Conditional Formatting in Spreadsheet Documents
- 5 minutes to read
Conditional formatting is used to highlight important information and make data interpretation easier. Conditional formats such as cell background color, border line style or font color can be applied to cells whose values meet a certain condition specified by a conditional formatting rule.
Warning
Transparency is not supported in conditional formatting.
All conditional formatting rules specified in a worksheet are stored in the ConditionalFormattingCollection collection, accessible from the Worksheet.ConditionalFormattings property. The table below lists the available types of conditional formatting rules.
To create this rule | Do the following | Example |
|---|---|---|
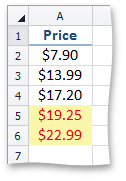
AverageConditionalFormatting - formats cells whose values are above or below the average or standard deviation in a range of cells.
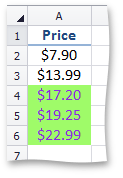
This image shows price data with conditional formatting, highlighting values that are above the average in the range of cells. | Call the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddAverageConditionalFormatting method. To specify a format applied if the condition is true, use the ISupportsFormatting.Formatting property of the AverageConditionalFormatting object. | How to: Format Cell Values that are Above or Below the Average |
ColorScale2ConditionalFormatting - formats cells by using a two-color scale.
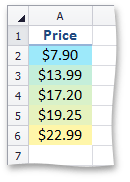
This image shows price distribution using a gradation of two colors. Blue represents the lower values and yellow represents the higher values. | Use the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddColorScale2ConditionalFormatting method, which also specifies conditional formatting options such as color for the maximum and minimum thresholds of a range. | |
ColorScale3ConditionalFormatting - formats cells by using a three-color scale.
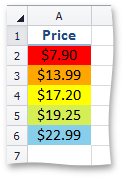
This image shows price distribution using a gradation of three colors. Red represents the lower values, yellow represents the medium values and sky blue represents the higher values. | Use the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddColorScale3ConditionalFormatting method, which also specifies conditional formatting options such as color for the minimum, midpoint and maximum thresholds of a range. | |
DataBarConditionalFormatting - formats cells by using data bars.
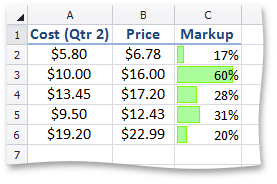
This image shows markup magnitude using data bars. | Use the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddDataBarConditionalFormatting method, which also specifies the data bars to be displayed. | |
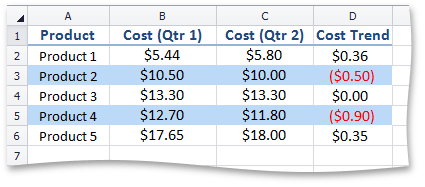
IconSetConditionalFormatting - formats cells by using icon sets.
This image shows upward and downward cost trends. | Use the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddIconSetConditionalFormatting method, which also specifies an icon set to be displayed. | |
ExpressionConditionalFormatting - formats cells whose values meet the criterion represented by a relational operator (=, ≠, <, >, ≤, ≥).
This image shows cost data with conditional formatting, highlighting values that are greater than $18. | Call the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddExpressionConditionalFormatting method. To specify a format applied if the condition is true, use the ISupportsFormatting.Formatting property of the ExpressionConditionalFormatting object. | How to: Format Cells that are Less than, Greater than or Equal to a Value |
FormulaExpressionConditionalFormatting - uses a formula to determine which cells to format.
This image shows a data table with conditional formatting that uses the MOD(ROW(),2)=1 formula to shade alternate rows in light blue. | Call the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddFormulaExpressionConditionalFormatting method. To specify a format applied if the condition is true, use the ISupportsFormatting.Formatting property of the FormulaExpressionConditionalFormatting object. | |
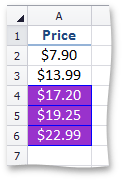
RangeConditionalFormatting - formats cells that are between or not between two specified values.
This image shows price data with conditional formatting, highlighting values that are less than $10 and greater than $19. | Call the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddRangeConditionalFormatting method. To specify a format applied if the condition is true, use the ISupportsFormatting.Formatting property of the RangeConditionalFormatting object. | How to: Format Cells that are Between or Not Between Two Values |
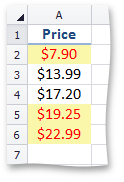
RankConditionalFormatting - formats top/bottom ranked values.
This image shows price data with conditional formatting, highlighting the top three values. | Call the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddRankConditionalFormatting method. To specify a format applied if the condition is true, use the ISupportsFormatting.Formatting property of the RankConditionalFormatting object. | |
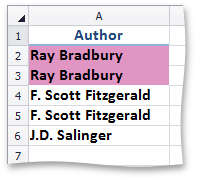
TextConditionalFormatting - formats cells that contain the given text.
This image shows a list of authors in which the name Ray Bradbury is highlighted. | Call the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddTextConditionalFormatting method. To specify a format applied if the condition is true, use the ISupportsFormatting.Formatting property of the TextConditionalFormatting object. | |
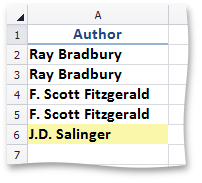
SpecialConditionalFormatting - formats empty cells, unique or duplicate values, formula errors, etc.
This image shows a list of authors in which the unique values are highlighted. | Call the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddSpecialConditionalFormatting method. To specify a format applied if the condition is true, use the ISupportsFormatting.Formatting property of the SpecialConditionalFormatting object. | How to: Format Unique or Duplicate Values, Blank Cells and Formula Errors |
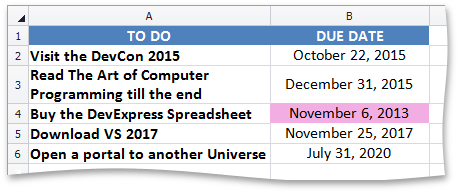
TimePeriodConditionalFormatting - formats cells containing dates that fall within a specified time period.
This image shows a table with conditional formatting that highlights today’s date. | Call the ConditionalFormattingCollection.AddTimePeriodConditionalFormatting method. To specify a format applied if the condition is true, use the ISupportsFormatting.Formatting property of the TimePeriodConditionalFormatting object. |
All of these objects inherit from the ConditionalFormatting base interface, which provides basic properties to specify a conditional formatting rule:
- the ConditionalFormatting.Priority property, which determines the evaluation order for multiple conditional formatting rules in a worksheet;
- the ConditionalFormatting.StopIfTrue property, which specifies whether or not rules with lower priority can be applied;
- the ConditionalFormatting.Range property, which specifies the contiguous or non-contiguous range (composed of multiple ranges by using the IRangeProvider.Union or CellRange.Union method) to which the conditional format is applied. For an example on how to add a rule to a combined range, refer to the How to: Apply Conditional Formatting to a Complex Range article.
To remove the conditional formatting rule from the collection, use the ConditionalFormattingCollection.Remove or ConditionalFormattingCollection.RemoveAt method. To remove all conditional formatting rules from a worksheet, use the ConditionalFormattingCollection.Clear method.