How to: Create Named Formulas
- 2 minutes to read
This example demonstrates how to define names for formulas. To do this, call the DefinedNameCollection.Add method with a name to be associated with a formula and the formula string passed as parameters. Use the Worksheet.DefinedNames or Workbook.DefinedNames property to access and modify the collection of defined names of a particular worksheet or entire workbook, depending on which scope you want to specify for a name.
Worksheet worksheet1 = workbook.Worksheets["Sheet1"];
Worksheet worksheet2 = workbook.Worksheets["Sheet2"];
// Create a name for a formula that sums up the values of all cells included in the "A1:C3" range of the "Sheet1" worksheet.
// The scope of this name will be limited by the "Sheet1" worksheet.
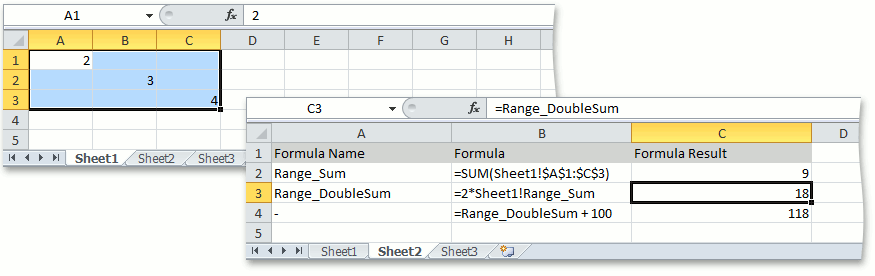
worksheet1.DefinedNames.Add("Range_Sum", "=SUM(Sheet1!$A$1:$C$3)");
// Create a name for a formula that doubles the value resulting from the "Range_Sum" named formula and
// make this name available within the entire workbook.
workbook.DefinedNames.Add("Range_DoubleSum", "=2*Sheet1!Range_Sum");
// Create formulas that use other formulas with the specified names.
worksheet2.Cells["C2"].Formula = "=Sheet1!Range_Sum";
worksheet2.Cells["C3"].Formula = "=Range_DoubleSum";
worksheet2.Cells["C4"].Formula = "=Range_DoubleSum + 100";
The image below shows how to use named formulas in worksheet cells (the workbook is opened in Microsoft® Excel®).
See Also