Formatting Cells in WPF Spreadsheet Control
- 5 minutes to read
Proper cell formatting improves document appearance and helps users read, find, and understand data more easily. When you format a cell, you can specify font settings, character style (bold, italic or underline), text alignment, fill color, and so on. This topic explains the following concepts:
For details on conditional formatting, refer to this topic: Conditional Formatting.
Document Themes
A document theme is a set of fonts, colors, and graphic effects you can use to change the entire look of your document. Every workbook has an associated theme returned by the IWorkbook.Theme property. You can use a custom theme for your document or change predefined theme colors, as described in this topic: How to: Apply or Modify a Workbook Theme.
Cell Styles
A style is a named set of predefined cell format characteristics (font settings, number format, content alignment, cell borders, and fill color). When you apply a style, all format settings are applied to a cell or cell range in a single step.
A workbook maintains all available styles in a StyleCollection collection, which is accessed via the IWorkbook.Styles property. By default, this collection contains a set of built-in cell styles similar to Microsoft® Excel® (including the Normal style, which is applied to all unformatted cells in the workbook by default). Identifiers of all built-in styles are listed by the BuiltInStyleId enumerator.
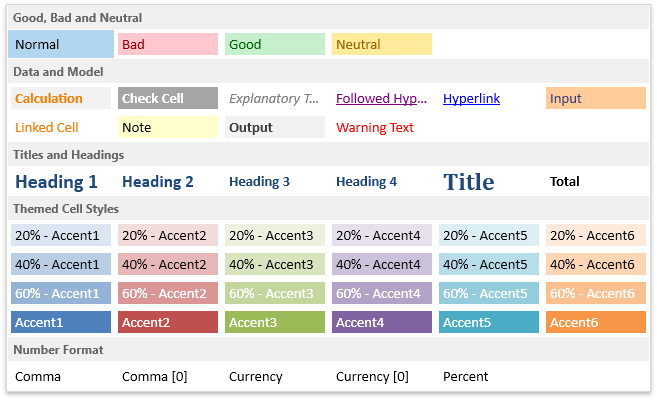
You can do the following to manage the workbook’s collection of cell styles.
- Modify an existing style by changing the properties of the corresponding Style object. Use the Formatting.BeginUpdate - Formatting.EndUpdate method pair to make multiple modifications to a style.
- Create a new custom style by adding a new Style object to the IWorkbook.Styles collection. Note that by default, new styles are created based on the Normal style.
- Duplicate an existing style by creating a new style and copying all format settings from the existing style via the Style.CopyFrom method.
Refer to the following topic for examples: How to: Create or Modify a Style.
Note
All custom styles of an Excel document that is loaded to a SpreadsheetControl are automatically added to the IWorkbook.Styles collection, and can be accessed by their names.
To format a cell or cell range by applying a style, assign the required Style object to the CellRange.Style property. Refer to this example for details: How to: Apply a Style to a Cell or Range of Cells.
Direct Cell Formatting
To change cell appearance, you can not only apply a style, but also set the required format characteristics directly for an individual cell or cell range. This is called direct cell formatting. In SpreadsheetControl, direct cell formatting options are available via the Ribbon interface (the Home tab) or in the Format Cells dialog.
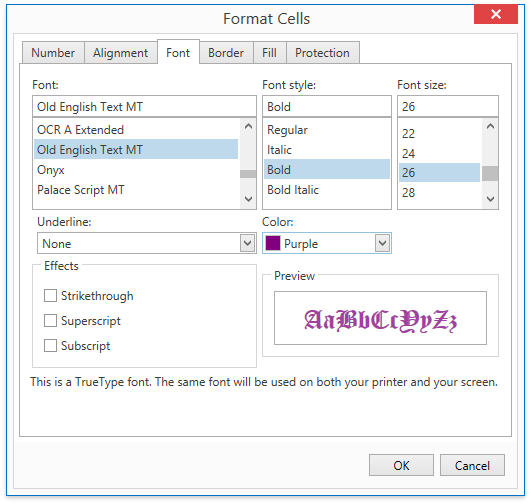
To perform direct cell formatting programmatically, change the cell or cell range properties that are inherited from the Formatting interface (Formatting.Fill, Formatting.Font, Formatting.Alignment, Formatting.Borders and Formatting.NumberFormat). By default, these properties are set according to the style applied to the cell. Use the following approaches.
- To format an individual cell, access the corresponding Cell object (see How to: Access a Cell in a Worksheet) and modify its formatting properties.
- To format a range of cells, access and modify the Formatting object using the CellRange.BeginUpdateFormatting - CellRange.EndUpdateFormatting method pair.
Thus, a Cell or CellRange object’s properties inherited from the Formatting interface provide access to the actual formatting specified for a cell or range of cells (including characteristics defined by an applied style and direct cell formatting attributes).
Style Flags
As mentioned above, the appearance of a cell is determined by the format settings of the applied style and the format settings of the cell itself. Each of these formatting types provides a set of flags (Formatting.Flags). Each flag corresponds to a specific group of format attributes, and indicates whether to use the attributes specified in the applied style or the attributes specified directly for the cell.
| Group | Attributes | Flag |
|---|---|---|
| Alignment | Horizontal and vertical alignment of cell content, indentation and text wrap. | StyleFlags.Alignment |
| Borders | Cell border line styles and colors. | StyleFlags.Borders |
| Fill | Cell background color. | StyleFlags.Fill |
| Font | Cell font settings (name, style, color and size). | StyleFlags.Font |
| Number Format | Cell number format. | StyleFlags.Number |
| Protection | Cell protection options (Locked and Hidden). | StyleFlags.Protection |
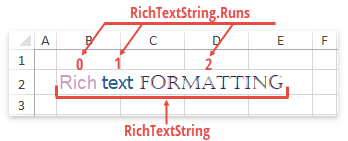
Rich Text Formatting
A cell in a worksheet can contain rich formatted text specified by the RichTextString object. Rich text is comprised of one or more text regions (or text runs), each with its own set of font characteristics. An individual text run is defined by the RichTextRun object and stored in the RichTextString.Runs collection.
Note
The WPF Spreadsheet control does not display, print or export (to PDF) rich format settings applied to a cell. However, it saves rich text to a document, so that you can view and print the document in Microsoft® Excel® or another spreadsheet application.
You can apply rich formatting to cell text as follows:
Use the RichTextString.AddTextRun method to compose cell text from individual text runs.
Use the RichTextString.Characters method overloads to format specific text characters.
Pass the RichTextString instance to the CellRange.SetRichText method to assign rich text to a cell.
Refer to the following topic for examples on how to apply different fonts to desired regions of cell text: How to: Apply Rich Formatting to Cell Text.
Examples
The following examples explain how to format worksheet cells in code:
- How to: Apply or Modify a Workbook Theme
- How to: Format a Cell or Range of Cells
- How to: Load and Use Custom Fonts
- How to: Apply Rich Formatting to Cell Text
- How to: Specify Number or Date Format for Cell Content
- How to: Change Cell Font and Background Color
- How to: Apply Gradient Fill
- How to: Align Cell Content
- How to: Add and Remove Cell Borders
- How to: Clear Cell Formatting