Prevent Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks
- 2 minutes to read
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks allow threat actors to inject malicious scripts into a web page. Once users open an infected page, injected scripts execute and can steal cookies/session tokens, modify web page content, or redirect to a “phishing” page. Web apps may be vulnerable to XSS attacks if user input is not validated or encoded (to learn more about XSS attacks, refer to the following Microsoft advisory: Prevent Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) in ASP.NET Core).
Microsoft Blazor includes a built-in XSS protection system to help prevent against cross-site scripting attacks. This system encodes all strings defined with standard razor syntax (the @ directive). To display HTML code as text, the system replaces service characters (for instance, < and >) with character entity references (< and >).
Important
The MarkupString class allows you to bypass HTML encoding and render a string value as HTML markup. For security reasons, you should not use this class to display values from an untrusted source (such as user input).
DevExpress UI components for Blazor use Microsoft’s built-in XSS protection system to encode content and values. You should always follow security-related best practices to minimize risks and security-related threats. For more information, refer to the following help topics:
HTML Editor Image Upload
When users insert an image into the HTML Editor From the Web dialog, treat the value as untrusted. Attackers may enter scriptable URLs (such as javascript: or data:) and/or targets that return HTML instead of an image.
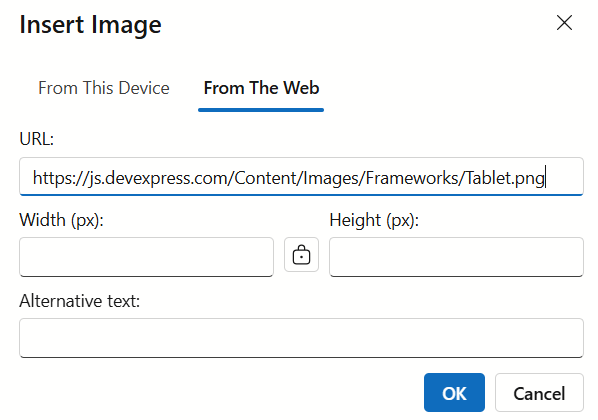
To block stored or reflected XSS attack vectors:
- Validate each URL.
- Route image retrieval through a server-side proxy and check returned information.
- Clean document HTML during save operations.
- Render with a restrictive Content Security Policy (CSP).
Important
SVG format allows the use of scripts. Apply SVG-aware sanitization or rasterize images on the server before use.