Rows
- 8 minutes to read
Row Height
There are two types of rows in the Data Grid: data rows (which display data source records) and non-data rows (group rows, new item rows, etc.).
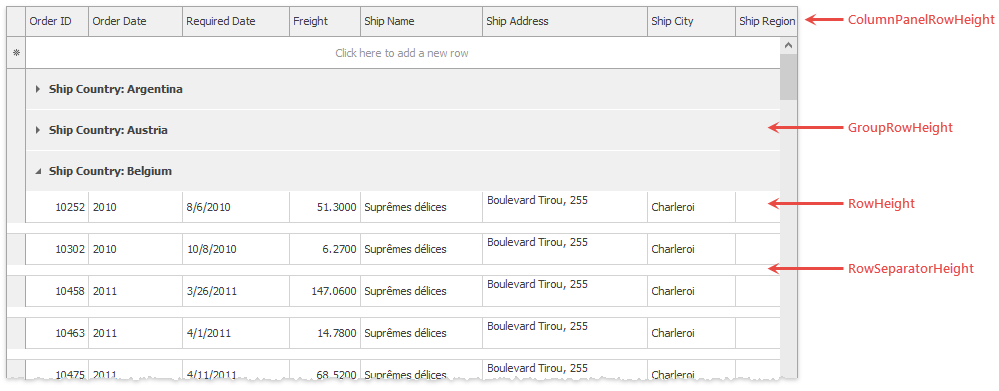
By default, row height is determined by font settings. The Data Grid exposes the following API to modify these heights.
-
Specifies the data row height in pixels. The default value is -1 (rows have no fixed height).
-
Specifies the height of column headers.
-
Gets or sets the height of group rows.
-
Specifies the vertical distance between rows. Setting this property to zero does not remove horizontal lines between rows. To do that, disable the GridOptionsView.ShowHorizontalLines setting.
-
This event is repeatedly raised for every row and allows you to set individual height parameters for each of them. The code snippet below illustrates how to set row heights based on values from the “RowHeight” data source field.
Auto Row Height
Row cells clip content that they cannot display entirely. To change this behavior, utilize the MemoEdit, TokenEdit, or PictureEdit editors as in-place editors for required columns and enable the GridOptionsView.RowAutoHeight setting. This will allow Data Grid data rows to dynamically adapt to the content and gain different heights.
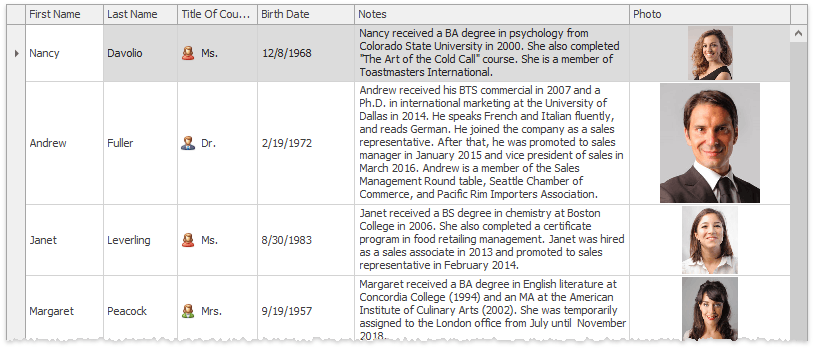
Demo: Auto Row Height
Hide Row Borders
You can hide column and row borders by disabling the GridOptionsView.ShowVerticalLines and GridOptionsView.ShowHorizontalLines settings.
Row Indicator Panel
A row indicator panel is a horizontal strip docked to the Data Grid’s left edge. Users can click this bar to select any Data Grid row.
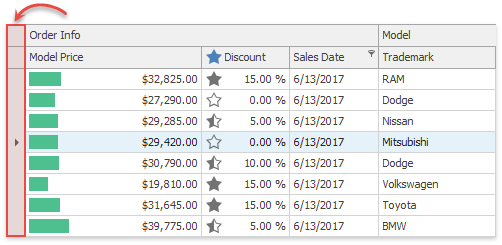
Row indicator panel displays various icons depending on what row is currently selected and which row operation is ongoing.
 — The focused row.
— The focused row. — The row cell is being edited by a user.
— The row cell is being edited by a user. — The row has been modified.
— The row has been modified. — The focused row is a new item row.
— The focused row is a new item row. — The focused row is an auto-filter row.
— The focused row is an auto-filter row. — Users can click this icon to maximize a detail View.
— Users can click this icon to maximize a detail View. — Users can click this icon to restore a detail View.
— Users can click this icon to restore a detail View. — The row contains errors.
— The row contains errors. — The focused row contains errors.
— The focused row contains errors.
Related API
GridOptionsView.ShowIndicator — Shows/hides the row indicator panel.
GridView.IndicatorWidth — Gets or sets the panel width.
GridView.CustomDrawRowIndicator — Manually redraws the panel.
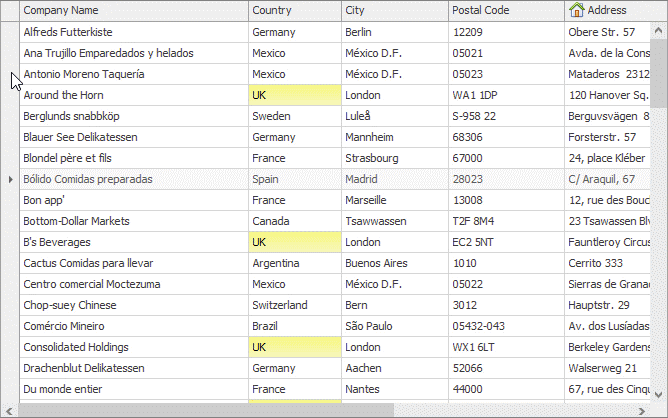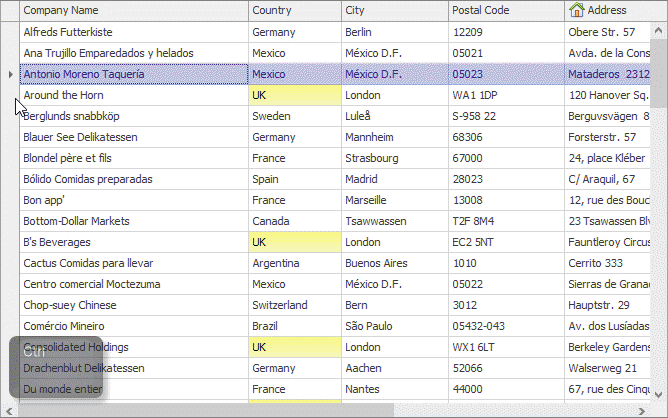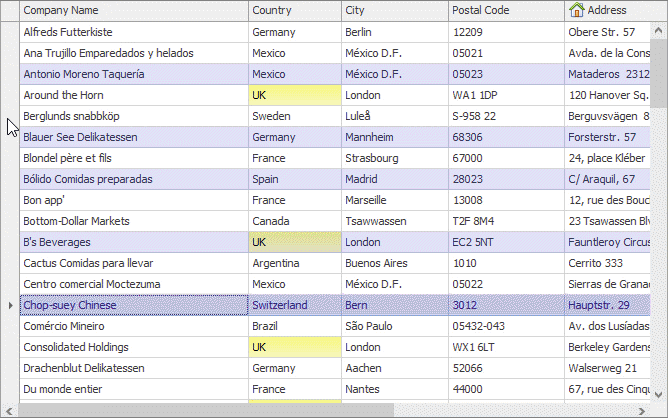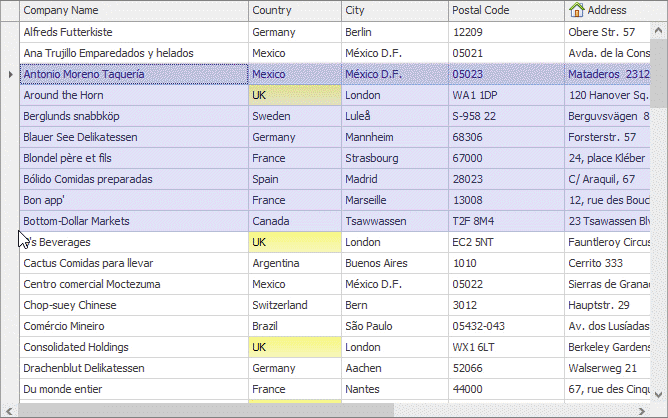
Row Multi-Select
If the ColumnViewOptionsSelection.MultiSelect option is enabled, end users are able to select multiple rows using marquee selection, the keyboard arrow keys, and mouse clicks with the Ctrl/Shift keys pressed.
Related API
ColumnView.SelectRow - Adds a row (card) to the current selection.
ColumnView.GetSelectedRows - Returns handles of the selected rows (or cards).
ColumnView.DeleteSelectedRows - Deletes the selected rows/cards in multiple selection mode or focused row/card in single selection mode.
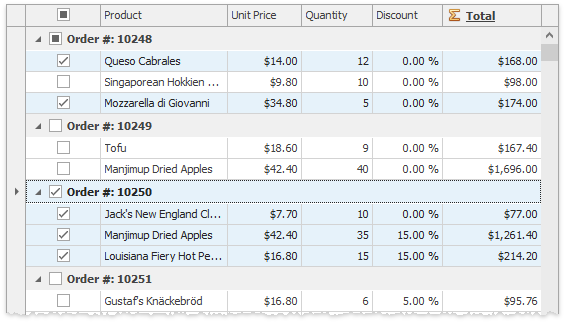
Web Style Row Selection
Along with clicking a row indicator panel, users can utilize check boxes to select data rows. To enable these check boxes, set the GridOptionsSelection.MultiSelectMode property to the GridMultiSelectMode.CheckBoxRowSelect value. Web style selection is available only when row multi-select is on.
Related API
GridOptionsSelection.ShowCheckBoxSelectorInColumnHeader — Enable this property to display a check box in the column header area. This feature allows users to select all Data Grid rows at once.
GridOptionsSelection.ShowCheckBoxSelectorInGroupRow — Enable this property to display check boxes in group rows. This feature allows users to select all Data Grid rows that belong to a specific group.
Demo: Web Style Row Selection
Accessing Rows in Code - Row Handles
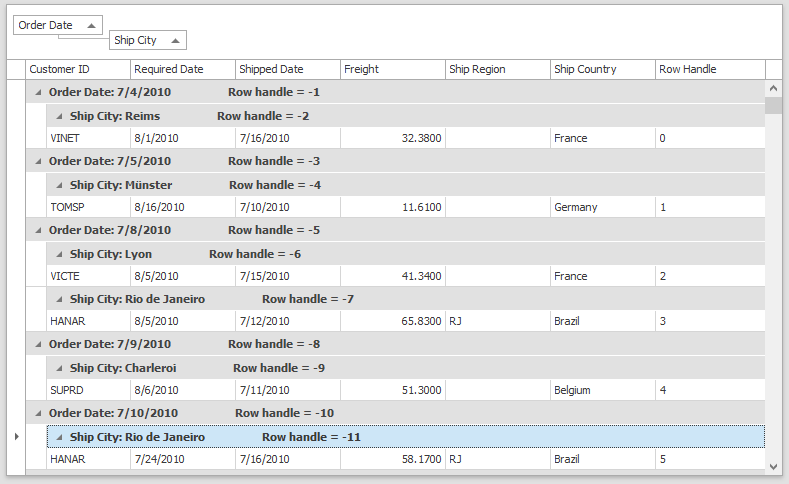
Every Data Grid row has three integer values that identify it: a data source index, a row handle and a visible index.
Data source indexes
- Specify zero-based row indexes in the bound list.
- Are constant values that do not change when you sort, group, or filter data.
- For group rows, they will point to the first data row in the group.
- Used for accessing data.
Row handles
- Zero-based indexes that correspond to row order from top to bottom.
- Group row handles are negative values that start with -1. The order matches the order of group rows from top to bottom.
- The grid specifies reserved row handles for the New Item Row, Auto Filter Row, and an Invalid Row.
- Row handles are re-assigned to rows after each data operation.
- When the View is filtered, rows and row handles are created only for rows that match the filter.
Visible indexes
- Zero-based indexes that match the order of visible rows, from top to bottom.
- Service rows are assigned negative indexes if displayed above data and group rows.
- Visible indexes are re-assigned after each data operation, including data sorting, grouping, and filtering.
- Visible indexes are only assigned to rows in expanded groups. Thus, the indexes are updated after each expand/collapse operation.
For master-detail data, all detail Views have their own unique visible indexes and row handles.
Related API
ColumnView.FocusedRowHandle — Returns the row handle of the currently focused row. To obtain the record displayed in the focused row, use the GetFocusedRow and GetFocusedDataRow methods.
ColumnView.LocateByValue — Allows you to obtain a row handle by a row cell value.
ColumnView.IsDataRow(Int32) — Returns whether a row with the given handle is a regular data row (not a group row, auto-filter row, etc.).
ColumnView.GetRowHandle, ColumnView.GetDataSourceRowIndex — Return row handles by indexes of related records in a data source and vice versa.
ColumnView.GetVisibleIndex, ColumnView.GetVisibleRowHandle — Return row handles by the visible indexes of rows and vice versa.
ColumnView.GetRow, ColumnView.GetDataRow — Return an object that is the row with the given handle.
GridControl.NewItemRowHandle, GridControl.AutoFilterRowHandle — Numeric constants that specify row handles for the new item and auto-filter rows, respectively.
GridControl.InvalidRowHandle — A constant that is returned when the Grid fails to obtain a particular row. For example, an invalid row handle is returned by the GridView.GroupRowCollapsing event arguments if this event fires when all Data Grid groups collapse at once (e.g., after calling the GridView.CollapseAllGroups method).
GridView.TopRowIndex — Scrolls a View up or down to the row with the required visible index.
Row Count
The GridView.RowCount property returns the number of records that are currently visible in the view. When the number changes, the BaseView.RowCountChanged event fires. For example, you can handle this event to show a form that allows a user to create a new record when no records meet the current search query.
using DevExpress.XtraGrid.Views.Grid;
private void gridView1_RowCountChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) {
GridView view = sender as GridView;
if(view.RowCount == 0) {
using(var form = new SpaceObjectForm())
form.ShowDialog();
}
}
Traversing Rows
When you need to process all Data Grid rows one by one, use the following technique.
- Obtain the BaseView.DataRowCount property value to determine the number of existing rows, or the BaseView.RowCount property to obtain the number of currently visible rows only.
- To alter all existing rows, implement a loop that traverses row handles starting from 0 to DataRowCount - 1.
- If you need to process visible rows only, begin with a row that has a zero handle and then obtain the next row by calling the ColumnView.GetNextVisibleRow method.
- Wrap your loop inside the ColumnView.BeginSort/ColumnView.EndSort method pair to prevent data reload while rows are being processed. Otherwise, changing cell values may change the row order (together with row handles), which will cause your row processing algorithm to malfunction.
The code sample below iterates through grid records and reduces the “Price” column values by 10 percent.
private void UpdatePrice(DevExpress.XtraGrid.Views.Base.ColumnView View) {
// Obtain the Price column.
DevExpress.XtraGrid.Columns.GridColumn col = View.Columns.ColumnByFieldName("Price");
if (col == null) return;
View.BeginSort();
try {
// Obtain the number of data rows.
int dataRowCount = View.DataRowCount;
// Traverse data rows and change the Price field values.
for (int i = 0; i < dataRowCount; i++) {
object cellValue = View.GetRowCellValue(i, col);
double newValue = Convert.ToDouble(cellValue) * 0.9;
View.SetRowCellValue(i, col, newValue);
}
} finally { View.EndSort(); }
}