DxDropDownListEditorBase<TData, TValue>.DataAsync Property
Specifies an asynchronous function that returns the editor’s data.
Namespace: DevExpress.Blazor.Base
Assembly: DevExpress.Blazor.v24.1.dll
NuGet Package: DevExpress.Blazor
Declaration
[DefaultValue(null)]
[Parameter]
public Func<CancellationToken, Task<IEnumerable<TData>>> DataAsync { get; set; }Property Value
| Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Func<CancellationToken, Task<IEnumerable<TData>>> | null | A function that returns ComboBox data. |
Remarks
Use the DataAsync property to bind the ComboBox/TagBox to a strongly typed collection that is loaded asynchronously (for instance, from an HTTP request). This property allows you to prevent the page with the ComboBox from excessive re-rendering.
This property specifies an asynchronous function that returns a Task<IEnumerable<T>> object and accepts a CancellationToken object as a parameter. An exception occurs if you declare the function with an incorrect signature.
@using System.Threading;
@using System.Threading.Tasks;
<DxComboBox DataAsync="@GetDataAsync"
@bind-Value="@Value">
</DxComboBox>
@code {
IEnumerable<string> Cities = new List<string>() {
"London",
"Berlin",
"Paris",
};
string Value { get; set; }
public Task<IEnumerable<string>> GetDataAsync(CancellationToken ct = default) {
return Task.FromResult(Cities);
}
}
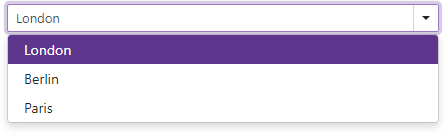
If you bind the ComboBox/TagBox to a data source that stores custom objects (IEnumerable<CustomType>), override the object’s Equals method and set the TextFieldName property. It specifies the custom object’s field name that returns strings to be shown in the editor’s drop-down window.
@using BlazorApp.Data
<DxComboBox DataAsync="@Staff.GetDataAsync"
@bind-Value="@SelectedPerson"
TextFieldName="@nameof(Person.Text)"
AllowUserInput="true">
</DxComboBox>
<DxTagBox DataAsync="@Staff.GetDataAsync"
@bind-Values="@SelectedPerson"
TextFieldName="@nameof(Person.Text)">
</DxTagBox>
@code {
Person SelectedPerson { get; set; } = Staff.DataSource[0];
}
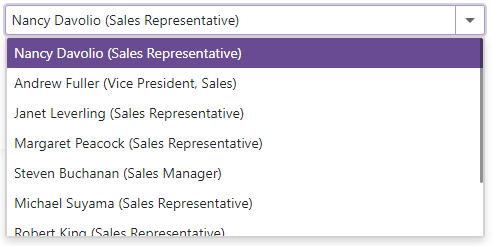
Otherwise, the editor’s items are populated with CustomType.ToString() values.
Use the Data property if a strongly typed collection is loaded synchronously. Use the CustomData property if your data is stored on a remote service and is loaded through a Web API.