Migrate WPF Applications to .NET
- 3 minutes to read
This topic describes how to upgrade a WPF application that uses DevExpress controls to .NET.
Important
Make sure you back up your projects prior to upgrading if you are not using source control.
Prerequisites
- .NET
- Visual Studio 2022 v17.0+ with .NET desktop development workload installed
To convert your DevExpress-powered .NET Framework application to the latest .NET version, do the following:
Convert DevExpress Assemblies to NuGet Packages
Use the DevExpress Project Converter tool to quickly replace DevExpress assemblies (dll) with corresponding DevExpress NuGet packages as follows:
Run the DevExpress Project Converter.
In Visual Studio, navigate to Extensions → DevExpress → Project Converter → Project Converter v25.2.
Click Advanced to expand additional settings and enable “Convert DevExpress assembly references to NuGet packages”.
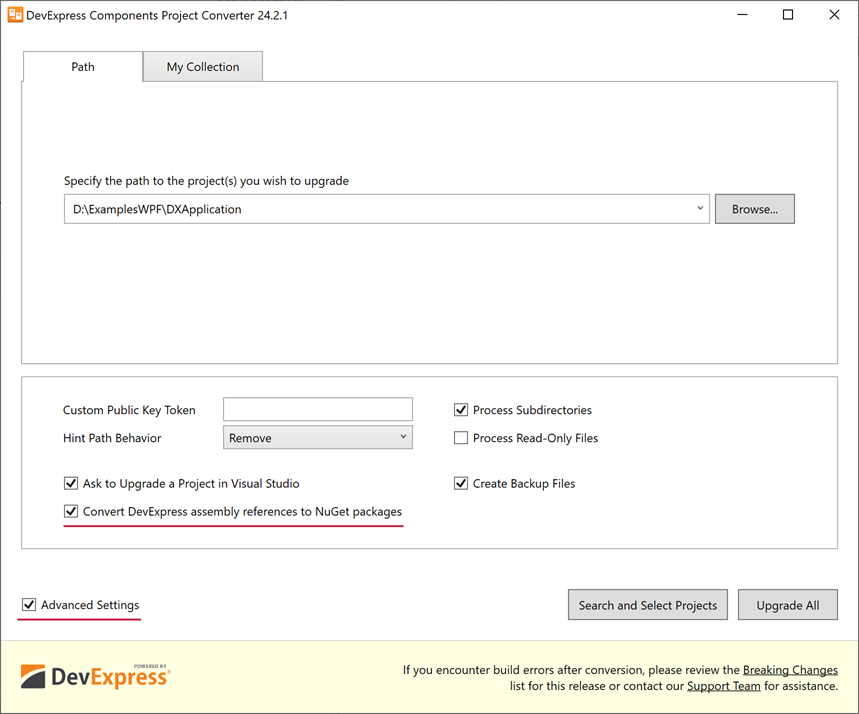
Once you click the “Convert DevExpress assembly references to NuGet packages” option, the warning message below automatically pops up:
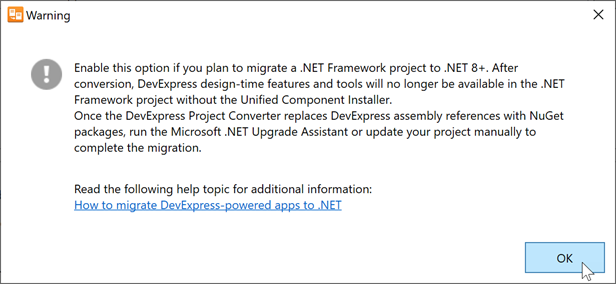
Click OK to proceed.
Click Upgrade All to convert all assemblies in your solution. To convert assemblies in specific projects only, click Search and Select Projects.
Note
If your project references satellite assemblies (localization resources) for cultures other than DE, ES, or JA, they will not be automatically converted to NuGet packages, as these resources are not available at nuget.devexpress.com.
Upgrade Your App to the Latest .NET Version
Follow the steps below to upgrade your .NET Framework application to the latest .NET version:
Right-click a project in the Solution Explorer window and select Upgrade:
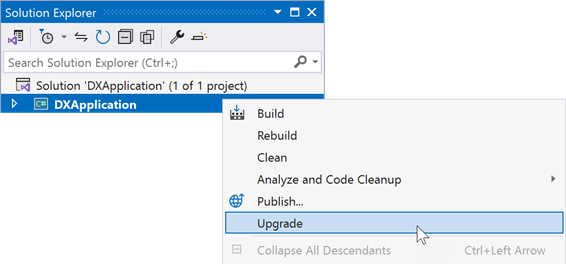
Select one of the following options based on your preferences:
- In-place project upgrade: Upgrades your project without making a copy.
- Side-by-side project upgrade: Copies your project and upgrades the copy.
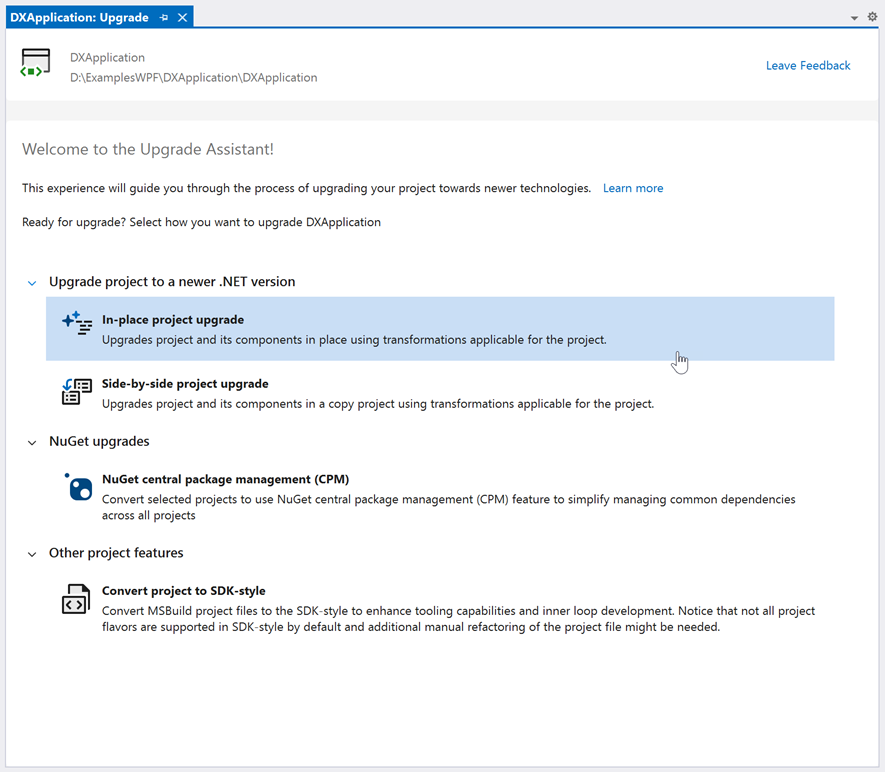
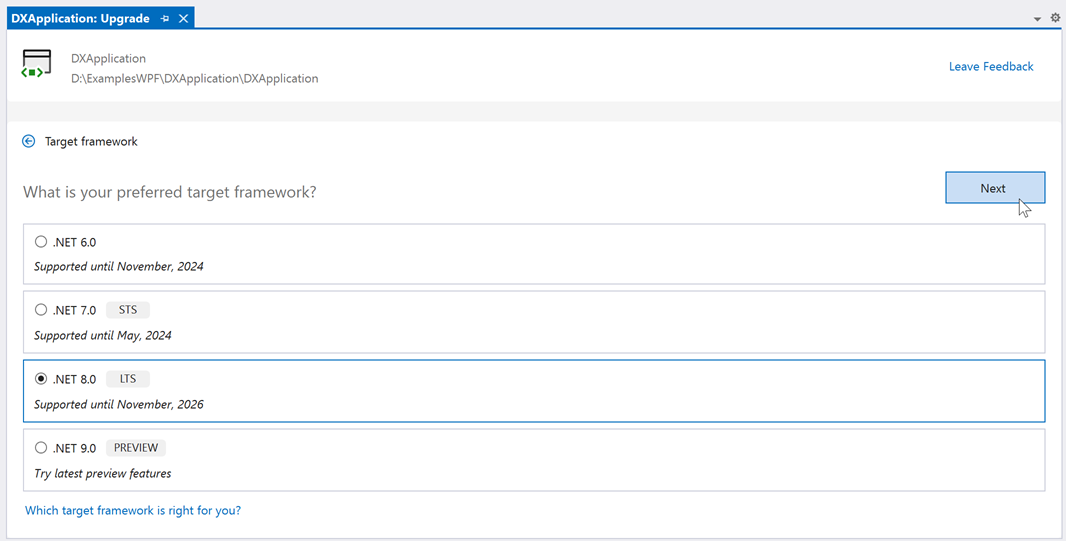
Select the target framework and proceed:
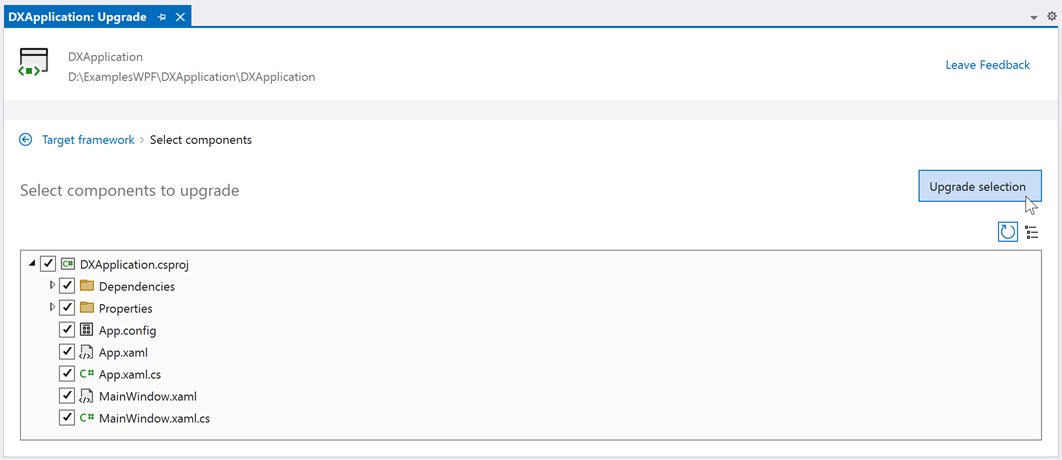
On the next page, select components to upgrade and click Upgrade selection.
Consider Portability Limitations
.NET is missing some APIs that are present in the .NET Framework. Use the .NET Portability Analyzer tool to determine whether your application uses such APIs.
Try to refactor your code to reduce the number of calls to missing APIs. Look for an alternative API with the required functionality.
Useful resource: .NET Framework technologies unavailable on .NET.
Update Non-DevExpress NuGet Packages
DevExpress NuGet packages are compatible with both .NET and .NET Framework platforms.
Check whether the non-DevExpress NuGet packages used within your project are compatible with .NET and whether newer compatible versions are available.
Update your project to reference the latest package versions, if necessary.
Tip
Perform this step even if Visual Studio does not show any compile-time errors. You may experience runtime exceptions if you build the application with packages that were not tested against the .NET Runtime.
Fix Build Issues
If Visual Studio shows build errors, follow the output to refactor your code until you can successfully compile it.
Tip
Use the Microsoft.Windows.Compatibility package to access Windows-specific APIs: Registry, WCF Client, ACL, etc.
Use conditional compilation to write small parts of code that are different for the .NET and .NET Framework.
Known Limitations
Visual Basic projects display the following warning after conversion:
.vbproj uses code generators which will not be handled by try-convert. You can edit your vbproj to add support or remove these dependencies.The default .NET platform is AnyCPU. If your .NET Framework solution has only the x86 platform configured, manually specify the platform in the project file:
<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk"> <PropertyGroup> <Platforms>x86;AnyCPU</Platforms> ... </PropertyGroup> ... </Project>
Test Your App
Run and test the upgraded app. Remember that runtime exceptions are possible even if the application was built without compile-time errors.
Useful Resources
The following Microsoft topic gives an overview of useful techniques and automated tools to port your code to .NET: Port your code from .NET Framework to .NET.