Connect the ASP.NET Core Dashboard to an Entity Framework data source
- 3 minutes to read
The example below shows how to create an Entity Framework Core data source in code to make it available for end users. This example uses the SQLite database.
Note
Prerequisites Before you begin, open the NuGet Package Manager and install the Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Sqlite package. This is the SQLite database provider for the Entity Framework Core.
In your application, create the Data folder and add the nwind.db database to it from the following folder:
C:\Users\Public\Documents\DevExpress Demos 19.1\Components\Data
Add a new OrdersContext.cs class and create a data context based on the Orders table of the nwind.db database. Define a connection string to the SQLite database by overriding the OnConfiguring method in the constructor.
namespace MvcCoreDashboard { using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using System; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; public partial class OrdersContext : DbContext { public OrdersContext() : base() { } protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder) { base.OnConfiguring(optionsBuilder); optionsBuilder.UseSqlite("Data Source=file:Data/nwind.db"); } public virtual DbSet<Order> Orders { get; set; } } public class Order { [Key] public int OrderID { get; set; } public string CustomerID { get; set; } public long? EmployeeID { get; set; } public DateTime? OrderDate { get; set; } public DateTime? RequiredDate { get; set; } public DateTime? ShippedDate { get; set; } public long? ShipVia { get; set; } public decimal? Freight { get; set; } public string ShipName { get; set; } public string ShipAddress { get; set; } public string ShipCity { get; set; } public string ShipRegion { get; set; } public string ShipPostalCode { get; set; } public string ShipCountry { get; set; } } }In the Startup.cs file, create a public method that returns a configured in-memory dashboard data source storage (DataSourceInMemoryStorage) and define the Entity Framework Core data source.
using DevExpress.DashboardCommon; using DevExpress.DataAccess.EntityFramework; public DataSourceInMemoryStorage CreateDataSourceStorage() { DataSourceInMemoryStorage dataSourceStorage = new DataSourceInMemoryStorage(); DashboardEFDataSource efDataSource = new DashboardEFDataSource("EF Core Data Source"); efDataSource.ConnectionParameters = new EFConnectionParameters(typeof(OrdersContext)); dataSourceStorage.RegisterDataSource("efDataSource", efDataSource.SaveToXml()); return dataSourceStorage; }Use the DashboardConfigurator.SetDataSourceStorage method to set the data source storage and pass the created CreateDataSourceStorage method to use the returned value as a parameter.
using DevExpress.AspNetCore; using DevExpress.DashboardAspNetCore; using DevExpress.DashboardWeb; public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services .AddMvc() .AddDefaultDashboardController(configurator => { // ... configurator.SetDataSourceStorage(CreateDataSourceStorage()); }); }As a result, the EF Core Data Source is displayed as a Web Dashboard’s predefined data source.
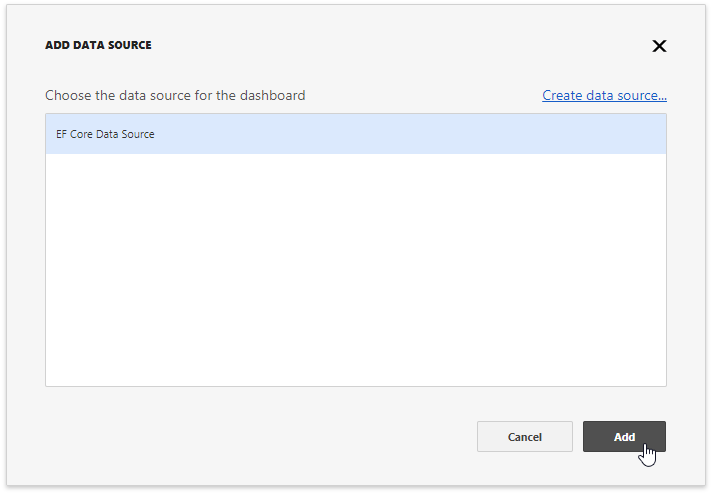
End users can now bind the dashboard items to data in the Web Dashboard’s UI. To learn more, see Binding Dashboard Items to Data in the Web Dashboard’s UI.