How to: Split Field Value Cells
- 3 minutes to read
The following example demonstrates how to split field value cells. In this example, the Grand Total column header is split into two cells: Price and Count.
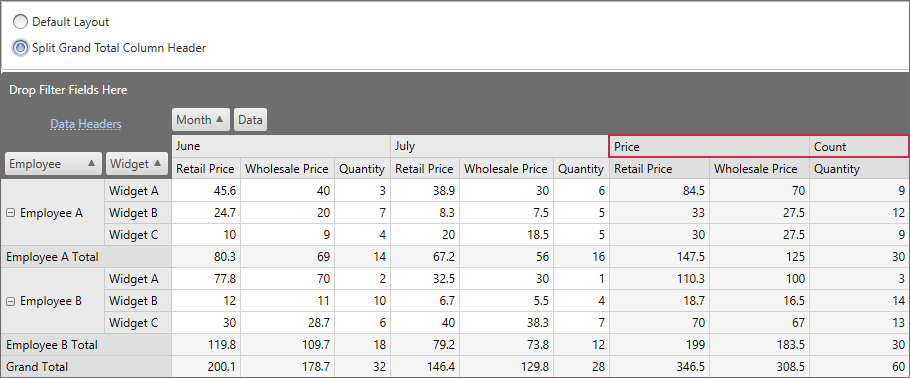
Handle the CustomFieldValueCells event and call the event parameter’s Split method. Cells that should be split are identified by a predicate that returns true for those cells. The quantity, size, and captions of newly created cells are specified by an array of cell definitions (the FieldValueSplitData objects).
<Window xmlns:dxpg="http://schemas.devexpress.com/winfx/2008/xaml/pivotgrid"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:dx="http://schemas.devexpress.com/winfx/2008/xaml/core"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
x:Class="DXPivotGrid_SplittingCells.Window1"
dx:ThemeManager.ThemeName="LightGray"
Height="580" Width="1200"
Loaded="Window_Loaded"
Title="Window1">
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<dxpg:PivotGridControl Grid.Row="1" Margin="2,2,2,0" Name="pivotGrid" AllowDrag="False"
FieldValueDisplayText="pivotGrid_FieldValueDisplayText"
AllowFilter="False" DataProcessingEngine="Optimized"/>
<GroupBox Grid.Row="0" Height="Auto" Margin="2,2,2,0"
Name="groupBox1" VerticalAlignment="Bottom">
<StackPanel Orientation="Vertical">
<RadioButton x:Name="rbDefault" IsChecked="True" Content="Default Layout"
Margin="0,0,0,2" Checked="rbDefault_Checked"/>
<RadioButton Checked="rbDefault_Checked" Margin="0,2,0,0"
Content="Split Grand Total Column Header"/>
</StackPanel>
</GroupBox>
</Grid>
</Window>
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Globalization;
using System.Windows;
using DevExpress.Xpf.PivotGrid;
using DevExpress.XtraPivotGrid.Data;
namespace DXPivotGrid_SplittingCells {
public partial class Window1 : Window {
public Window1() {
InitializeComponent();
pivotGrid.CustomFieldValueCells +=
new PivotCustomFieldValueCellsEventHandler(pivotGrid_CustomFieldValueCells);
}
void Window_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) {
PivotHelper.FillPivot(pivotGrid);
pivotGrid.DataSource = PivotHelper.GetDataTable();
pivotGrid.BestFit();
}
void pivotGrid_CustomFieldValueCells(object sender, PivotCustomFieldValueCellsEventArgs e) {
if (pivotGrid.DataSource == null) return;
if (rbDefault.IsChecked == true) return;
// Creates a predicate that returns true for the Grand Total
// headers, and false for any other column/row header.
// Only cells that match this predicate are split.
Predicate<FieldValueCell> condition =
new Predicate<FieldValueCell>(delegate(FieldValueCell matchCell) {
return matchCell.ValueType == FieldValueType.GrandTotal &&
matchCell.Field == null;
});
// Creates a list of cell definitions that represent newly created cells.
// Two definitions are added to the list. The first one identifies
// the Price cell, which has two nested cells (the Retail Price and Wholesale Price
// data field headers). The second one identifies the Count cell with
// one nested cell (the Quantity data field header).
List<FieldValueSplitData> cells = new List<FieldValueSplitData>(2);
cells.Add(new FieldValueSplitData("Price", 2));
cells.Add(new FieldValueSplitData("Count", 1));
// Performs splitting.
e.Split(true, condition, cells);
}
void pivotGrid_FieldValueDisplayText(object sender, PivotFieldDisplayTextEventArgs e) {
if(e.Field == pivotGrid.Fields[PivotHelper.Month]) {
e.DisplayText = CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.DateTimeFormat.GetMonthName((int)e.Value);
}
}
private void rbDefault_Checked(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) {
pivotGrid.LayoutChanged();
}
}
}