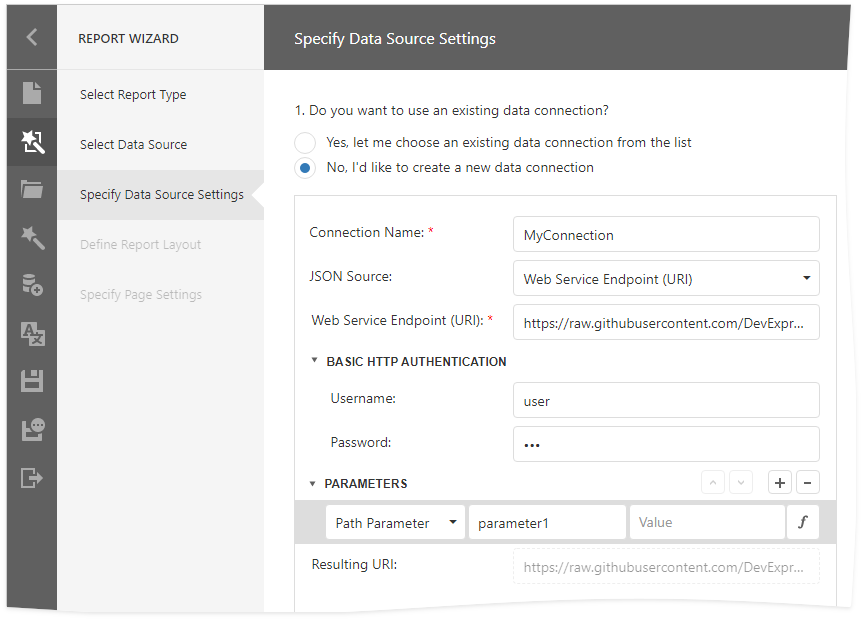
Register JSON Data Connections (ASP.NET Core)
- 4 minutes to read
This document describes how to provide JSON data connections to the Web Report Designer. The Data Source Wizard displays these connections when users create new JSON data sources.
The Data Source Wizard allows you to create a new JSON data source if a JSON data connection provider is registered in the application. You can register a built-in connection provider or implement and register a custom provider:
- Built-in connection provider
- The provider obtains connections from the application’s configuration file (appsettings.json).
- Custom connection provider
- The provider allows you to create connection strings at runtime and use custom storage to store/load connection strings and credentials.
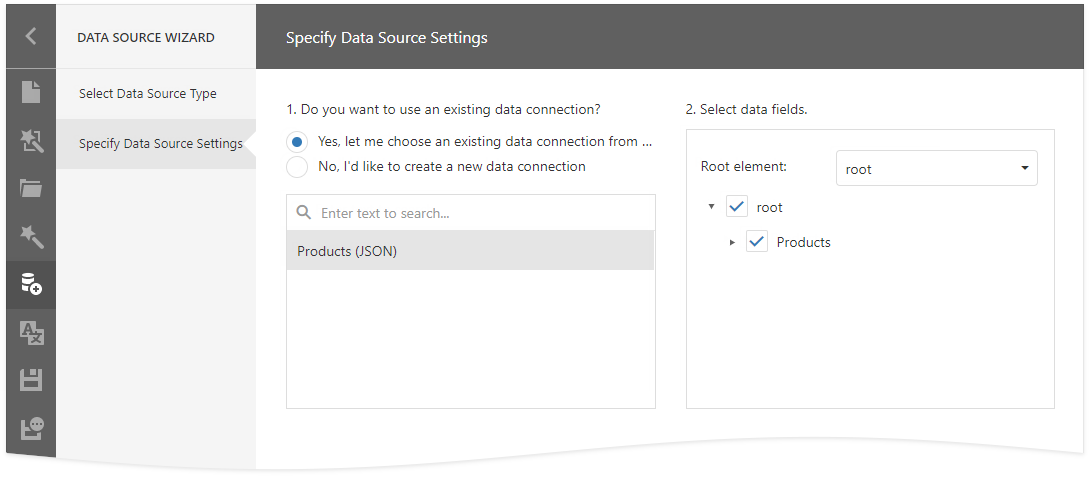
Use the Application Configuration File
Follow the steps below to use connection strings from the application configuration file:
Add data connections to the application’s configuration file (appsettings.json).
{ "ConnectionStrings": { "JsonConnection": "Uri=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DevExpress-Examples/DataSources/master/JSON/customers.json" } }Register the built-in connection string provider. Call the static ReportDesignerConfigurationBuilder.RegisterDataSourceWizardConfigFileJsonConnectionStringsProvider method at application startup.
using DevExpress.AspNetCore.Reporting; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); builder.Services.ConfigureReportingServices(configurator => { configurator.ConfigureReportDesigner(designerConfigurator => { designerConfigurator.RegisterDataSourceWizardConfigFileJsonConnectionStringsProvider(); }); }); var app = builder.Build();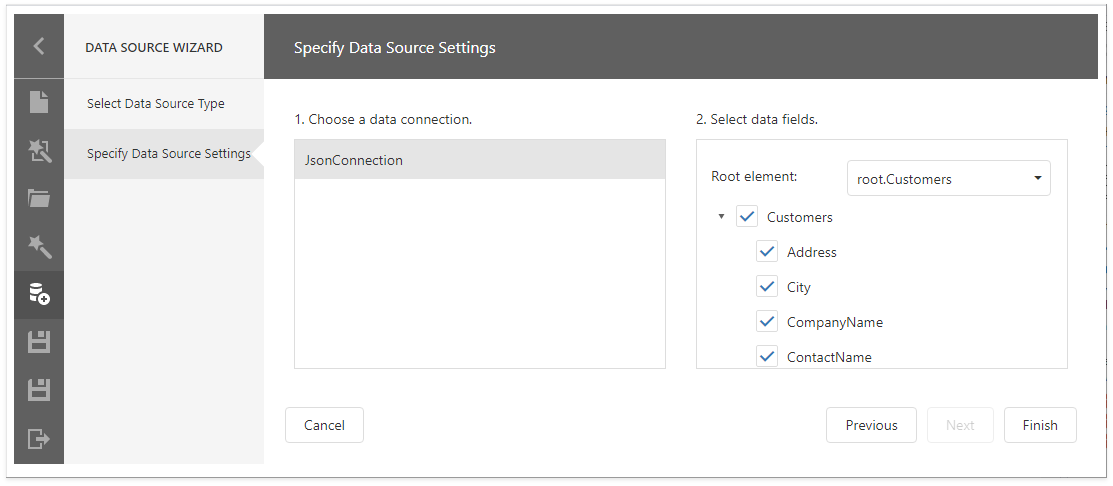
If you use data connections from appsettings.json, you cannot use a custom connection string provider described in the next section.
Implement a Custom Connection String Provider
A custom connection provider allows you to manage JSON connections that are accessible to users:
- Modify connections at runtime (for example, depending on a user)
- Allow users to create new connections
- Validate connections and keep them in a separate storage
- Store credentials securely
Tip
To review a sample JSON connection provider and storage implementation, use DevExpress templates to create an ASP.NET Core Reporting application. When creating the project, enable the Add Sample JSON Data Connection Storage option. Refer to the following help topic for more information: Use DevExpress Visual Studio Templates to Create an ASP.NET Core Reporting App with a Report Designer.
To use a custom JSON connection provider, follow the steps below:
Create a class that implements the IDataSourceWizardJsonConnectionStorage interface. The implementation below stores connections in a session.
Tip
Review the Access HttpContext.Session in Services topic for information on how to use session in methods implemented in a custom connection provider class.
Show codeusing System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using DevExpress.DataAccess.Json; using DevExpress.DataAccess.Web; using DevExpress.DataAccess.Wizard.Services; using ReportWizardCustomizationServiceAspNetCoreExample.Data; // ... public class CustomDataSourceWizardJsonDataConnectionStorage : IDataSourceWizardJsonConnectionStorage { protected ReportDbContext DbContext { get; } public CustomDataSourceWizardJsonDataConnectionStorage(ReportDbContext dbContext) { DbContext = dbContext; } public List<JsonDataConnectionDescription> GetConnections() { return DbContext.JsonDataConnections.ToList(); } bool IJsonConnectionStorageService.CanSaveConnection { get { return DbContext.JsonDataConnections != null; } } bool IJsonConnectionStorageService.ContainsConnection(string connectionName) { return GetConnections().Any(x => x.Name == connectionName); } IEnumerable<JsonDataConnection> IJsonConnectionStorageService.GetConnections() { return GetConnections().Select(x => CreateJsonDataConnectionFromString(x)); } JsonDataConnection IJsonDataConnectionProviderService.GetJsonDataConnection(string name) { var connection = GetConnections().FirstOrDefault(x => x.Name == name); if(connection == null) throw new InvalidOperationException(); return CreateJsonDataConnectionFromString(connection); } void IJsonConnectionStorageService.SaveConnection(string connectionName, JsonDataConnection dataConnection, bool saveCredentials) { var connections = GetConnections(); var connectionString = dataConnection.CreateConnectionString(); foreach(var connection in connections) { if(connection.Name == connectionName) { connection.ConnectionString = connectionString; DbContext.SaveChanges(); return; } } DbContext.JsonDataConnections.Add(new JsonDataConnectionDescription() { Name = connectionName, ConnectionString = connectionString }); DbContext.SaveChanges(); } public static JsonDataConnection CreateJsonDataConnectionFromString(DataConnection dataConnection) { return new JsonDataConnection(dataConnection.ConnectionString) { StoreConnectionNameOnly = true, Name = dataConnection.Name }; } }Create a new class (
CustomJsonDataConnectionProviderFactoryin this example) that implements the IJsonDataConnectionProviderFactory interface.The Designer’s preview loads data using this class. The class collects all JSON connections for the preview when it starts on a separate thread. To resolve a connection name to a connection, create a class (
WebDocumentViewerJsonDataConnectionProviderin this example) that implements the IJsonDataConnectionProviderService interfaceShow codeusing System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using DevExpress.DataAccess.Json; using DevExpress.DataAccess.Web; using ReportWizardCustomizationServiceAspNetCoreExample.Data; // ... public class CustomJsonDataConnectionProviderFactory : IJsonDataConnectionProviderFactory { protected ReportDbContext DbContext { get; } public CustomJsonDataConnectionProviderFactory(ReportDbContext dbContext) { DbContext = dbContext; } public IJsonDataConnectionProviderService Create() { return new WebDocumentViewerJsonDataConnectionProvider(DbContext.JsonDataConnections.ToList()); } } public class WebDocumentViewerJsonDataConnectionProvider : IJsonDataConnectionProviderService { readonly IEnumerable<DataConnection> jsonDataConnections; public WebDocumentViewerJsonDataConnectionProvider(IEnumerable<DataConnection> jsonDataConnections) { this.jsonDataConnections = jsonDataConnections; } public JsonDataConnection GetJsonDataConnection(string name) { var connection = jsonDataConnections.FirstOrDefault(x => x.Name == name); if(connection == null) throw new InvalidOperationException(); return CustomDataSourceWizardJsonDataConnectionStorage.CreateJsonDataConnectionFromString(connection); } }Register services at application startup:
Show codevar builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); builder.Services.ConfigureReportingServices(configurator => { configurator.ConfigureReportDesigner(designerConfigurator => { designerConfigurator.RegisterDataSourceWizardJsonConnectionStorage<CustomDataSourceWizardJsonDataConnectionStorage>(true); configurator.ConfigureWebDocumentViewer(viewerConfigurator => { viewerConfigurator.RegisterJsonDataConnectionProviderFactory<CustomJsonDataConnectionProviderFactory>(); }); }); var app = builder.Build();
After you register a custom JSON connection provider, you can do the following:
Use an existing connection to create a new JSON data source:
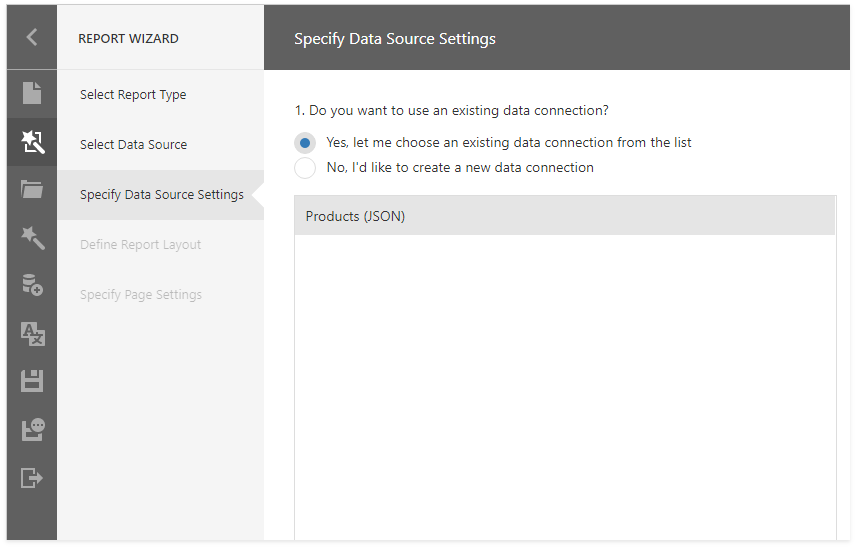
Create a new JSON connection: