Export to XLS
- 7 minutes to read
This document describes the specifics of exporting a document to an XLS format (Microsoft Excel® 2000-2003).
Tip
A code example illustrating how to export a report to XLS is available at How to export a report to XLS format.
The options that can be specified for a document exported to an XLS file are stored in the XlsExportOptions class, and can be accessed via a report’s ExportOptions.Xls property.
File options
Among these options, the XlsExportOptions.ExportMode property determines the way in which a document is exported to XLS. For instance, it may be exported to a single file (with a single page header at the beginning and a single page footer at the end). Or it may be exported page-by-page to either a single file or different files.
To export every report page to an individual sheet of an XLS file, use the page-by-page setting along with single file. The sheets are then named by appending consecutive indexes to the specified XlExportOptionsBase.SheetName value.
Note
Composite report documents created from multiple merged documents cannot be exported to the XLS format in the XlsExportMode.SingleFile (continuous) mode.
As a workaround, use subreports to combine multiple reports to a single document. Alternatively, export all your reports to XLS files separately and then join all the exported data to a single file.
To overcome the warning on exceeding the number of rows and columns permissible in an XLS format, use the XlsExportOptions.Suppress256ColumnsWarning and XlsExportOptions.Suppress65536RowsWarning properties. These options determine whether you should be notified if the resulting XLS file exceeds these limitations. The number of rows and columns permitted has been significantly increased in the more recent XLSX format (Microsoft Excel® 2007).
Note
When the number of characters in a control’s XRControl.Text exceeds 32,767, which is the total number of characters that a worksheet cell can contain, the remaining text is truncated in the exported Excel document without displaying any warning. To learn more, see Excel specifications and limits.
For a sample code illustrating how to export different groups in a report onto different sheets of an Excel file, see the following online example: How to export a report to the different sheets in the XLS file.
Encryption Options
To encrypt an XLS file, specify the XlEncryptionOptions.Password property of the XlEncryptionOptions object returned by the XlExportOptionsBase.EncryptionOptions property. The default empty password cannot be used for file encryption.
Important
Excel passwords are saved with report definitions in clear text. Make sure that only trusted parties have access to report definition files.
XLS files support only ARC4 encryption (except for RC4CryptoAPI) and the XlEncryptionOptions.Type property is ignored for such files. To learn more, see the following topic in MSDN: Office Document Cryptography Structure.
The encryption is supported for both the WYSIWYG and DataAware export modes.
Print options
To enable the “Fit All Columns on One Page“ option available in the Print dialog of an Excel document, use the XlExportOptionsBase.FitToPrintedPageHeight property.
To enable the “Fit All Rows on One Page“ option available in the Print dialog of an Excel document, use the XlExportOptionsBase.FitToPrintedPageWidth property.
When both these properties are set to true, this enables the “Fit Sheet on One Page“ option in the Print dialog of an Excel document.
Data shaping options
The following two modes of Excel export are available.
Data-Aware Export
This export mode is optimized for subsequent data analysis within Microsoft Excel. Various data shaping options that are applied within the control are retained in the output XLS-XLSX documents (such as native Excel grouping, sorting and filtering settings, as well as improved support for Excel formulas).
Printing links (in WinForms and WPF) do not support this export mode and to use the data-aware export, it is required to call the corresponding methods of specific controls (e.g., GridControl).
WYSIWYG Export
With this export mode, the layout of a control’s cells is retained in the resulting Excel documents while specific data shaping options may not be retained.
This is the only export method that is supported by printing links.
Document content options
To only export your report’s actual data to XLS, ignoring non-relevant elements (such as images, graphic content, font and appearance settings), use the XlExportOptionsBase.RawDataMode option.
To specify whether vector images (e.g., pictures, charts or bar codes) should be rasterized on export to Excel, use the PageByPageExportOptionsBase.RasterizeImages property. When this option is enabled, you can also define the image resolution using the PageByPageExportOptionsBase.RasterizationResolution property.
Document layout options
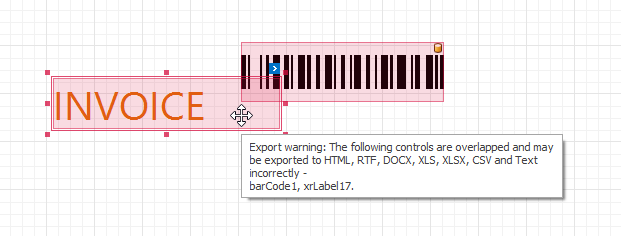
Only the report controls that do not intersect with each other can be correctly exported to XLS. In other cases, the resulting XLS file layout may be corrupted.
To make sure that your report layout will be preserved in an XLS format, enable the report’s DesignerOptions.ShowExportWarnings property at design time, and check to ensure there are no exclamation marks shown for intersecting controls (colored in red).
Hyperlink options
The export to XLS supports the following three types of links.
- Email address - a URL must start with the “mailto:“ prefix.
- Web page - a URL must start with the “https://“ or “http://“ prefix.
File - a URL must start with the “file:///“ prefix.
At present, only absolute URLs are supported for file hyperlinks.
Data format options
The XlExportOptionsBase.TextExportMode property determines whether both the .NET and native Excel formatting of data fields in the bound dataset should be preserved for the cells in the resulting XLS document. If this property is set to Text, all data fields are exported to the XLS file as strings (with the corresponding formatting embedded into those strings), and the XRControl.XlsxFormatString property of the report’s controls will have no effect.
Note
If you are using the XRRichText control in your report during export to XLS, all the control’s formatting will be lost and its content will be exported as plain text.
Because the XLS format accepts only the Double type for values with a floating point, we recommend that you set this data type instead of Float.
When the XlExportOptionsBase.TextExportMode property is set to Value, you can supply a native XLS format string to the content of the XRLabel and XRTableCell controls via their XRControl.XlsxFormatString property. The formatting specified via this property will be applied to the corresponding cells in the resulting XLS file.
Values of custom types are not exported to XLS and the corresponding cells display the “#VALUE!” error.
When exporting values that have been assigned only the .NET format without specifying their native Excel format at the same time, the original .NET format is automatically replaced with a best matching substitute from the following list of supported Excel formats.
- 0
- 0.00
- #,##0
- #,##0.00
- #,##0_);(#,##0)
- #,##0_);[Red](#,##0)
- #,##0.00_);(#,##0.00)
- #,##0.00_);[Red](#,##0.00)
- $#,##0_);($#,##0)
- $#,##0_);[Red]($#,##0)
- $#,##0.00_);($#,##0.00)
- $#,##0.00_);[Red]($#,##0.00)
- 0%
- 0.00%
- 0.00E+00
- ##0.0E+0
- # ?/?
- # ??/??
- m/d/yyyy
- d-mmm-yy
- d-mmm
- mmm-yy
- h:mm AM/PM
- h:mm:ss AM/PM
- h:mm
- h:mm:ss
- m/d/yyyy h:mm
- mm:ss
- mm:ss.0
- @
- [h]:mm:ss
- ($* #,##0);($* (#,##0);($* “-“);(@_)
- (* #,##0);(* (#,##0);(* “-“);(@_)
- ($* #,##0.00);($* (#,##0.00);($* “-“??);(@_)
- (* #,##0.00);(* (#,##0.00);(* “-“??);(@_)
For information on these format specifiers, refer to the following topic from the MS Excel documentation: Create or delete a custom number format.
An XLS format string can contain specific locale code. For example, the following XLS format string appends the Euro sign to data values: “[$€-0407] 0.00” (where “0407” is an identifier for the German language). To learn about the available language identifiers, refer to the following topic in MSDN: Language Identifier Constants and Strings.