Remove .NET Framework (WinForms / ASP.NET Web Forms) & Legacy .NET API
- 16 minutes to read
XAF v25.2 ends support for .NET Framework applications (Web Forms and Windows Forms). We removed all .NET Framework modules/APIs and legacy Security System implementations from our source code.
Our focus now is on modern .NET development (ASP.NET Core Blazor, Windows Forms, Web API Service) and on building scalable, multi-tenant/SaaS applications. Migrating from removed modules and APIs to their .NET-based alternatives will help you deliver a better user experience and stronger security. For more information, see the following documents:
- XAF v25.2 Roadmap (see sections titled “Why” and “What’s Next/Main Focus”)
- General Security Considerations
Note
For the complete list of removed assemblies, refer to the Removed-XAF-XPO-Assemblies.docx file attached to the following knowledge base article: T1312589 - XAF - Legacy .NET Framework (WinForms and ASP.NET WebForms) APIs, .NET-based API/Modules, and Security System have been removed from distribution.
Migration from XAF Windows Forms/ASP.NET Web Forms (.NET Framework) to Windows Forms/ASP.NET Core Blazor (.NET)
Follow our migration guidelines:
- Port an Existing XAF Application to .NET
- Share Code Between Legacy .NET Framework and Modern .NET Apps
Note
- There are many standard Microsoft .NET Framework APIs that are not available in .NET or ASP.NET Core. For more information, review public community resources like Microsoft Learn | Overview of upgrading .NET apps. This consulting is outside the scope of our support service.
- If you work with XAF versions prior to v25.2 and develop apps for both .NET Framework and .NET/ASP.NET Core Blazor, configure .NET multi-targeting in v25.1 or older (in v25.2 it is not possible due to the removed .NET Framework assemblies).
- Understanding of Microsoft platforms (.NET, .NET Core, ASP.NET Core, ASP.NET Core Blazor) is a prerequisite for XAF ASP.NET Core Blazor development (you cannot follow this migration guide without this framework knowledge). Review the following articles for additional information: Frequently Asked Questions - ASP.NET Core Blazor UI (FAQ) and Microsoft Learn | ASP.NET Core Blazor.
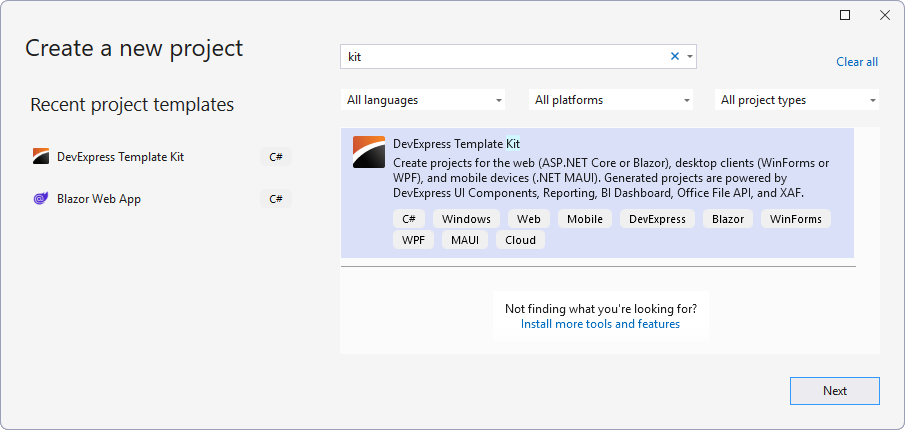
Use the New DevExpress Cross-IDE Template Kit
The legacy Solution Wizard no longer allows you to create new XAF project and item templates. Instead, use the new DevExpress Template Kit that is now automatically added as a Visual Studio extension by our Unified Component Installer.
- To access the DevExpress Template Kit for project templates, select File → New → Project… in Visual Studio 2022+.
- To access the DevExpress Template Kit for item templates, invoke context menu in Solution Explorer and select Add | New Item…
For more information, refer to the following help topic: Template Kit.
Note
The new Template Kit also supports Rider and VS Code.
Legacy and Redundant XAF Windows Forms Modules (.NET)
Pivot Chart (aka Analysis) and KPI Modules
We removed the following XAF Windows Forms (.NET) modules, because the Dashboards Module handles many data analytics use-cases much better as we mentioned in the following article: XAF - 2021 Roadmap (Cross-Platform .NET App UI and Security API).
You can also use our standalone WinForms List Editors from the Pivot Grid and Chart modules (PivotGridListEditor and ChartListEditor), as well as their XAF Blazor counterparts.
- DevExpress.ExpressApp.PivotChart (PivotChartModuleBase)
- DevExpress.ExpressApp.PivotChart.Win (PivotChartWindowsFormsModule)
- DevExpress.ExpressApp.Kpi (KpiModule )
Script Recorder Module (a part of EasyTest)
We removed the following XAF Windows Forms (.NET) modules, because functional/e2e tests with xUnit and C# are easier to implement and maintain (as we first described in 2022).
- DevExpress.ExpressApp.ScriptRecorder (ScriptRecorderModuleBase )
- DevExpress.ExpressApp.ScriptRecorder.Win (ScriptRecorderWindowsFormsModule)
Note
You can still run and debug .ets files with the TestExecutor utility. We also maintain and improve our EasyTest engine and recommend it to customers (to maintain high quality of their XAF UI-based apps). Internally, we have multiple XAF functional tests, and use xUnit/C#-based functional tests for any new XAF development (instead of .ets files generated by the Script Recorder).
Legacy Entity Framework 6 (EF 6) Support
We removed the following EF 6-based packages:
- DevExpress.ExpressApp.EF6
- DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.EF6
- DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF6
For more information, refer to the following help topics:
- Porting from EF 6 to EF Core
- Business Model Design with Entity Framework Core (as recommended since 2019).
Legacy Security System Implementations
XAF v25.2 removes several deprecated security system APIs. Projects that use these old APIs cannot compile after upgrading to v25.2.
Note
For the complete list of removed APIs grouped by assembly, refer to the Removed-Security-API.txt file attached to the following knowledge base article: T1312589 - XAF - Legacy .NET Framework (WinForms and ASP.NET WebForms) APIs, .NET-based API/Modules, and Security System have been removed from distribution.
Migrating your code to new APIs requires manual steps, listed below. We provide a tool to automate some routine tasks and simplify the update, but you will still need to manually modify and review the code.
Important
If your application uses legacy security APIs, update the APIs before upgrading the project to v25.2.
Perform the following steps before you start updating legacy Security APIs:
- Upgrade your project to v25.1.
- Verify that your project compiles and runs.
- Make a backup of your databases.
Convert User Data in the Database to a New Format
Complete the steps below if your application uses any of the following legacy classes:
- DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemUser
- DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemRole
- DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.User
- DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.Role
Step 1. Convert Existing User Data, Roles, and Security Permissions
This step creates new tables in your database for users, roles, and permissions in the new format.
- Ensure that PermissionPolicyUser, PermissionPolicyRole, SecuritySystemUser, and SecuritySystemRole types are added as exported types.
Add the following code to the SolutionName.Module/DatabaseUpdate/Updater.cs file.
Display codeusing System; using System.Linq; using DevExpress.ExpressApp; using DevExpress.Data.Filtering; using DevExpress.Persistent.Base; using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Updating; using DevExpress.Xpo; using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Xpo; using DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl; using DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.PermissionPolicy; using System.Collections.Generic; using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy; namespace SolutionName.Module.DatabaseUpdate { public class Updater : ModuleUpdater { public Updater(IObjectSpace objectSpace, Version currentDBVersion) : base(objectSpace, currentDBVersion) { } public override void UpdateDatabaseAfterUpdateSchema() { base.UpdateDatabaseAfterUpdateSchema(); foreach(SecuritySystemUser securitySystemUser in ObjectSpace.GetObjects<SecuritySystemUser>()) { CopyUser(securitySystemUser); } foreach(SecuritySystemRole securitySystemRole in ObjectSpace.GetObjects<SecuritySystemRole>()) { CopyRole(securitySystemRole, null); } ObjectSpace.CommitChanges(); } private void CopyUser(SecuritySystemUser securitySystemUser) { PermissionPolicyUser permissionPolicyUser = ObjectSpace.FindObject<PermissionPolicyUser>(new BinaryOperator("UserName", securitySystemUser.UserName)); if(permissionPolicyUser == null) { permissionPolicyUser = ObjectSpace.CreateObject<PermissionPolicyUser>(); permissionPolicyUser.UserName = securitySystemUser.UserName; permissionPolicyUser.IsActive = securitySystemUser.IsActive; permissionPolicyUser.ChangePasswordOnFirstLogon = securitySystemUser.ChangePasswordOnFirstLogon; foreach(SecuritySystemRole securitySystemRole in securitySystemUser.Roles) { CopyRole(securitySystemRole, permissionPolicyUser); } } } private void CopyRole(SecuritySystemRole securitySystemRole, PermissionPolicyUser permissionPolicyUser) { PermissionPolicyRole permissionPolicyRole = ObjectSpace.FindObject<PermissionPolicyRole>(new BinaryOperator("Name", securitySystemRole.Name)); if(permissionPolicyRole == null) { permissionPolicyRole = ObjectSpace.CreateObject<PermissionPolicyRole>(); permissionPolicyRole.Name = securitySystemRole.Name; permissionPolicyRole.PermissionPolicy = SecurityPermissionPolicy.DenyAllByDefault; permissionPolicyRole.IsAdministrative = securitySystemRole.IsAdministrative; permissionPolicyRole.CanEditModel = securitySystemRole.CanEditModel; foreach(SecuritySystemTypePermissionObject securitySystemTypePermissionObject in securitySystemRole.TypePermissions) { CopyTypePermissions(securitySystemTypePermissionObject, securitySystemRole, permissionPolicyRole); } foreach(SecuritySystemRole parentRole in securitySystemRole.ParentRoles) { CopyParentRole(parentRole, permissionPolicyRole); } } if(permissionPolicyUser != null) { permissionPolicyUser.Roles.Add(permissionPolicyRole); } } private void CopyParentRole(SecuritySystemRole parentRole, PermissionPolicyRole permissionPolicyRole) { if(parentRole.IsAdministrative) { permissionPolicyRole.IsAdministrative = true; } if(parentRole.CanEditModel) { permissionPolicyRole.IsAdministrative = true; } foreach(SecuritySystemTypePermissionObject securitySystemTypePermissionObject in parentRole.TypePermissions) { CopyTypePermissions(securitySystemTypePermissionObject, parentRole, permissionPolicyRole); } foreach(SecuritySystemRole subParentRole in parentRole.ParentRoles) { CopyParentRole(subParentRole, permissionPolicyRole); } } private void CopyTypePermissions(SecuritySystemTypePermissionObject securitySystemTypePermissionObject, SecuritySystemRole securitySystemRole, PermissionPolicyRole permissionPolicyRole) { PermissionPolicyTypePermissionObject permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject = ObjectSpace.FindObject<PermissionPolicyTypePermissionObject>(new BinaryOperator("TargetType", securitySystemTypePermissionObject.TargetType)); permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject = ObjectSpace.CreateObject<PermissionPolicyTypePermissionObject>(); permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject.TargetType = GetTargetType(securitySystemTypePermissionObject.TargetType); permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject.Role = permissionPolicyRole; if(securitySystemTypePermissionObject.AllowRead) { permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject.ReadState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } if(securitySystemTypePermissionObject.AllowWrite) { permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject.WriteState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } if(securitySystemTypePermissionObject.AllowCreate) { permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject.CreateState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } if(securitySystemTypePermissionObject.AllowDelete) { permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject.DeleteState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } if(securitySystemTypePermissionObject.AllowNavigate) { permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject.NavigateState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } foreach(SecuritySystemObjectPermissionsObject securitySystemObjectPermissionsObject in securitySystemTypePermissionObject.ObjectPermissions) { CopyObjectPermissions(securitySystemObjectPermissionsObject, permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject); } foreach(SecuritySystemMemberPermissionsObject securitySystemMemberPermissionsObject in securitySystemTypePermissionObject.MemberPermissions) { CopyMemberPermission(securitySystemMemberPermissionsObject, permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject); } permissionPolicyRole.TypePermissions.Add(permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject); } private void CopyMemberPermission(SecuritySystemMemberPermissionsObject securitySystemMemberPermissionsObject, PermissionPolicyTypePermissionObject permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject) { PermissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObject permissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObject = ObjectSpace.CreateObject<PermissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObject>(); permissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObject.TypePermissionObject = permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject; if(securitySystemMemberPermissionsObject.AllowRead) { permissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObject.ReadState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } if(securitySystemMemberPermissionsObject.AllowWrite) { permissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObject.WriteState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } permissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObject.Members = securitySystemMemberPermissionsObject.Members; permissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObject.Criteria = securitySystemMemberPermissionsObject.Criteria; permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject.MemberPermissions.Add(permissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObject); } private void CopyObjectPermissions(SecuritySystemObjectPermissionsObject securitySystemObjectPermissionsObject, PermissionPolicyTypePermissionObject permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject) { PermissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject permissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject = ObjectSpace.CreateObject<PermissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject>(); permissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject.TypePermissionObject = permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject; if(securitySystemObjectPermissionsObject.AllowRead) { permissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject.ReadState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } if(securitySystemObjectPermissionsObject.AllowWrite) { permissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject.WriteState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } if(securitySystemObjectPermissionsObject.AllowDelete) { permissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject.DeleteState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } if(securitySystemObjectPermissionsObject.AllowNavigate) { permissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject.NavigateState = SecurityPermissionState.Allow; } permissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject.Criteria = securitySystemObjectPermissionsObject.Criteria; permissionPolicyTypePermissionObject.ObjectPermissions.Add(permissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject); } private Type GetTargetType(Type currentType) { Type outType; if(!SecurityAssociationClassDictionary.TryGetValue(currentType, out outType)) { outType = currentType; } return outType; } private static Dictionary<Type, Type> SecurityAssociationClassDictionary = new Dictionary<Type, Type>(){ { typeof(SecuritySystemUser),typeof(PermissionPolicyUser) }, { typeof(SecuritySystemRole),typeof(PermissionPolicyRole) }, { typeof(SecuritySystemTypePermissionObject ),typeof(PermissionPolicyTypePermissionObject ) }, { typeof(SecuritySystemObjectPermissionsObject ),typeof(PermissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObject ) }, { typeof(SecuritySystemMemberPermissionsObject ),typeof(PermissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObject ) } }; } }Run your application in debug mode and ensure that the added code is executed.
Note
- This section includes code for the SecuritySystemUser, SecuritySystemRole, and related persistent classes. The code works with eXpress Persistent Objects (XPO). If you use Entity Framework (EF), change the code to use User, Role, and related classes.
- These instructions help with migration by focusing on common permission cases. Old classes use different permission systems and some permissions may not transfer properly. You should manually check and update permissions if issues arise.
- This code does not remove database tables for old security classes because other applications may be relying on these tables.
- Converted permission records use new key values. This code does not copy old keys to new permission objects.
- In some cases, it is better to rework permissions so that they match the new security system. For instance, a permission where all objects are allowed except those that use a complex criterion may be replaced with a permission where some objects are denied using a simple criterion.
Step 2. Copy User Passwords to New Tables.
Run the following SQL query in your database. Note that this query copies data from SecuritySystemUser to PermissionPolicyUser in the MS SQL Server database. If your project uses another database or other user types, change the code to match your data types.
update PermissionPolicyUser
set StoredPassword = (select StoredPassword from SecuritySystemUser where SecuritySystemUser.UserName = PermissionPolicyUser.UserName)
Instead of copying passwords, you can generate new passwords for users. Refer to the following section for more information: Update Legacy SHA-512-Hashed User Passwords.
Step 3. Check Results and Remove Unnecessary Code
- Run the application. Check that the database contains new user data tables.
- Remove the code you added to the application in the first and second steps.
Update Application Code (Remove Outdated Security APIs)
This step is required if your application uses built-in user and role types other than PermissionPolicyUser and PermissionPolicyRole (for instance, SecuritySystemUser / SecuritySystemRole ), or legacy feature toggles: EnableRfc2898, SupportLegacySha512, or AutoAssociationPermissions.
You can use the converter tool to update legacy APIs or update code manually.
Use the Converter Tool to Update Legacy APIs
Tip
Use a version control system to review changes made by the converter.
We provide a tool to update legacy APIs in your application. You can find the tool source code in the following GitHub repository: XafApiConverter. Compile the XafApiConverter project. Once completed, run the result file from the command line:
XafApiConverter.exe security-update <PathToYourSolution>
<PathToYourSolution> is the full path to your solution. If you specify a folder, the tool processes every solution in the folder and its subfolders.
After the tool finishes, check that your solution compiles and runs. The tool updates deprecated API uses, but it does not ensure that the code compiles or functions correctly afterward. Manual review and additional fixes are necessary if the tool misses something or if issues arise after the update.
Update Legacy APIs Manually
Follow these steps to update APIs manually:
Replace old classes with new classes according to the following list.
Display the list of classesOld Class New Class DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemUser
DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.SecurityUserBaseDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.UserDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.SimpleUserDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.BasicUserDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.PermissionPolicy.PermissionPolicyUser DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemRole DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.RoleDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.PermissionPolicy.PermissionPolicyRole DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemTypePermissionObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.PermissionPolicy.PermissionPolicyTypePermissionObjectDevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemObjectPermissionsObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.PermissionPolicy.PermissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObjectDevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemMemberPermissionsObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.PermissionPolicy.PermissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.User DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.PermissionPolicy.PermissionPolicyUser DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.Role DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.PermissionPolicy.PermissionPolicyRole DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.TypePermissionObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.PermissionPolicy.PermissionPolicyTypePermissionObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.SecuritySystemObjectPermissionsObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.PermissionPolicy.PermissionPolicyObjectPermissionsObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.SecuritySystemMemberPermissionsObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.PermissionPolicy.PermissionPolicyMemberPermissionsObjectDevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.SecurityComplexDevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.SecuritySimpleDevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.SecurityBaseDevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.SecurityStrategyComplex Update
AllowCreate,AllowRead,AllowWrite,AllowDelete, andAllowNavigateproperties of the following classes:DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemTypePermissionObjectDevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemObjectPermissionsObjectDevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemMemberPermissionsObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.TypePermissionObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.SecuritySystemObjectPermissionsObjectDevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.SecuritySystemMemberPermissionsObject
Change these properties to
CreateState,ReadState,WriteState,DeleteState, andNavigateState, as shown below:// old code permission.AllowRead = true; permission.AllowDelete = false; // new code permission.ReadState = DevExpress.Persistent.Base.SecurityPermissionState.Allow; permission.DeleteState = DevExpress.Persistent.Base.SecurityPermissionState.Deny;Remove usage of
ParentRolesandChildRolesproperties fromSecuritySystemRoleandEF.Roleclasses. Change user roles and access rights if necessary.Remove the following feature toggles from your code:
DevExpress.Persistent.Base.PasswordCryptographer.EnableRfc2898DevExpress.Persistent.Base.PasswordCryptographer.SupportLegacySha512DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Strategy.SecuritySystemRole.AutoAssociationPermissions
Check that your project compiles and runs.
Update Legacy SHA-512-Hashed User Passwords
We have disabled support for the SHA-512 password hashing algorithm.
Important
If your application uses SHA-512, you must update old passwords before you upgrade the project to v25.2.
Your application likely uses SHA-512 if any of the following conditions apply:
- The FrameworkSettingsCompatibilityMode property is set to
v20_1. - The
PasswordCryptographer.SupportLegacySha512property is set totrue. - The
PasswordCryptographer.EnableRfc2898property is set tofalse. - The database contains users created before v20.2 who have not updated their passwords.
You can update outdated passwords in the following ways:
- Require users with outdated passwords to change their passwords when they log in.
- Update outdated passwords to administrator-generated passwords.
Note
The code samples in this topic use the ApplicationUser type to store user data. If your application uses another type, change the code to match your user type.
Require Users to Update Outdated Passwords on Next Login
These steps force users with SHA-512-hashed passwords to change their passwords when they log in.
Add the following code to the
Mainmethod in your project’s Program.cs file to enable both password hashing algorithms:public static int Main(string[] args) { PasswordCryptographer.EnableRfc2898 = true; PasswordCryptographer.SupportLegacySha512 = true; // ... }Ensure that you do not set DefaultSettingsCompatibilityMode to
v20_1. Use compatibility mode for a newer version or delete the DefaultSettingsCompatibilityMode setting code.Add the following code to the UpdateDatabaseAfterUpdateSchema() method in SolutionName.Module\DatabaseUpdate\Updater.cs to execute it during the database update, or to a controller action’s Execute event handler to let the administrator execute it later:
void ExpireSha512Passwords() { var users = ObjectSpace.GetObjectsQuery<ApplicationUser>(); foreach (var user in users) { if (IsOldSha512Hash(user.StoredPassword)) { user.ChangePasswordOnFirstLogon = true; } } ObjectSpace.CommitChanges(); } bool IsOldSha512Hash(string passwordHash) { return passwordHash != null && passwordHash.Length == 97 && passwordHash.Contains('*'); }You can run a similar SQL query directly on your database. For example, the following code activates the
ChangePasswordOnFirstLogonproperty for users with SHA-512 passwords in a Microsoft SQL Server table:update [PermissionPolicyUser] set ChangePasswordOnFirstLogon = 1 where LEN(StoredPassword)=97 and CHARINDEX('*', StoredPassword) > 0Wait until all users with old passwords update their passwords.
Remove the code you added to the application in the previous steps.
Update Outdated Passwords to Administrator-Generated Passwords
These steps set new administrator-generated passwords for users with SHA-512-hashed passwords. In this case, you do not need to wait until all users update their passwords before upgrading your project.
The application saves the list of users and their new passwords in a text file. The administrator must inform users about their new passwords. Users must change the auto-generated password on their next login.
Add the following code to the
Mainmethod in your project’s Program.cs file to enable both password hashing algorithms:PasswordCryptographer.EnableRfc2898 = true; PasswordCryptographer.SupportLegacySha512 = true;Ensure you do not set DefaultSettingsCompatibilityMode to
v20_1. Use compatibility mode for a newer version or delete the DefaultSettingsCompatibilityMode setting code.Add the following code to the UpdateDatabaseAfterUpdateSchema() method in SolutionName.Module\DatabaseUpdate\Updater.cs to execute it during the database update, or to a controller action’s Execute event handler to let the administrator execute it later:
void SetRandomRfcPasswords() { var data = new List<string>(); var users = ObjectSpace.GetObjectsQuery<ApplicationUser>(); foreach (var user in users) { if (IsOldSha512Hash(user.StoredPassword)) { byte[] bytes = RandomNumberGenerator.GetBytes(6); string newPassword = Convert.ToBase64String(bytes); user.SetPassword(newPassword); user.ChangePasswordOnFirstLogon = true; data.Add($"Login: {user.UserName} Password: {newPassword}"); } } ObjectSpace.CommitChanges(); File.WriteAllLines("NewPasswords.txt", data, Encoding.UTF8); } bool IsOldSha512Hash(string passwordHash) { return passwordHash != null && passwordHash.Length == 97 && passwordHash.Contains('*'); }Run your application in debug mode and ensure that the added code is executed.
Inform users about their new passwords. Users are required to change their passwords when they log in.
Remove the code you added to the application in the previous steps.
You can also use the Reset Password action to change a password for individual users.
Additional Steps to Support New Authentication Methods
Complete these steps if you want to add new authentication methods, such as Microsoft Entra ID. You need to update the user class and database structure.
Tip
If your application uses a user class that inherits from PermissionPolicyUserand implements the ISecurityUserWithLoginInfo interface, you can skip the following steps.
Create an
ApplicationUserLoginInfoclass. This class must implement the ISecurityUserLoginInfo interface. See the interface documentation for an example.If your application uses
PermissionPolicyUserdirectly (without a custom descendant), create a descendant class calledApplicationUser. Update your application so it uses this class as the user type.Implement the ISecurityUserWithLoginInfo interface in your
ApplicationUserclass. See the interface documentation for an example.Register
ApplicationUserLoginInfoandApplicationUseras business objects as described in the following topic: Ways to Add a Business Class.Update your application to use the CreateUser method to create a new user.
Note
To enable new authentication methods, configure your application and authentication providers. The steps in this section prepare your code for future authentication options but do not enable them. Refer to the following help topic for additional information:
XPO Middle-Tier Security for WCF
- Remove any code related to the deprecated WCF client and server (
WcfSecuredClient,WcfDataServerHelper,MiddleTierSerializableObjectLayerClient,SerializablePermissionRequest,SecuredDataServer,ClientInfo, and so on). - Create an ASP.NET Core-based project as outlined in the following help topic: Create a .NET Application with the XPO Middle Tier Security.
Certain DevExpress.Persistent.Base / DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.Xpo API
Note
For the complete list of removed APIs grouped by assembly, refer to Removed-BaseImpl-Base-DC-API.txt and Removed-DC-API.txt attached to the following knowledge base article: T1312589 - XAF - Legacy .NET Framework (WinForms and ASP.NET WebForms) APIs, .NET-based API/Modules, and Security System have been removed from distribution.
XPO Demo Classes and Helpers from the DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl Namespace
We removed multiple XPO-based demo classes under the DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl namespace:
Address,Country,StateOrganization,Party,Person,PhoneNumber,Note,TaskPhoneType,PropertyBag,PropertyBagDescriptor,PropertyDescriptor,PropertyValue
DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.Xpo now contains only persistent classes required for the operation of XAF-specific modules (for example, PermissionPolicyUser, ReportData). For more information, refer to the following help topic: Built-in Business Classes & Interfaces.
Our motivation was the same as for the DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EFCore library in the past. Additionally, we aim to avoid naming and UI/layout conflicts with existing customer classes.
To see the source code of these removed demo classes, download and install v25.1 with the Source & Symbols installer option, and navigate to c:\Program Files\DevExpress 25.1\Components\Sources\DevExpress.Persistent\DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.Xpo\.
Demo Class UI/Layout Settings (aka the DevExpress.ExpressApp.Objects Module)
The Project Converter automatically removes the DevExpress.ExpressApp.Objects project and code references, so no action is required in most cases. UI and layout settings for built-in persistent classes now ship with DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.Xpo and DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EFCore packages.
Domain Component (DC) Interfaces
Remove any DCBaseObject mentions and migrate DC interfaces to pure XPO classes.
Legacy XPO Sequence Number Generators
Remove any mentions of the DistributedIdGeneratorHelper, OidGenerator, and ServerPrefix classes from the DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl namespace and follow Auto-Generate Unique Number Sequence instead.