Semantic Search
- 9 minutes to read
Semantic search enables users to locate relevant data quickly and accurately within large datasets. Unlike standard keyword-based search, semantic search leverages Natural Language Processing (NLP) to analyze search queries beyond exact keyword matching.
Applies To
How It Works
Semantic search uses an embedding generator to convert text into numerical vector representations. Vector embeddings are stored in a vector store (for example, a database, in-memory collection, or a custom implementation that stores vector values in files). When a user enters a search query, the search engine computes similarity scores between the query vector and stored data vectors to return the most relevant results.
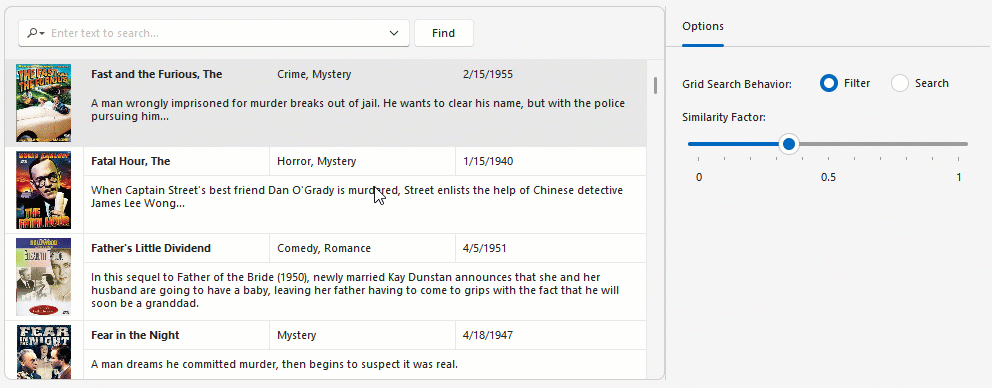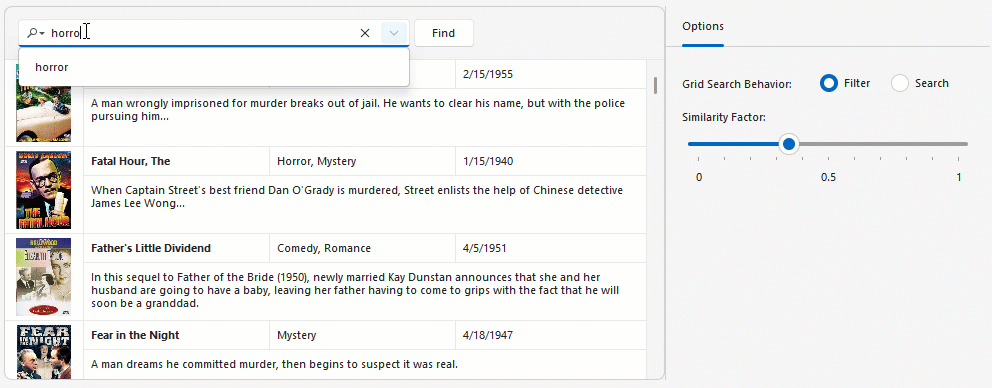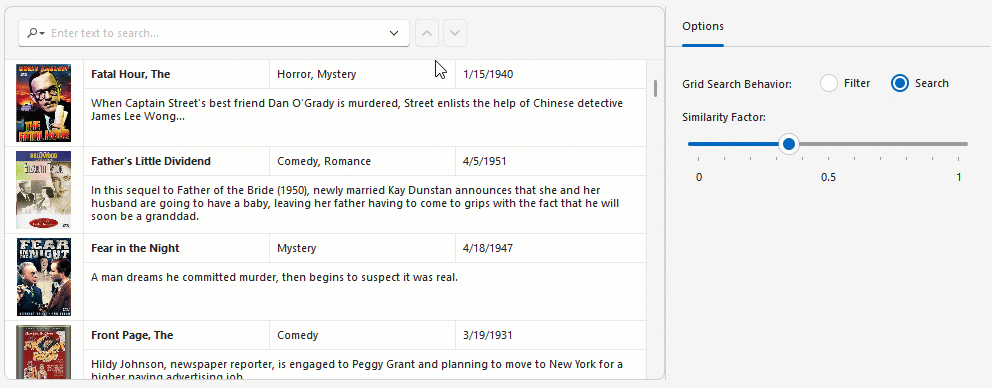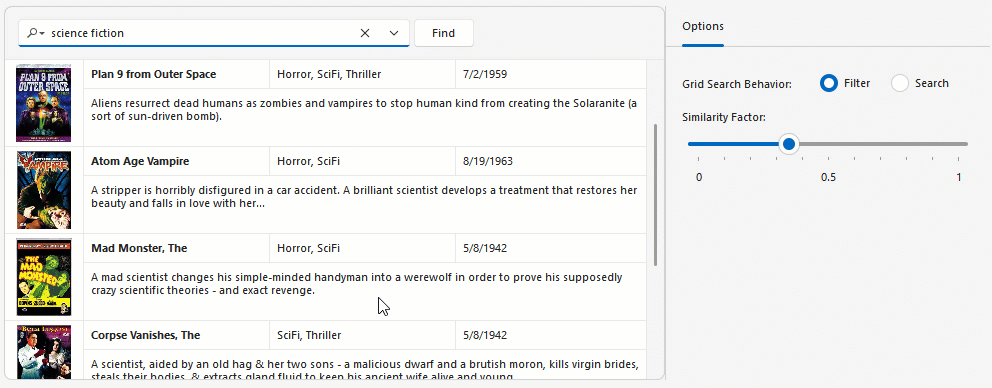
Semantic search can operate in two modes:
- Filter Mode
- Displays only matching records.
- Search Mode
- Highlights relevant data rows for more intuitive data discovery.
Tip
Use the GridView.OptionsFind.Behavior property to specify filter or search mode.
Activate Semantic Search
Install DevExpress NuGet Packages
DevExpress.AIIntegration.WinForms.SemanticSearchDevExpress.Win.Design(enables design-time features for DevExpress UI controls)
See the following help topics for information on how to obtain the DevExpress NuGet Feed and install DevExpress NuGet packages:
- Choose Between Offline and Online DevExpress NuGet Feeds
- Install NuGet Packages in Visual Studio, VS Code, and Rider
Note
Install NuGet packages required by an AI Client used in your project (for example, OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Ollama, etc.). See the following help topic for additional information: Prerequisites.
Register Embedding Generator and Vector Store
The following code snippet does the following:
- Initializes an embedding generator to convert text into numerical vectors.
- Creates an in-memory vector store for vectorized records and registers it in the AI container.
Note
Requires the following Microsoft NuGet Packages:
Azure.AI.OpenAI (2.2.0-beta.5)Microsoft.Extensions.AI.OpenAI (9.7.1-preview.1.25365.4)Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Connectors.InMemory (1.62.0-preview)
using Azure.AI.OpenAI;
using DevExpress.AIIntegration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.AI;
using Microsoft.SemanticKernel.Connectors.InMemory;
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
internal static class Program {
[STAThread]
static void Main() {
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
var container = AIExtensionsContainerDesktop.Default;
// The following code uses an Azure OpenAI embedding model.
var embeddingGenerator = new AzureOpenAIClient(AzureOpenAIEndpoint, AzureOpenAIKey)
.GetEmbeddingClient("text-embedding-3-small").AsIEmbeddingGenerator();
// Create an in-memory vector collection to store vectorized records.
var vectorCollection = new InMemoryCollection<string, VectorStoreRecord>("Cars", new InMemoryCollectionOptions{ EmbeddingGenerator = embeddingGenerator});
// Register the vector collection in the AI container.
container.RegisterVectorCollection(vectorCollection);
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
}
Initialize Vector Store
Supply a vector store or database to hold and retrieve vectorized data. The following code snippet does the following:
- Defines a record stored in the vector store for semantic search (
VectorStoreRecord). - Initializes an in-memory vector store (for demo purposes).
Tip
Production AI applications use vector databases and services to improve relevancy. You can use any vector store that implements the IVectorStore interface to store embeddings. See the following topics for additional information:
using DevExpress.AIIntegration;
using DevExpress.AIIntegration.SemanticSearch;
using DevExpress.AIIntegration.WinForms;
using Microsoft.Extensions.VectorData;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
public partial class Form1 : DevExpress.XtraBars.Ribbon.RibbonForm {
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
// Bind the Grid Control to data.
gridControl1.DataSource = DataHelper.Items;
// Enable search mode.
gridView1.OptionsFind.Behavior = DevExpress.XtraEditors.FindPanelBehavior.Search;
// Initialize the vector store.
Task.Run(InitializeVectorStore);
}
async Task InitializeVectorStore() {
// Get the default AI extensions container.
var container = AIExtensionsContainerDesktop.Default;
try {
// Create a vector store collection named "Cars" with DataHelper.Items data.
var collection = container.GetVectorCollection<string, VectorStoreRecord>("Cars");
if (await collection.CollectionExistsAsync())
return;
var records = DataHelper.Items.Select((item, index) => new VectorStoreRecord{
Key = item.Id.ToString(), // Use the item ID as the key.
Vector = string.Join(". ", item.Trademark, item.Model, item.Description) // Store the generated vector.
});
await collection.EnsureCollectionExistsAsync();
await collection.UpsertAsync(records);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Display an error message if the operation fails.
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
}
// Define a record stored in the vector store for semantic search.
public class VectorStoreRecord {
[VectorStoreKey]
// A unique identifier for the record in a vector store.
public string Key { get; set; }
// Azure OpenAI (embedding model) produces 1536-dimensional vectors.
// Specify how vector data is stored and compared in a vector store.
// Use cosine similarity as the distance function for comparisons.
[VectorStoreVector(1536, DistanceFunction = DistanceFunction.CosineDistance)]
public string Vector { get; set; }
}
public class DataItem {
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Trademark { get; set; }
public string Model { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
}
Create and Configure Semantic Search Behavior
- Drop the
BehaviorManagercomponent from the Toolbox onto a Form. - Add a SemanticSearchBehavior and attach it to a DevExpress UI control (GridControl, GridLookUpEdit, or SearchLookUpEdit).
Configure behavior settings:
Property Name Description DataSourceKeyField Gets or sets the key field in the data source that uniquely identifies records. VectorCollectionName Gets or sets the name of the collection with embeddings in the vector store. ScoreThreshold Gets or sets the similarity score threshold at which search results are considered relevant. ScoreThresholdFilter Controls how the ScoreThreshold is applied during filtering. SearchMode Gets or sets a control’s search mode. SearchResultCount Gets or sets the maximum number of semantic search results returned by a vector store for a query. EmbeddingGeneratorName Gets or sets the embedding generator name. Set this property if you registered multiple embedding generators in the AI container.
The following code snippet activates semantic search for a GridLookUpEdit:
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
gridLookUpEdit1.Properties.DataSource = DataHelper.Items;
gridLookUpEdit1.Properties.DisplayMember = "Model";
gridLookUpEdit1.Properties.ValueMember = "Id";
behaviorManager1.Attach<SemanticSearchBehavior>(gridLookUpEdit1.Properties.View, behavior => {
behavior.Properties.VectorCollectionName = "Cars";
behavior.Properties.DataSourceKeyField = "Id";
behavior.Properties.SearchResultCount = 10;
behavior.Properties.SearchMode = ControlSearchMode.Semantic;
// It is implied, that Cosine Distance filtering is used for the vector store.
// Lower = more similar
behavior.Properties.ScoreThreshold = 0.5D;
behavior.Properties.ScoreThresholdFilter = ScoreThresholdFilter.LessOrEqual;
});
}
Note
Call the BehaviorInitializer.Initialize() method at application startup if your project targets the .NET Framework and you create AI-powered behaviors in code. Otherwise, an exception is thrown.
internal static class Program {
[STAThread]
static void Main() {
//...
// The Initialize() method forcibly initializes the behavior manager in .NET Framework apps.
DevExpress.AIIntegration.WinForms.BehaviorInitializer.Initialize();
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
}
Similarity Filtering
In your vectorized data model, you must annotate a vector field with the VectorStoreVector attribute and specify the desired similarity metric using the DistanceFunction property:
using Microsoft.Extensions.VectorData;
// Define a record stored in the vector store for semantic search.
public class VectorStoreRecord {
// A unique identifier for the record in a vector store.
[VectorStoreKey]
public string Key { get; set; }
// Azure OpenAI (embedding model) produces 1536-dimensional vectors.
// Specify how vector data is stored and compared in a vector store.
// This example uses cosine similarity as the distance function for comparisons.
[VectorStoreVector(1536, DistanceFunction = DistanceFunction.CosineDistance)]
public string Vector { get; set; }
}
Warning
The VectorStoreVector attribute indicates the preferred distance function, but the vector store ultimately determines which similarity metric is supported. If your vector store does not support the specified function, it will throw a runtime error.
Use the following properties to configure similarity filtering:
Score Threshold
The SemanticSearchBehavior.Properties.ScoreThreshold property specifies the minimum or maximum score at which search results are considered relevant. The actual meaning of the score depends on the selected similarity metric/distance function. For example:
- Cosine Similarity
Value Description 1.0Vectors are identical (maximum similarity) 0.0Vectors are orthogonal (no similarity) -1.0Vectors are opposite - Cosine Distance
Value Description 0.0Vectors are identical (maximum similarity) 1.0Vectors are orthogonal (no similarity) 2.0Vectors are opposite
Score Threshold Filter
The SemanticSearchBehavior.Properties.ScoreThresholdFilter property specifies how the ScoreThreshold is applied during filtering:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
None |
No filtering is applied. All results are returned regardless of score. |
GreaterOrEqual |
Include results with a score greater than or equal to ScoreThreshold. Used with Cosine Similarity, where higher scores mean greater similarity. |
LessOrEqual |
Include results with a score less than or equal to ScoreThreshold. Used with Cosine Distance, where lower scores mean greater similarity. |
Examples
- Cosine Similarity Filtering
Returns results with similarity scores from
0.5to1.0:// Higher = more similar semanticSearchBehavior.ScoreThreshold = 0.5; semanticSearchBehavior.ScoreThresholdFilter = ScoreThresholdFilter.GreaterOrEqual;- Cosine Distance Filtering
Returns results with distance scores from
0.0to0.5:// Lower = more similar semanticSearchBehavior.ScoreThreshold = 0.5; semanticSearchBehavior.ScoreThresholdFilter = ScoreThresholdFilter.LessOrEqual;
Search Modes
Once AI-driven semantic search is enabled, a drop-down button appears within the Grid control’s search field. This button opens a popup menu that allows users to specify search mode:
- Standard
- Semantic
- Hybrid (a combination of standard and semantic search)
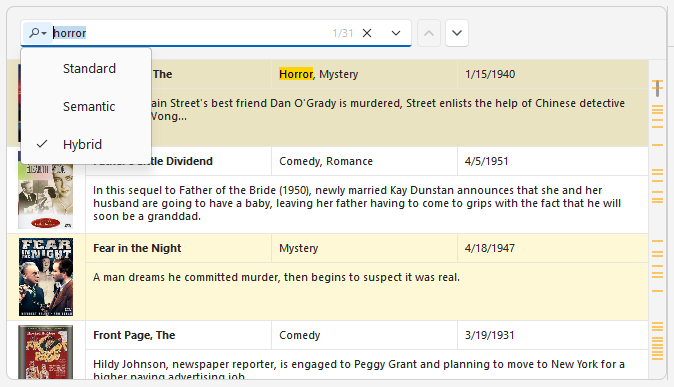
Note
In GridLookUpEdit, users cannot specify search mode. Use the SemanticSearchBehavior.Properties.SearchMode property to specify search mode.
Specific Notes
Semantic search does not support Server Mode.