Cell Data Types
- 4 minutes to read
Each cell in a worksheet has a value that is specified by the CellValue object. To access this object, use the Range.Value property. A cell value is determined by the data contained within the cell:
- If the cell does not contain any data, the cell value is empty (CellValue.IsEmpty is set to true).
- The cell value is determined by a constant assigned to the cell via the Range.Value property. In this case, the cell value is neither calculated nor changed.
- The cell value is determined by a value resulting from a formula assigned to a cell via the Range.Formula property. In this case, the cell value is calculated dynamically.
A cell value can be of one of the following types: numeric, text, Boolean or error. Data values of these types can have various display formats. For example, a numeric value can be displayed as a decimal number, a percentage or currency value, a date or time value, etc.
Use the properties of the CellValue object returned by the Range.Value property to retrieve information about the cell value type, and get the cell value itself as an object of the corresponding type. To get the string specifying the formatted value as it is displayed in a cell, use the Cell.DisplayText property.
The table below lists the available cell value types and provides examples of how a value of each type can be input, formatted, displayed and obtained.
Cell Value Type | Cell Content | Sample Input | Sample Display Format | Displayed String | Identify the Type | Obtain the Cell Value Object |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
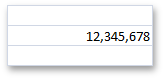
Numeric | The cell’s Range.Value property is assigned to a value of any numeric type (e.g., Int32, Double, etc.). - or - The cell’s Range.Formula property is assigned to an expression that returns a number. | cell.Value = 12345678 - or - cell.Formula = “= SUM(12000000,345678)” | cell.NumberFormat = “#,#” |
| CellValue.IsNumeric = true | |
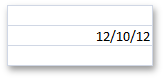
The cell’s Range.Value property is assigned to the DateTime object, an object returned by the CellValue.FromDateTime method, or a numeric value representing a serial number of a date or time. - or - The cell’s Range.Formula property is assigned to an expression that returns the serial number of a date or time. For details, refer to the Dates and Times in Cells document. | cell.Value = new DateTime(2012, 12, 10); - or - workbook.DocumentSettings.Calculation.Use1904DateSystem = true; cell.Value = CellValue.FromDateTime(new DateTime(2012, 12, 10), true); - or - cell.Value = 41253; - or - cell.Formula = “=DATE(2012,12,10)”; | cell.NumberFormat = “m/d/yy” |
| CellValue.IsNumeric = true CellValue.Type = CellValueType.DateTime CellValue.IsDateTime = true | ||
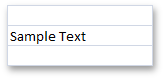
Text | The cell’s Range.Value property is assigned to the String object. - or - The cell’s Range.Formula property is assigned to an expression that returns text. | cell.Value = “Sample Text” - or - cell.Formula = “= PROPER(“sample text”)” |
| CellValue.IsText = true | ||
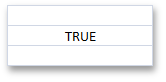
Boolean | The cell’s Range.Value property is assigned to the Boolean object. - or - The cell’s Range.Formula property is assigned to an expression that returns TRUE or FALSE. | cell.Value = true - or - cell.Formula = “= TRUE()” |
| CellValue.IsBoolean = true | ||
The cell’s Range.Value property is assigned to the CellValue object returned by the CellValue.Error* field (for example, CellValue.ErrorDivisionByZero, CellValue.ErrorInvalidValueInFunction, CellValue.ErrorName, etc.). - or - The cell’s Range.Formula property is assigned to an error code (e.g., “=#DIV/0!”, “=#N/A”, etc.) or an expression that cannot be calculated correctly (for example, an expression containing an invalid function name, value, division by zero, etc.) | cell.Value = CellValue.ErrorDivisionByZero - or - cell.Formula = “= #DIV/0!” - or - cell.Formula = “=5/0” |
| CellValue.IsError = true |