How to: Import Data to a Worksheet in the WPF Spreadsheet Control
- 7 minutes to read
The WorksheetExtensions class exposes the Import extension method that you can use to import data from different sources to a spreadsheet. For example, you can import data from arrays, lists, or data tables.
To use WorksheetExtensions in your project, reference the DevExpress.Docs.v25.2.dll assembly or add the DevExpress.Document.Processor NuGet package. Note that the use of this library in production code requires a license to the DevExpress Office File API or Universal Subscription. Refer to the following page for pricing information: Choose a 12-Month Subscription that’s Right for You.
Spreadsheet API also allows you to import images from a data source. The following image data types are available:
Byte[]System.IO.StreamSystem.Drawing.Image- DXImage
- OfficeImage
Import Data from an Array
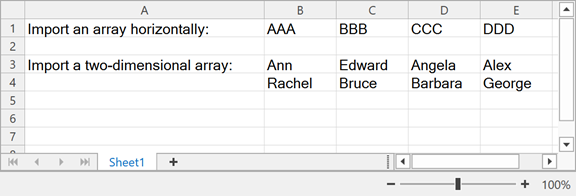
The following example loads data from arrays:
<!-- The Book1.xlsx test file's build action is Resource -->
<dxsps:SpreadsheetControl x:Name="spreadsheet"
DocumentSource="pack://application:,,,/Data/Book1.xlsx"
DocumentLoaded="spreadsheet_DocumentLoaded">
</dxsps:SpreadsheetControl>
using System.Windows;
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
namespace WpfSpreadsheet {
public partial class MainWindow : Window {
public MainWindow() {
InitializeComponent();
}
private void spreadsheet_DocumentLoaded(object sender, EventArgs e) {
spreadsheet.Document.BeginUpdate();
try {
Worksheet worksheet = spreadsheet.Document.Worksheets[0];
// Create an array containing string values.
string[] array = ["AAA", "BBB", "CCC", "DDD"];
// Import the array into the worksheet and insert it horizontally, starting with cell B1.
worksheet.Import(array, 0, 1, false);
// Create a two-dimensional array containing string values.
string[,] names = new string[2, 4] {
{ "Ann", "Edward", "Angela", "Alex" },
{ "Rachel", "Bruce", "Barbara", "George" }
};
// Import the two-dimensional array into the worksheet and insert it, starting with cell B3.
worksheet.Import(names, 2, 1);
}
finally {
spreadsheet.Document.EndUpdate();
}
}
}
}
Import Data from a List
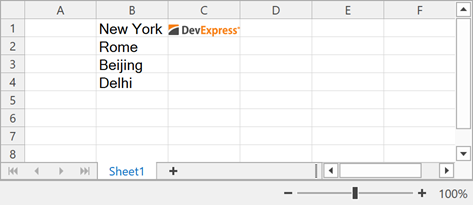
The following example loads data from a list:
<!-- The Book1.xlsx test file's build action is Resource -->
<dxsps:SpreadsheetControl x:Name="spreadsheet"
DocumentSource="pack://application:,,,/Data/Book1.xlsx"
DocumentLoaded="spreadsheet_DocumentLoaded">
</dxsps:SpreadsheetControl>
using System.IO;
using System.Windows;
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
namespace WpfSpreadsheet {
public partial class MainWindow : Window {
public MainWindow() {
InitializeComponent();
}
private void spreadsheet_DocumentLoaded(object sender, EventArgs e) {
spreadsheet.Document.BeginUpdate();
try {
Worksheet worksheet = spreadsheet.Document.Worksheets[0];
byte[] imageBytes1 = File.ReadAllBytes("D:\\DevExpress-Logo-Large-Color.png");
List<string> cities = new List<string> { "New York", "Rome", "Beijing", "Delhi" };
// Import the list into the worksheet and insert it vertically, starting with the B1 cell.
worksheet.Import(cities, 0, 1, true);
List<byte[]> imageList = new();
imageList.Add(imageBytes1);
// Import the image list into the worksheet and insert it vertically.
worksheet.Import(imageList, 0, 2, true, new DataImportOptions());
}
finally {
spreadsheet.Document.EndUpdate();
}
}
}
}
Import Data from a List of Custom Objects
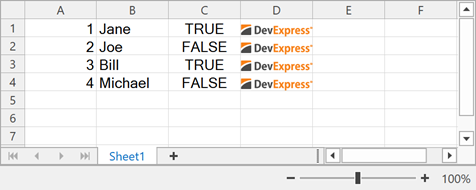
The following example loads worksheet data from a list of custom objects:
<!-- The Book1.xlsx test file's build action is Resource -->
<dxsps:SpreadsheetControl x:Name="spreadsheet"
DocumentSource="pack://application:,,,/Data/Book1.xlsx"
DocumentLoaded="spreadsheet_DocumentLoaded">
</dxsps:SpreadsheetControl>
using System.IO;
using System.Windows;
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
namespace WpfSpreadsheet {
public partial class MainWindow : Window {
public MainWindow() {
InitializeComponent();
}
private void spreadsheet_DocumentLoaded(object sender, EventArgs e) {
Worksheet worksheet = spreadsheet.Document.Worksheets[0];
byte[] imageBytes1 = File.ReadAllBytes("D:\\DevExpress-Logo-Large-Color.png");
worksheet.Clear(worksheet.GetUsedRange());
System.Collections.ArrayList listDataSource = new System.Collections.ArrayList() {
new TestObject(1, "Jane", true, imageBytes1),
new TestObject(2, "Joe", false, imageBytes1),
new TestObject(3, "Bill", true, imageBytes1),
new TestObject(4, "Michael", false, imageBytes1),
};
worksheet.Import(listDataSource, 0, 0);
}
class TestObject {
public TestObject(int intValue, string value, bool boolValue, byte[] imageValue) {
this.intValue = intValue;
this.Value = value;
this.BoolValue = boolValue;
this.ImageValue = imageValue;
}
public int intValue;
private int privateValue { get { return 123; } }
public int IntValue { get { return intValue + privateValue - 123; } }
public string Value { get; set; }
public bool BoolValue { get; set; }
public byte[] ImageValue { get; set; }
public int this[int index] { get { return index; } }
public string ImageBase64 { get; set; }
}
}
}
Import Data from a Data Table
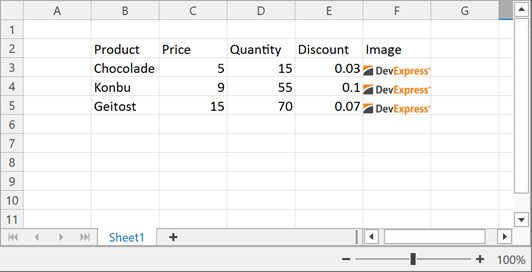
The following example imports data from a DataTable object to a worksheet.
Note that cell data types are set automatically according to the data types of the source column. The Spreadsheet control sets cell formats to the default cell data type value. Refer to the following topic for information on how to change this behavior: How to: Specify Number or Date Format for Cell Content.
<!-- The Book1.xlsx test file's build action is Resource -->
<dxsps:SpreadsheetControl x:Name="spreadsheet"
DocumentSource="pack://application:,,,/Data/Book1.xlsx"
DocumentLoaded="spreadsheet_DocumentLoaded">
</dxsps:SpreadsheetControl>
using System.Data;
using System.IO;
using System.Windows;
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
namespace WpfSpreadsheet {
public partial class MainWindow : Window {
public MainWindow() {
InitializeComponent();
}
private void spreadsheet_DocumentLoaded(object sender, EventArgs e) {
Worksheet worksheet = spreadsheet.Document.Worksheets[0];
byte[] imageBytes1 = File.ReadAllBytes("D:\\DevExpress-Logo-Large-Color.png");
// Create a "Products" DataTable object with four columns.
DataTable sourceTable = new DataTable("Products");
sourceTable.Columns.Add("Product", typeof(string));
sourceTable.Columns.Add("Price", typeof(float));
sourceTable.Columns.Add("Quantity", typeof(Int32));
sourceTable.Columns.Add("Discount", typeof(float));
sourceTable.Columns.Add("Image", typeof(byte[]));
sourceTable.Rows.Add("Chocolade", 5, 15, 0.03, imageBytes1);
sourceTable.Rows.Add("Konbu", 9, 55, 0.1, imageBytes1);
sourceTable.Rows.Add("Geitost", 15, 70, 0.07, imageBytes1);
// Import data from the data table into the worksheet and insert it, starting with the B2 cell.
worksheet.Import(sourceTable, true, 1, 1);
}
}
}