Validation Contexts
- 4 minutes to read
When you create a validation rule, you define the conditions under which the rule is checked — this is called the validation context.
You can use the RuleBaseAttribute.TargetContextIDs property to specify one or several validation contexts for a rule. This value is assigned to the TargetContextIDs property of the IModelRuleBase node. You can also customize the context identifier list directly in the Model Editor.
Predefined Contexts
The XAF validation module implements the following predefined validation contexts:
- Save
- The validation rule is checked each time the object or its properties is saved to a database.
Note that in-place validation is initially enabled for this context (the AllowInplaceValidation property is set totrue), so the rule is also checked after the input focus leaves the validated value until you disable the in-place validation. - Delete
- The validation rule is checked before the object is deleted.
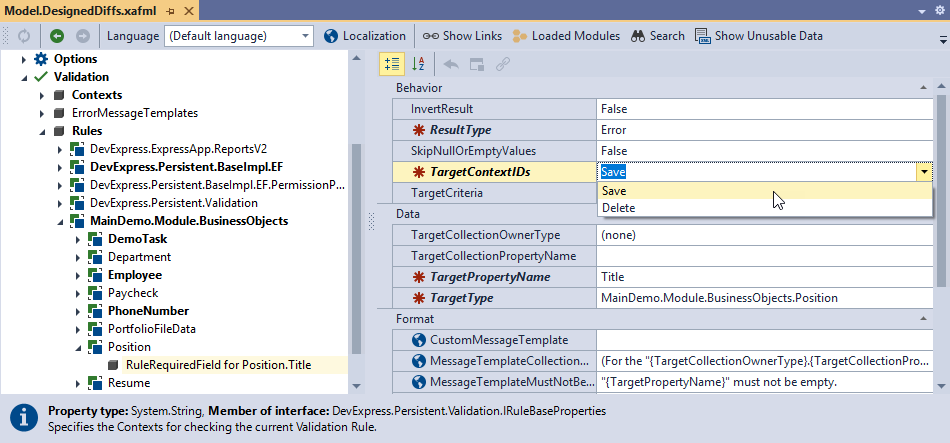
Assign DefaultContexts.Save or DefaultContexts.Delete value to the RuleBaseAttribute.TargetContextIDs property to validate the rule in the predefined context.
[RuleRequiredField("RuleRequiredField for Position.Title", DefaultContexts.Save, "A title must be specified.")]
public virtual string Title { get; set; }
In the Model Editor, select Validation | Rules | <ApplicationName>.Module.BusinessObjects | <ClassName> | <Rule Name> and specify a value for the TargetContextIDs property.
Custom Contexts
If predefined contexts do not satisfy your requirements and you need to perform validation outside of save and delete actions, you can create a custom validation context.
Assign a custom context identifier to a rule and then trigger validation in this context. Note that there are no objects that store contexts, only a context identifier. The validation module’s engine automatically collects all rules associated with this context and checks that the specified object(s) comply with the rules.
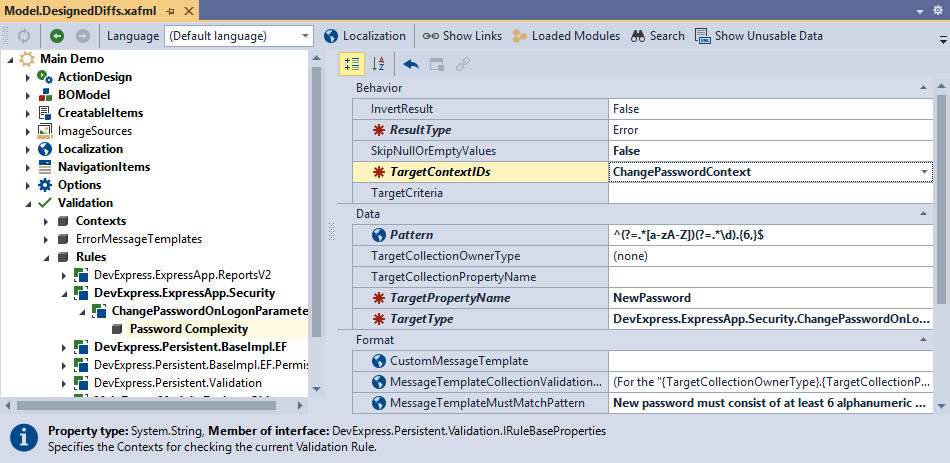
Specify the RuleBaseAttribute.TargetContextIDs property to assign a custom context to a rule.
[RuleRegularExpression("PasswordComplexity", "ChangePasswordContext", @"^(?=.*[a-zA-Z])(?=.*\d).{6,}$")]
public virtual String NewPassword { get; set; }
In the Model Editor, select Validation | Rules | <ApplicationName>.Module.BusinessObjects | <ClassName> | <Rule Name> and specify a value for the TargetContextIDs property.
Trigger Validation in a Custom Context
You can trigger rule validation in a custom context as follows:
- Trigger validation when an action is executed
Associate a context identifier with a particular Action to check all rules associated with this context when the action is executed.
In the Model Editor, select ActionDesign | Actions | <Action> and specify a value for the ValidationContexts property. You can associate any number of context identifiers separated by a semicolon.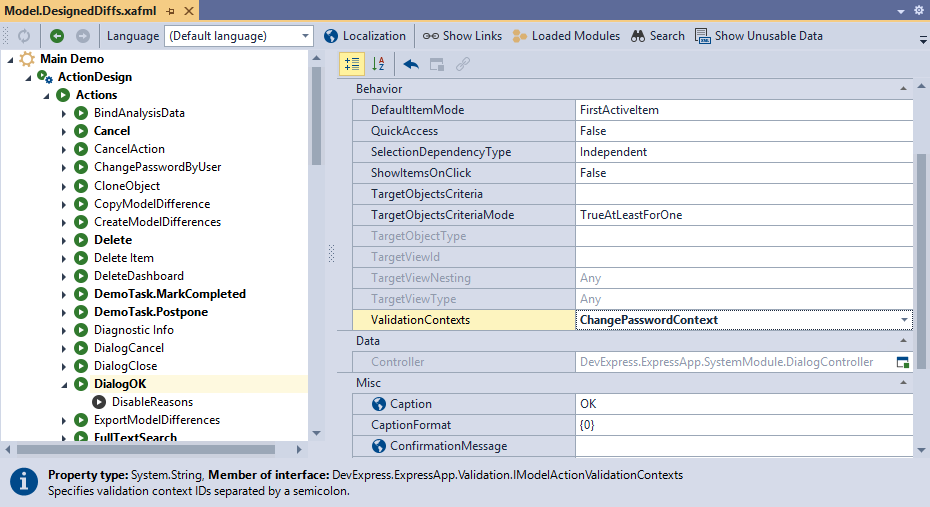
- Trigger validation programmatically
Call a
IRuleSet.Validate*method in any place in your code and specify the custom context identifier as a parameter to trigger validation of all rules associated with this context.private void MyApplicationController_Activated(object sender, EventArgs e) { IRuleSet ruleSet = Validator.GetService(Application.ServiceProvider); RuleSetValidationResult result = ruleSet.ValidateTarget( View.ObjectSpace, View.CurrentObject, "ChangePasswordContext" ); if (result.ValidationOutcome > ValidationOutcome.Information) ((Contact)View.CurrentObject).Notes += "[Validation Error] " + result.Results[0].ErrorMessage; }Refer to the following topic for more information: Trigger Validation Programmatically and Customize Default Rule Behavior.
Validate Objects in Custom Object Spaces
The validation module’s engine works automatically only for object spaces assigned to views. If you manually instantiate a BaseObjectSpace and perform object modifications through this object space, these modifications are not validated.
To validate such modifications, trigger validation manually. Refer to the following topic for more information: Trigger Validation Programmatically and Customize Default Rule Behavior.
Target Criteria
You can specify additional contextual criteria for a validation rule. Specify the TargetCriteria property to trigger validation only if the specified criteria is satisfied.
public class Contact : BaseObject {
// The SpouseName value is required only when the IsMarried property is set to true
[RuleRequiredField("SpouseNameIsRequiredWhenMarried", DefaultContexts.Save,
SkipNullOrEmptyValues = false, TargetCriteria = "[IsMarried] == True")]
public virtual String SpouseName { get; set; }
public virtual bool IsMarried { get; set; }
// ...
}