Deploy .NET Applications
- 2 minutes to read
.NET allows you to publish WPF applications in the following ways:
Framework-Dependent Executable
A published application includes its dependencies, but not the .NET runtime. Use this mode if your application is deployed to workstations with the installed .NET runtime.
Self-Contained Deployment
Published application includes all its dependencies and the .NET runtime. This mode allows you to deploy your application to any workstation: your application does not depend on the .NET runtime version installed on the target machine.
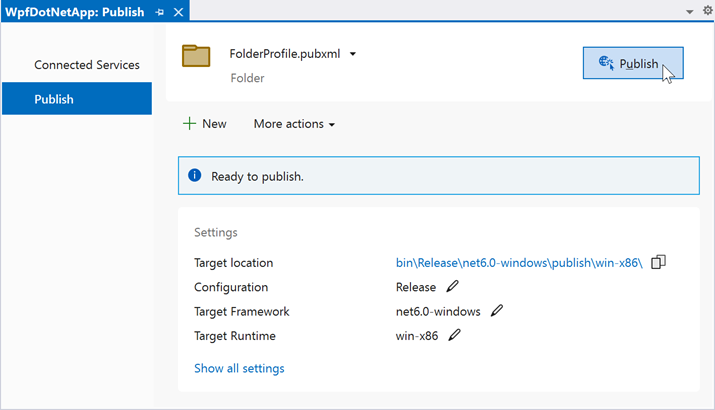
Publish in Visual Studio
To publish an application, right-click the project file and select Publish.
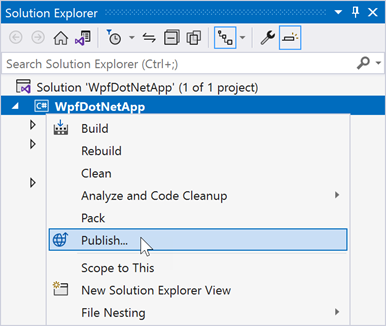
Create a new publish profile, if you have not done so already:
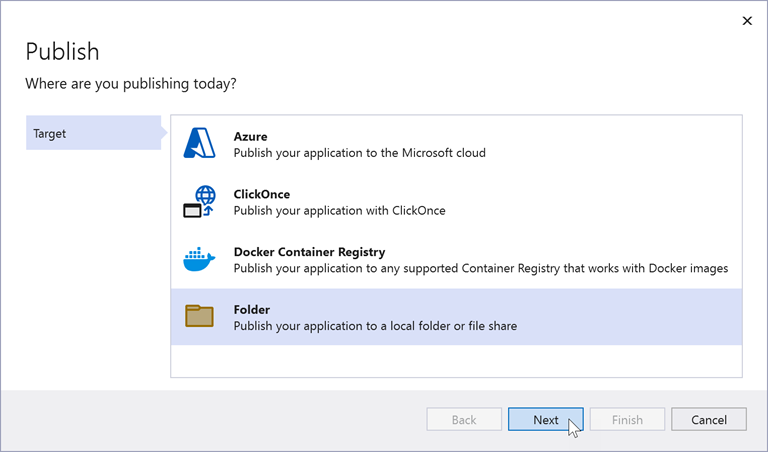
To change the mode, click the Edit publish profile button:
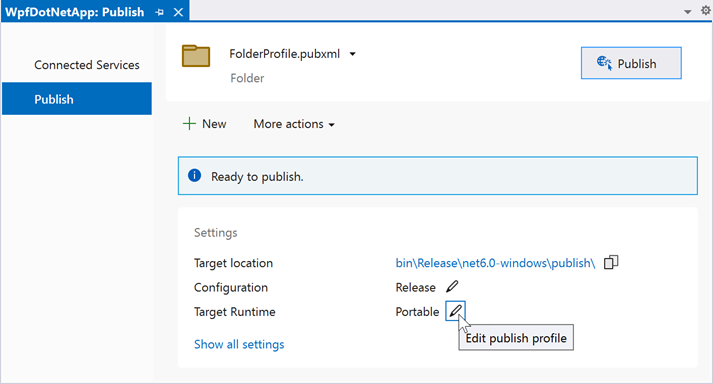
In the Profile Settings window, select the Deployment Mode and click Save:
Click Publish to publish your app to the specified folder.
Publish in Command Line
# <RID> - Runtime Identifier: win-x86, win-x64, etc.
# Framework-dependent executable:
dotnet publish -c Release
# Self-contained deployment:
dotnet publish -c Release -r <RID> --self-contained true
Deployment Options
Single Executable
You can pack your application, its dependencies, and the .NET runtime (if included in deployment) into a single-file executable. This executable contains everything your app requires to run.
To publish your app as a single file, add the following options to your project file:
<PropertyGroup>
<RuntimeIdentifier>win10-x64</RuntimeIdentifier>
<PublishSingleFile>true</PublishSingleFile>
</PropertyGroup>
ReadyToRun Images
.NET allows you to improve the application startup time by compiling your application to ReadyToRun (R2R) format.
R2R binaries contain native code similar to what the just-in-time (JIT) compiler produces. The native code is used to reduce the amount of work the JIT compiler needs to do as your application loads.
To publish an app in the R2R format, set the <PublishReadyToRun> option to true in your project file:
<PropertyGroup>
<PublishReadyToRun>true</PublishReadyToRun>
</PropertyGroup>
The R2R binaries are larger, because they contain both the native and Intermediate Language (IL) code.