Generate EF Core Business Classes from an Existing Database for .NET Blazor and WinForms Applications (Database First)
- 4 minutes to read
You can use the PMC or CLI tool to generate a business model from an existing database with Entity Framework Core (database-first approach). For implementation details of the code-first approach, refer to the following tutorial: Implement a Data Model: Basics. The sections below describe the general approach for Blazor or WinForms .NET 8+ XAF applications.
Set Up the Project
- Create a new Blazor XAF or WinForms XAF project and name it MyEFSolution, for example.
Add the Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools NuGet package to the MyEFSolution.Module project. The package version must correspond to the EF Core version currently supported in XAF. You can use the following Package Manager Console command:
install-package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools -version 7.0.5 -ProjectName MyEFSolution.ModuleBuild the solution.
In the application configuration file, change the connection string’s
Initial Catalogparameter to use the existing database:{ "ConnectionStrings": { "ConnectionString": "Integrated Security=SSPI;Pooling=false;MultipleActiveResultSets=true;Data Source=(localdb)\\mssqllocaldb;Initial Catalog=MyDataBase;ConnectRetryCount=0;", // ... } // ... }In this example,
MyDataBaseis the name of the existing database.
Integrate the Model into the Project
Run the
Scaffold-DbContextcommand. This command generates models from the MyTask and Contact tables of the MyDataBase database and places them in the Model folder:Scaffold-DbContext "Server=(localdb)\mssqllocaldb; DataBase=MyDataBase; Trusted_Connection=True;" Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir MyModels -Project MyEFSolution.Module -StartupProject MyEFSolution.Module -Tables MyTask,Contact -Context MyEFSolutionEFCoreDbContextNew -NoOnConfiguring -DataAnnotationsFor more information about scaffolding, review the following:
- Refer to the following EF tutorial: Creating a Model for an Existing Database in Entity Framework Core.
- Use the following command in the Package Manager console:
get-help scaffold-dbcontext –detailed.
Your app now has two
DbContextentities:MyEFSolutionEFCoreDbContext(located in MyEFSolution.Module\BusinessObjects) created by the Solution WizardMyEFSolutionEFCoreDbContextNew(located in MyEFSolution.Module\MyModels) created in the previous step
Change the namespace of all scaffolded classes to
MyEFSolution.Module.BusinessObjectsand mark all of their properties as virtual to support UseChangeTrackingProxies. For more information, refer to The Importance of Property Change Notifications for Automatic UI Updates and Change Tracking in EF Core DbContext and Performance Considerations.Remove the
TypesInfoInitializerattribute from theMyEFSolutionEFCoreDbContextclass and add this attribute to theMyEFSolutionEFCoreDbContextNewclass. Add the requiredusingstatement and modify theOnModelCreatingmethod:using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Design; namespace MyEFSolution.Module.BusinessObjects { [TypesInfoInitializer(typeof(DbContextTypesInfoInitializer<MyEFSolutionEFCoreDbContextNew>))] public partial class MyEFSolutionEFCoreDbContextNew : DbContext { // ... } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { //.. OnModelCreatingPartial(modelBuilder); modelBuilder.HasChangeTrackingStrategy(ChangeTrackingStrategy.ChangingAndChangedNotificationsWithOriginalValues); modelBuilder.UsePropertyAccessMode(PropertyAccessMode.PreferFieldDuringConstruction); } }Remove the
MyEFSolutionEFCoreDbContextclass declaration. Rename the MyEFSolutionEFCoreDbContextNew file to MyEFSolutionEFCoreDbContext. In the invoked window, click Yes to rename all corresponding references.
In the default configuration, the EF Core scaffolder generates
List<T>for the inner implementations of collection properties (if you have relationships between business objects). ReplaceList<T>withObservableCollection<T>manually or automatically based on T4 templates to ensure correct operation of UI updates and other standard XAF functionality. For more information, refer to the following topics:
- The Importance of Property Change Notifications for Automatic UI Updates
- Configure a One-to-Many Relationship
- Show the
ContactandMyTaskclasses in the Navigation Control.
After this, you can see data from the existing database in your application:
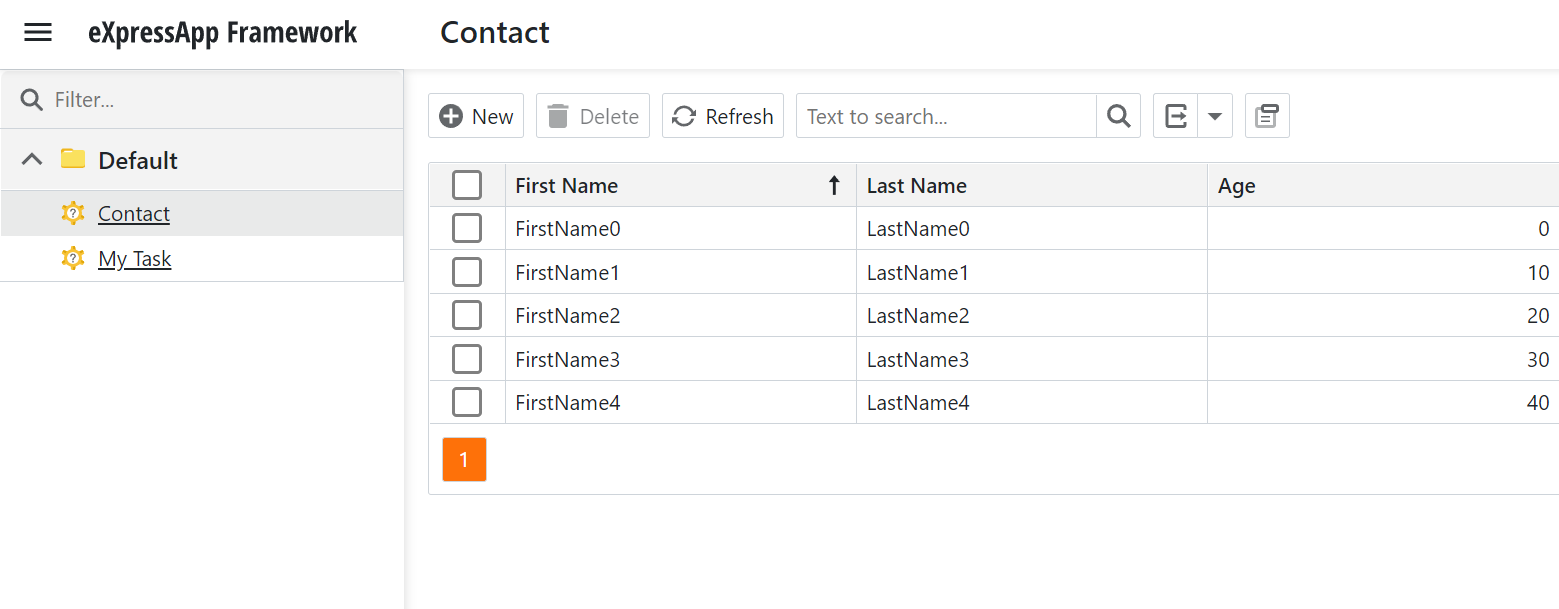
For more information on EF Core scaffolding, refer to the following Microsoft help topic: Reverse Engineering.
Important
XAF’s EF Core implementation does not support the following data model configurations: entities with composite/compound keys (multiple properties as an entity key), keyless entity types, and owned entity types. In such scenarios, inherit your EF Core entity from XAF’s BaseObject class or define your own class with a single Guid, numeric (Int32, Int64 ), or String primary key. You can also use non-persistent objects to integrate XAF UI with legacy systems.