Getting Started
- 4 minutes to read
This tutorial provides step-by-step instructions on how to create a simple application with the AccordionControl:
- Step 1. Add a Data Model
- Steps 2-3. Add a View Model
- Steps 4-5. Add the AccordionControl to a View
- Steps 6-7. Bind the AccordionControl to Data
- Steps 8. Get the Result
Tip
See the complete example to learn more: How to: Create a Simple Application with the AccordionControl.
Step 1. Add a Data Model
The AccordionControl can be bound to any object that implements the IEnumerable interface or its descendant (for example, IList, ICollection).
The code sample below demonstrates a simple data model that is used in this tutorial:
using System.Collections.Generic; namespace DxAccordionGettingStarted { public class Employee { public int ID { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public string Position { get; set; } public string Department { get; set; } public override string ToString() { return Name; } } public static class Stuff { public static List<Employee> GetStuff() { List<Employee> stuff = new List<Employee>(); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 1, Name = "Gregory S. Price", Department = "Management", Position = "President" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 2, Name = "Irma R. Marshall", Department = "Marketing", Position = "Vice President" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 3, Name = "John C. Powell", Department = "Operations", Position = "Vice President" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 4, Name = "Christian P. Laclair", Department = "Production", Position = "Vice President" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 5, Name = "Karen J. Kelly", Department = "Finance", Position = "Vice President" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 6, Name = "Brian C. Cowling", Department = "Marketing", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 7, Name = "Thomas C. Dawson", Department = "Marketing", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 8, Name = "Angel M. Wilson", Department = "Marketing", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 9, Name = "Bryan R. Henderson", Department = "Marketing", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 10, Name = "Harold S. Brandes", Department = "Operations", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 11, Name = "Michael S. Blevins", Department = "Operations", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 12, Name = "Jan K. Sisk", Department = "Operations", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 13, Name = "Sidney L. Holder", Department = "Operations", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 14, Name = "James L. Kelsey", Department = "Production", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 15, Name = "Howard M. Carpenter", Department = "Production", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 16, Name = "Jennifer T. Tapia", Department = "Production", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 17, Name = "Judith P. Underhill", Department = "Finance", Position = "Manager" }); stuff.Add(new Employee() { ID = 18, Name = "Russell E. Belton", Department = "Finance", Position = "Manager" }); return stuff; } } }
Steps 2-3. Add a View Model
Create a view model that retrieves data from the data model:
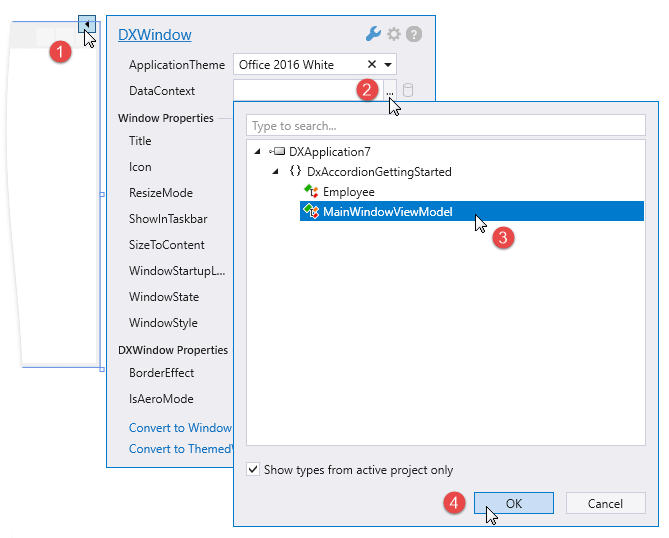
using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Collections.ObjectModel; using System.Linq; namespace DxAccordionGettingStarted { public class MainWindowViewModel { public MainWindowViewModel() { var employeeDepartments = Stuff.GetStuff() .GroupBy(x => x.Department) .Select(x => new EmployeeDepartment(x.Key, x.ToArray())); EmployeeDepartments = new ObservableCollection<EmployeeDepartment>(employeeDepartments.ToArray()); } public ObservableCollection<EmployeeDepartment> EmployeeDepartments { get; set; } } public class EmployeeDepartment { public string Name { get; set; } public ObservableCollection<Employee> Employees { get; set; } public EmployeeDepartment(string name, IEnumerable<Employee> employees) { Name = name; Employees = new ObservableCollection<Employee>(employees); } public override string ToString() { return Name; } } }Build the solution. Invoke the main window’s smart tag and define its data context as shown in the image below:
Steps 4-5. Add the AccordionControl to a View
Drag the AccordionControl from the DX.19.1: Navigation & Layout Toolbox tab and drop it onto the main window:
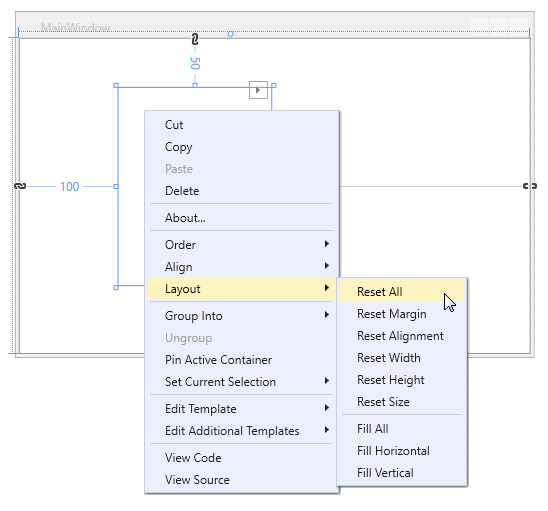
Right-click the control and select Layout | Reset All to allow the AccordionControl to fill the entire window:
Steps 6-7. Bind the AccordionControl to Data
Invoke the AccordionControl’s smart tag and define the ItemsSource field:
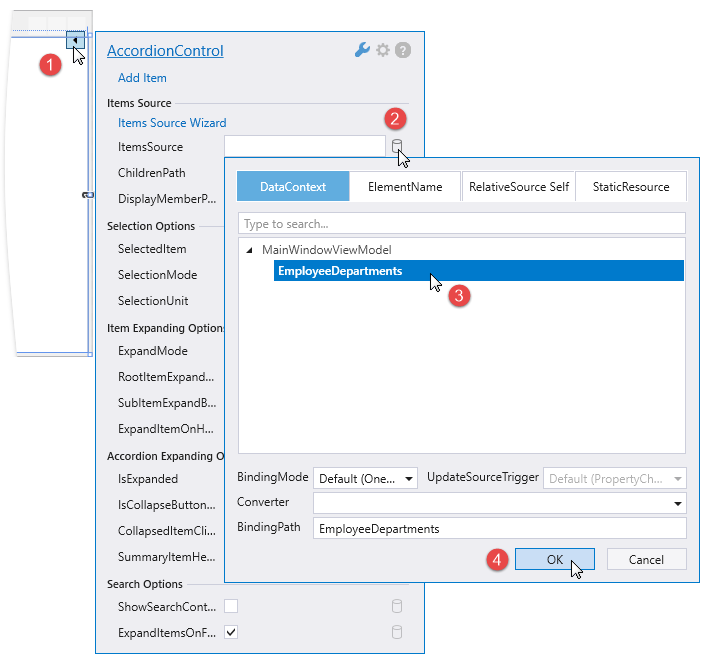
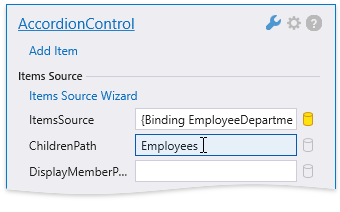
Define the ChildrenPath field that specifies the path to the property that contains an accordion item’s children:
Tip
Refer to the Data Binding topic for details on different approaches to binding the AccordionControl to data.
The code sample below demonstrates the generated code:
<dx:ThemedWindow xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:dx="http://schemas.devexpress.com/winfx/2008/xaml/core" xmlns:dxb="http://schemas.devexpress.com/winfx/2008/xaml/bars" xmlns:dxa="http://schemas.devexpress.com/winfx/2008/xaml/accordion" xmlns:local="clr-namespace:DxAccordionGettingStarted" x:Class="DxAccordionGettingStarted.MainWindow" Title="MainWindow" Height="350" Width="525"> <dx:ThemedWindow.DataContext> <local:MainWindowViewModel/> </dx:ThemedWindow.DataContext> <Grid> <dxa:AccordionControl ItemsSource="{Binding EmployeeDepartments}" ChildrenPath="Employees"/> </Grid> </dx:ThemedWindow>
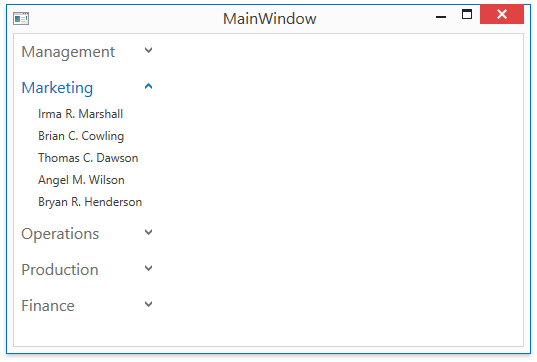
Step 8. Get the Result
Run the solution to see the result: