CalculatedField.Expression Property
Specifies the expression of the calculated field.
Namespace: DevExpress.XtraReports.UI
Assembly: DevExpress.XtraReports.v25.2.dll
NuGet Package: DevExpress.Reporting.Core
Declaration
[DefaultValue("")]
[SRCategory(ReportStringId.CatData)]
public string Expression { get; set; }Property Value
| Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| String | String.Empty | A String containing a calculated field’s expression. |
Remarks
Use the Expression property, to specify an expression for a calculated field. at design time within Visual Studio, this property provides access to the Expression Editor.
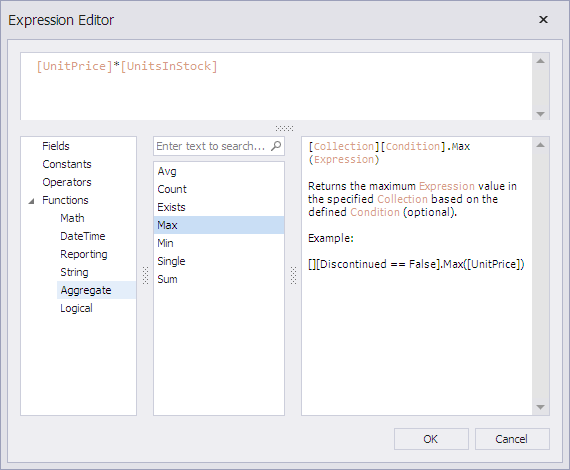
For the expressions, numerous date-time, logical, math and string functions, operators and constants are supported. For a complete list of these functions, refer to Expressions.
You can calculate aggregated functions in a calculated field expression, as well.
To refer to a data field (that is specified by the CalculatedField.DataSource and CalculatedField.DataMember properties) within an expression, enclose its name in [square brackets]. And, parameters are inserted using a question mark before their names.
A calculated field’s expression also can evaluate the values of other calculated fields.
Date-time constants must be wrapped in #hashes# ([OrderDate] >= #1/1/2009#). To represent a null reference (one that does not refer to any object), use a question mark ([Region] != ?). And, to denote strings, use ‘apostrophes‘, otherwise, an error occurs.
The type of value returned by a calculated field is defined by its CalculatedField.FieldType property.
To learn more, refer to Calculated Fields Overview.
For a code example, refer to Creating a Calculated Field (Runtime Sample).
Related GitHub Examples
The following code snippet (auto-collected from DevExpress Examples) contains a reference to the Expression property.
Note
The algorithm used to collect these code examples remains a work in progress. Accordingly, the links and snippets below may produce inaccurate results. If you encounter an issue with code examples below, please use the feedback form on this page to report the issue.