Graphics Performance and High DPI
- 7 minutes to read
This article explains how to develop DevExpress-based applications that can be viewed on high DPI devices without loss of quality. For more information about what DPI is and how different Windows versions scale your applications on high resolution displays, refer to the following links:
- DPI and Device-Independent Pixels
- An in-depth article that explains DPI concepts.
- Writing DPI-Aware Desktop and Win32 Applications
- A complete Microsoft guide on writing DPI-aware applications.
- DPI Scaling Level for Displays
- An article that describes three different ways to change system display DPI settings in Windows 10.
Note
Do not use Visual Inheritance in Per-Monitor and Per-Monitor V2 modes to avoid scaling issues.
DPI Awareness Mode
DPI Awareness Mode specifies the way an application is displayed when shown on a high resolution screen.
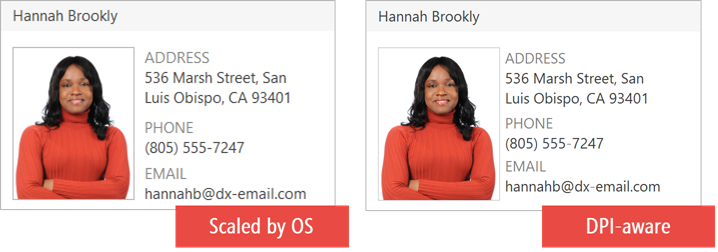
- Unaware
- This mode works on all Windows versions prior to Windows Vista. In this mode, applications assume that all displays have the default
96DPI (100%) scaling. When shown on a High-DPI device, every element of an application is rendered with its original size and then bitmap-stretched to match the screen DPI. This keeps the application layout intact at the cost of quality – blurry images, fuzzy captions, thick separator lines and borders, etc. Any WinForms application you create is initially DPI-unaware. - System
- This mode was introduced in Windows Vista. In this mode, applications are rendered according to the DPI of the display that is the primary display when the user session starts. When shown on displays with different DPI values, Windows bitmap-scales such applications. This means that applications remain sharp with one DPI factor only, and become blurry on devices with different DPI factors.
- Per-Monitor and Per-Monitor V2
- These modes allow applications to dynamically adapt to displays with different DPIs. As a result, an app looks crisp on any display. In Per-Monitor modes, Windows bitmap-scales only images and non-client areas. The app itself renders the rest of the application – as a developer, you need to track system WM_DPICHANGED messages, obtain the current display DPI, and resize/realign controls depending on this value. The first Per-Monitor mode was introduced in Windows 8.1, with the V2 iteration replacing it in Windows 10 Creators Update (build 1703). Microsoft recommends that you always use Per-Monitor V2.
How to Enable DPI Awareness in DevExpress Applications
To make your WinForms DevExpress-based application DPI-aware, open the Project Settings Page and choose the required awareness mode.
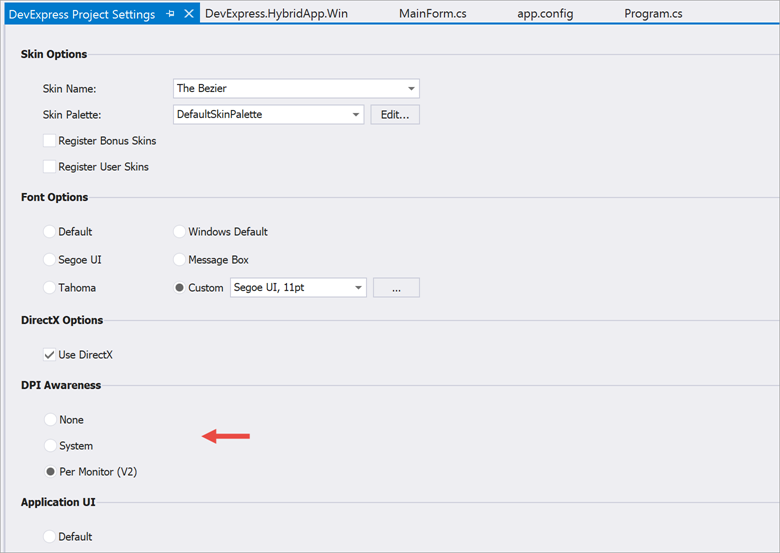
Alternatively, call the following methods on application startup:
- WindowsFormsSettings.SetDPIAware()
- Enables system DPI awareness mode for the current process.
- WindowsFormsSettings.SetPerMonitorDpiAware()
- Enables “Per-Monitor (v2)” DPI awareness mode for the process if it runs on versions greater than Windows 10 Creators Update (build 1703). On older Windows OS versions, enables system DPI awareness mode.
Do not use the application manifest file to enable DPI awareness as it may lead to a number of issues (for example, incompatibility with ClickOnce).
Do not use the Microsoft Windows graphics device interface (GDI) before the application is set as DPI-aware. This may lead to unexpected behavior. That is, do not use any graphic objects such as Bitmaps, Brushes, or Fonts. Also, do not invoke any subsystems that might use them (for example, do not apply a skin to the application).
Call the static (Shared in VB.NET) WindowsFormsSettings.ForcePaintApiDiagnostics method to ensure DPI awareness is activated correctly. See the following section for more information: Troubleshooting.
How to Build HighDPI-Ready Applications
Common Recommendations and Settings
Important
- Log out and log back in or restart the system after changing the monitor DPI configuration to avoid scaling issues in Windows OS.
- You can scale the Form at design time if its
AutoScaleModeproperty is set toAutoScaleMode.Fontand the font size is changed. This behavior may cause incorrect scaling on other monitors.
Avoid creating and customizing controls in code; opt for Visual Studio’s design time.
Visual Studio should run on a standard
96DPI screen. If you must create your application at a resolution greater than96DPI, see the following KB article for additional guidance: How to improve the Visual Studio WinForms Designer experience on High DPI.Set AutoScaleMode properties for forms to either
FontorDPI.- Use the latest version of .NET to avoid scaling issues that existed in earlier versions.
Note
Create custom-sized UI controls (for example, PopupContainerControl) in the Visual Studio Designer for Per Monitor (V2) applications to avoid scaling issues (do not specify the size of UI controls in code).
Control Sizes and Layout
Since your app needs to resize according to display DPI values, keep the layout flexible. If possible, use LayoutControl, TablePanel, and StackPanel containers that auto-adjust the layout of controls when the parent container size changes.
Images
Regardless of the DPI Awareness mode, raster images appear blurry when scaled. To maintain a crisp application appearance, use vector images: Vector Skins and SVG Icons.
![]()
The following example scales a SVG image within the WinForms Scheduler’s CustomDrawAppointment event handler:
void schedulerControl1_CustomDrawAppointment(object sender, CustomDrawObjectEventArgs e) {
Point imageLocation = new Point(e.Bounds.Location.X, e.Bounds.Location.Y);
DevExpress.Utils.Svg.SvgImage svgImage = svgImageCollection1[0];
float factor = ScaleDPI.ScaleFactor.Width;
e.Cache.DrawSvgImage(svgImage, imageLocation, null, factor);
//Custom paint other appointment elements as needed.
//...
e.Handled = true;
}
If you prefer raster item icons, use the DPIAwareImageCollection storage: it stores independent image packs for each DPI value, and dynamically switches between them depending on the display.
Custom Draw
Many DevExpress controls expose CustomDraw<VisualElement> events that allow you to redraw control elements. For instance, the CustomDrawFooter demo module illustrates how to redraw the Data Grid footer and cells.
Before the DPI Awareness was supported, these events exposed the e.Graphics property that returned the Graphics object. You could call this object’s methods to draw custom content (for example, shapes).
Now all CustomDraw<VisualElement> event arguments expose the e.Cache property that returns the GraphicsCache object – a DevExpress counterpart for Graphics. GraphicsCache exposes the same API as the standard Graphics class, and is optimized for High-DPI and DirectX-rendered applications. You should always use paint methods available from the e.Cache property.
Individual Control Settings
- BarManagerProperties.ScaleEditors | RibbonProperties.ScaleEditors
- These BarAndDockingController properties allow editors to automatically increase their sizes when the DPI factor changes.
- BarManagerProperties.ScaleIcons | RibbonProperties.ScaleIcons
- When these BarAndDockingController properties are set to true, Bar and Ribbon icon sizes are automatically increased when set to higher DPI values.
Troubleshooting
To trace all APIs that are not recommended for use with DirectX-rendered and Per-Monitor DPI-aware applications, call the static WindowsFormsSettings.ForcePaintApiDiagnostics method and set the security level as the first parameter:
- Throw
- Unsupported APIs result in exceptions.
- Trace
- Unsupported APIs show results in warnings displayed in the Visual Studio Output window.
Disable
: Ignores unsupported API. - Default
- The same as Trace if DirectX and/or Per-Monitor HiDPI support is enabled; otherwise, the same as Disable.
Graphics Performance Optimization in Remote Environments
Remote users constantly receive snapshots of an application’s visual appearance. The more visual effects the application has, the more updates are required. If the connection is poor and the refresh rate is low, the application may seem unresponsive. In some low-performance environments you may run into similar issues, for example when you target embedded systems with WinForms applications.
To reduce traffic consumption and improve overall performance in remote environments, you can selectively disable optional effects. See this blog post for more information: WinForms Tips & Tricks - Boosting Application Performance.
In v21.1 or newer, enable the OptimizeRemoteConnectionPerformance property to minimize the amount of visual effects and animations.