Permissions for Associated Objects
- 6 minutes to read
The XAF Security System allows you to manage permissions to access a non-aggregated or aggregated property in semi-automatic mode: you can specify permissions only for one side of an association, and XAF sets them for the other side. This topic explains how the Security System processes permissions for associations and reference properties.
Non-Aggregated Objects
The Security System allows users to read/write a non-aggregated associated property if you explicitly granted access to one association’s side.
For example, the Contact and Department business objects have a one-to-many relationship, and Department implements the Contacts collection property. When you grant access to the Department‘s Contacts collection, the Security System allows access to the Contact‘s Department property. The Security System also allows access to the associated objects’ default property. This property is used to display the collection in human-readable format.
Note
The Contact List View is displayed even if you did not allow access to this type explicitly.
Aggregated Objects
If you specify a permission that allows a user to read the aggregated collection and do not specify permissions for another side of an association, the Security System allows to read the aggregated type. If you specify a permission that allows a user to write the aggregated collection, the Security System allows the write/create/delete operations for the aggregated type.
For example, the Contact and Note business objects have a one-to-many relationship, and Contact implements the Notes aggregated collection property. When you grant permissions to read the Contact‘s Notes collection, the Security System automatically allows users to read the Note type. When you grant permissions to write this collection, the Security System automatically allows users to create, write, and delete the Note type objects.
Reference Objects
The Security System requires explicitly specified permissions for a reference property and its type. Refer to the Reference Properties Access topic for more information.
For example, the Order business object has the Customer reference property of the Customer type. Add permissions that allow users to read the Order‘s Customer property and the Customer type to allow access to the Order‘s Customer property.
Associated Object Permissions’ Processing Modes
The AssociationPermissionsMode enumeration lists modes that determine how the Security System processes permissions for associated objects. To change the mode, set the SecurityStrategy.AssociationPermissionsMode property to one of the following values:
Value | Description |
|---|---|
Auto | The default mode. This mode does not process criteria in permissions for the ‘Many’ association’s side but works faster than ExtendedAuto. If you have criteria in these permissions, set permissions on both sides of an association or use the ExtendedAuto mode. |
ExtendedAuto | This mode handles all scenarios but is slower than Auto. If this mode slows down your application, set permissions with criteria on both sides of the association. |
Manual | Use this mode to configure permissions for both sides of the association. Refer to the How to: Manually Configure Permissions for Associated Collections and Reference Properties topic for more information on this approach. |
Permission Request Calculation Process
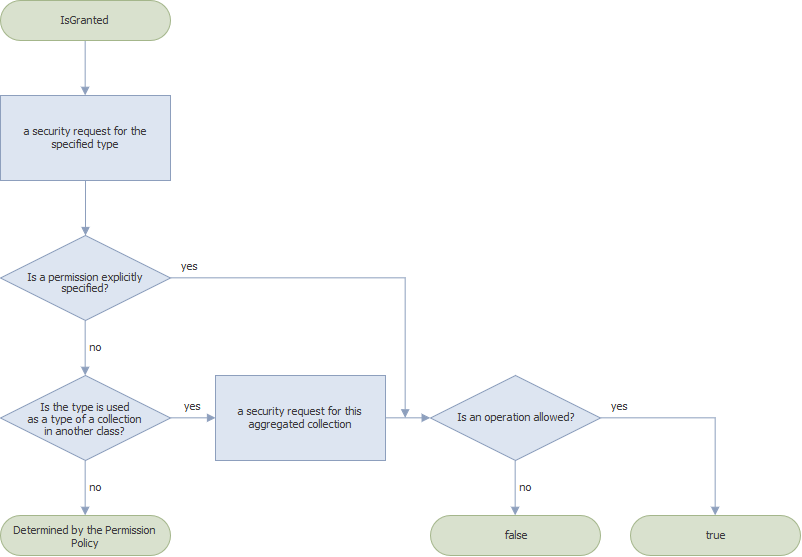
Use the SecuritySystem.IsGranted method to check whether a member, type, or object has permissions that allows/denies a user to make an operation.
Check Permissions for a Member
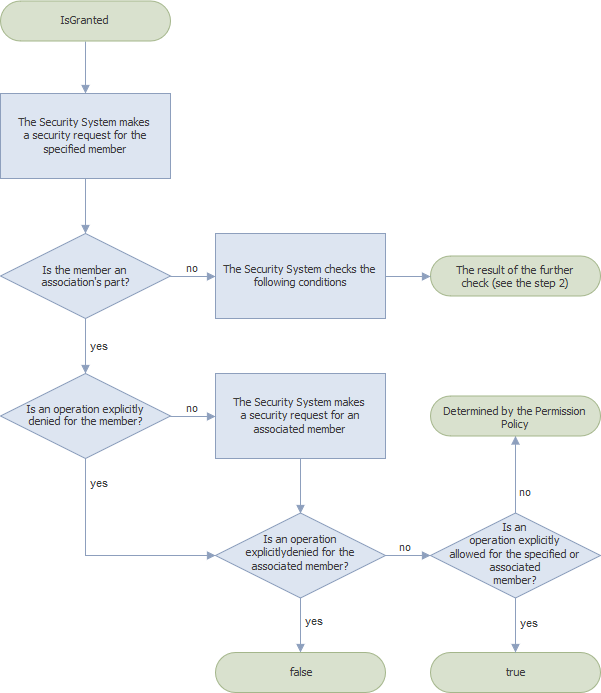
The Security System makes a permission request for the specified member and checks if this member is a part of an association (see IMemberInfo.IsAssociation). If this condition is satisfied, the IsGranted method returns one of the following values; otherwise, the Security System checks the next condition (step 2).
- If the specified member has a permission that explicitly denies an operation (you set “Deny” for the operation), the IsGranted method returns false.
- If the specified member does not have a permission that explicitly denies an operation, the Security System makes a permission request for the associated member. The IsGranted method returns one of the values listed below:
- false - if the associated member has a permission that explicitly denies the operation;
- true - if the specified or associated member has a permission that explicitly allows the operation;
- a value determined by the Permission Policy - if the associated member does not have any explicitly specified permissions.
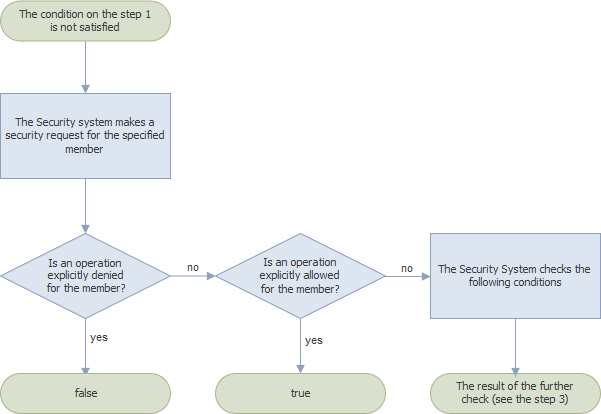
If an association was not found at the first step, the Security System checks if the member has explicitly specified permissions. If this condition is satisfied, the IsGranted method returns one of the values listed below; otherwise, the Security System checks the next condition (step 3).
- false - if the specified member has a permission that explicitly denies an operation (you set “Deny” for the operation);
- true - if the specified member has a permission that explicitly allows an operation.
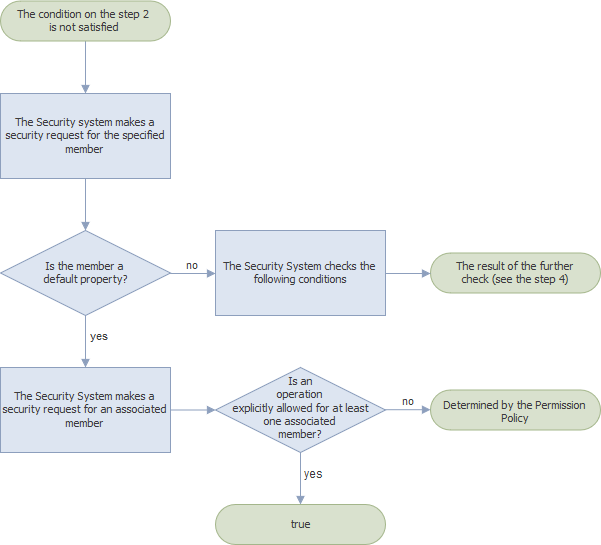
If an association was not found at the first step and the member does not have explicitly specified permissions, the Security System checks if the specified member is a default property (see XafDefaultPropertyAttribute). If this condition is satisfied, the Security System makes a permission request for all associations in the class that implements this member; otherwise, it checks the next condition (step 4). The IsGranted method returns one of the values listed below:
- true - if at least one association in the class has a permission that explicitly allows the operation;
- a value determined by the Permission Policy - if no one association in this class has explicitly specified permissions.
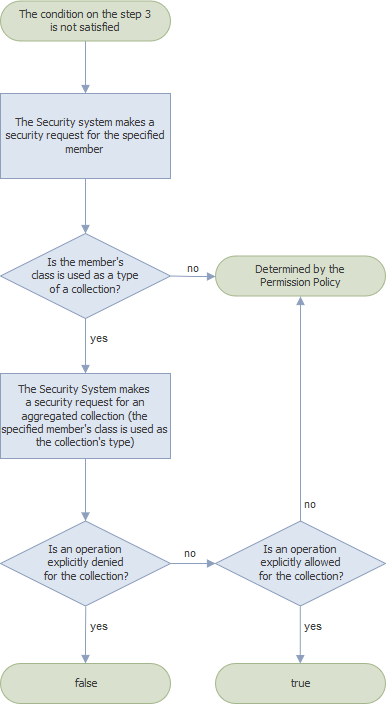
If no condition in any previous step was met, the Security System checks if the class that implements this member is used in another class as a type of an aggregated collection. The IsGranted method returns one of the values listed below:
- false - if the aggregated collection has a permission that explicitly denies the operation;
- true - if the aggregated collection has a permission that explicitly allows the operation;
- a value determined by the Permission Policy - if the aggregated collection does not have explicitly specified permissions or the condition is not satisfied.
Check Permissions for a Type or an Object
- The Security System requests permission for the specified type. If a Type Permission is explicitly allowed/denied (you set “Allow”/“Deny” for the operation), the IsGranted method returns true/false.
- If the Type Permission was not found at the previous step, the Security System checks if the specified type is used in another class as the type of an aggregated collection. If this condition is satisfied, the Security System makes a permission request for this collection. If the aggregated collection has a permission that explicitly allows/denies the operation, the IsGranted method returns true/false.
- If the conditions listed above are not satisfied, the IsGranted method returns a value determined by the Permission Policy.
Note
The Security System does not process permission requests for the association’s Navigate operation.