Handling Client-side Scripts
- 2 minutes to read
This topic describes the ASP.NET Chart Control’s client-side scripting feature, and demonstrates an easy way to access client-side events.
The WebChartControl supports the AJAX technology, which implements end-user interaction with callbacks rather than standard postbacks. Callbacks get only a specific set of data through targeted round trips to the server, so the entire web page does not need to be refreshed when a page changes. This reduces traffic and increases the performance of your web application. With the Web Chart Control, implementation of client-side scripts is made as easy as possible.
To quickly handle a client-side event, click the WebChartControl’s smart tag, and choose Client Side Events… in the invoked Tasks list. Or, in the Properties window, expand the WebChartControl.ClientSideEvents property and click the ellipsis button for the required event.
In the invoked WebChartControl Designer, write the JavaScript code (or names of the JavaScript handle functions) for the required events.
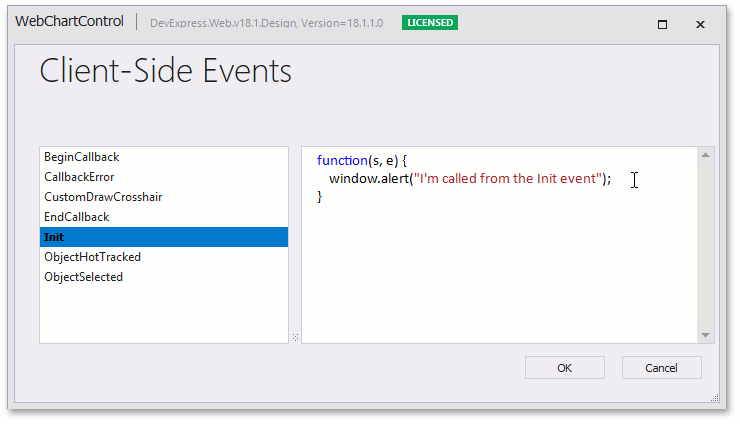
The ChartClientSideEvents class contains the list of available client-side events.
In these event handlers, call the ASPxClientWebChartControl.GetChart method to access a chart’s client-side equivalent (an ASPxClientWebChart object). Then, you can access its main elements (diagram, panes, axes, etc.) and their properties.
Note that the following properties may affect the performance of your web application, so you should use them carefully.
Use the WebChartControl.EnableCallBacks property to specify whether the callback or postback technology is used to manage round trips to the server.
Note
When the WebChartControl is used within an ASPxCallbackPanel, the WebChartControl.EnableCallBacks property should be disabled. Refer to the following help topic for more information: How to: Add a Chart to an ASPxCallbackPanel during its Callback (Runtime Sample).
- Use the WebChartControl.EnableCallbackCompression property to apply compression to callbacks. This option may boost the client-server interaction when a large number of callbacks are performed.