment.Horizontal = SpreadsheetHorizontalAlignment.Center;
cellB2.Alignment.Vertical = SpreadsheetVerticalAlignment.Center;
cellB2.Alignment.RotationAngle = 15;
Cell cellB3 = worksheet.Cells["B3"];
cellB3.Value = "The Alignment.WrapText property is applied to wrap the text within a cell";
cellB3.Alignment.WrapText = true;
Related GitHub Examples
The following code snippets (auto-collected from DevExpress Examples) contain references to the WrapText property.
Note
The algorithm used to collect these code examples remains a work in progress. Accordingly, the links and snippets below may produce inaccurate results. If you encounter an issue with code examples below, please use the feedback form on this page to report the issue.