Custom SQL Queries
- 3 minutes to read
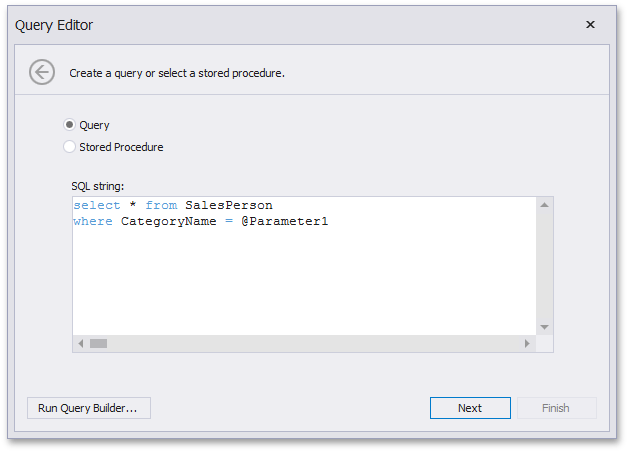
You can allow users to specify custom SQL queries in the Query Editor or Query Builder. To enable this capability, set the SqlWizardSettings.EnableCustomSql property to true. Use the DataSourceWizard property to get access to the DataSourceWizard’s settings.
Warning
The use of custom SQL queries can lead to inadvertent or unauthorized modifications to your data/database structure. Ensure that you follow best practices and implement the appropriate user read/write privileges at database level.
Note
Various SQL extensions can require a special character as the variable’s first character. For instance, this can be the “at” sign (@) for Transact-SQL or the colon (:) for PL/SQL. Insert the required character before the parameter name within the custom SQL query.
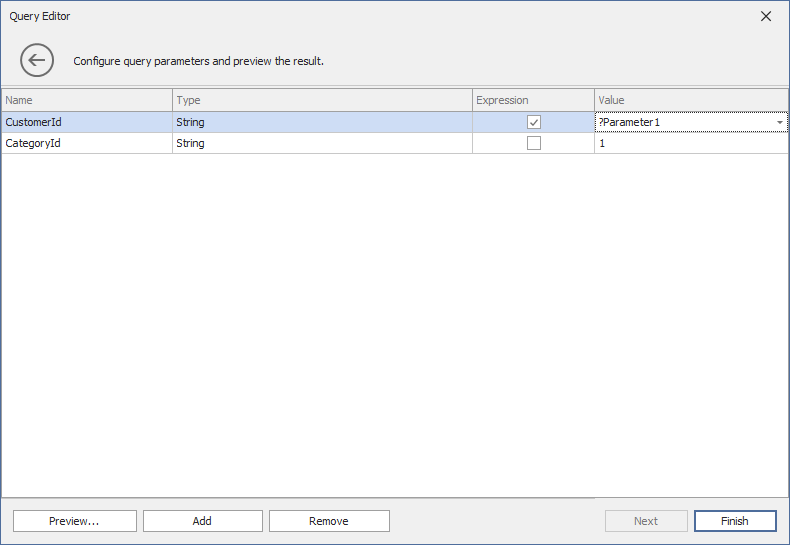
After you have specified the SQL query, click Next. On the next page, you can add query parameters and specify their settings. Refer to the following article for more information about different parameter types: Pass Query Parameters.
Custom SQL Query Validation
The Query Editor allows you to use only SELECT statements in the query. If necessary, you can disable query validation and allow users to include other statements in addition to SELECT statements in SQL queries. To accomplish this, follow the steps below:
- Set the static SqlDataSource.DisableCustomQueryValidation property to
true. The DashboardSqlDataSource class exposes theDisableCustomQueryValidationproperty. - Handle one of the
ValidateCustomSqlQueryevents to manage validation of custom SQL queries. Override the value of the ValidateCustomSqlQueryEventArgs.Valid flag and corresponding ValidateCustomSqlQueryEventArgs.ExceptionMessage message. Be careful when you set thee.Validoption totruebecause this setting skips the default validation.
The following events allow you to specify validation logic:
- IDashboardControl.ValidateCustomSqlQuery
- DashboardDesigner.ValidateCustomSqlQuery
- DashboardViewer.ValidateCustomSqlQuery
- Dashboard.ValidateCustomSqlQuery
The following code snippet shows how to handle the DashboardDesigner.ValidateCustomSqlQuery event to restrict access to the Invoices table in a custom query.
- Default Validation Section
- Checks the validity of the custom query. If the custom query contains statements other than SELECT, or the query is specified incorrectly, the e.Valid property is set to
false. - Custom Validation Section
- Specifies the custom validation logic and the e.ExceptionMessage text.
// ...
dashboardDesigner1.ValidateCustomSqlQuery += dashboardDesigner1_ValidateCustomSqlQuery;
// ...
private void dashboardDesigner1_ValidateCustomSqlQuery(object sender, ValidateDashboardCustomSqlQueryEventArgs e) {
// Default Validation
if(!e.Valid) return;
// Custom Validation
if(e.CustomSqlQuery.Sql.Contains("Invoices"))
{
e.Valid = false;
e.ExceptionMessage = "You do not have access to Invoices";
}
}