How to: Import Data to a Worksheet in Spreadsheet Document API
- 9 minutes to read
You can import data to worksheet cells from different data sources (for example, arrays, lists, and data tables). To import data into a worksheet, call the WorksheetExtensions.Import method and pass the following parameters:
- An object that specifies a data source;
- Row and column indexes of the start cell in the destination cell range;
- A Boolean value that specifies whether to insert data vertically or horizontally. Use this parameter when you import data from a one-dimensional array or list.
- A DataSourceImportOptions instance that contains import options (optional).
Spreadsheet Document API allows you to import image data from a data source. The following image data types are available:
Byte[]System.IO.StreamSystem.Drawing.Image- DXImage
- OfficeImage
Important
The WorksheetExtensions class is defined in DevExpress.Docs.v25.2.dll. Add this assembly to your project to use worksheet extensions. You need a license for the DevExpress Office File API Subscription or DevExpress Universal Subscription to use this assembly in production code.
Import Data from an Array
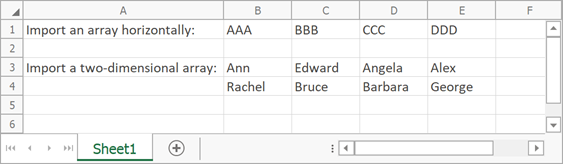
The following code snippet imports data from an array to a worksheet:
void ImportArrays(Worksheet worksheet)
{
// Create an array containing string values.
string[] array = new string[] { "AAA", "BBB", "CCC", "DDD" };
// Import the array into the worksheet and insert it horizontally, starting with cell B1.
worksheet.Import(array, 0, 1, false);
// Create a two-dimensional array containing string values.
String[,] names = new String[2, 4]{
{"Ann", "Edward", "Angela", "Alex"},
{"Rachel", "Bruce", "Barbara", "George"}
};
// Import the two-dimensional array into the worksheet and insert it, starting with cell B3.
worksheet.Import(names, 2, 1);
}
Import Data from a List
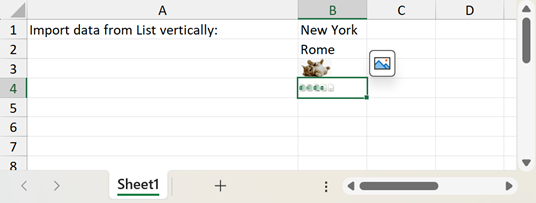
The following code snippet imports data from a list of string objects:
byte[] imageBytes1 = File.ReadAllBytes("images//img.png");
byte[] imageBytes2 = File.ReadAllBytes("images//x-docserver.png");
// ...
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.BeginUpdate();
try
{
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
worksheet.Clear(worksheet.GetUsedRange());
worksheet.Cells["A1"].ColumnWidthInCharacters = 35;
worksheet.Cells["A1"].Value = "Import data from List vertically:";
ImportList(worksheet);
}
finally
{
workbook.EndUpdate();
workbook.SaveDocument("result.xlsx");
Process.Start(new ProcessStartInfo("result.xlsx") { UseShellExecute = true });
}
workbook.Dispose();
}
// ...
void ImportList(Worksheet worksheet)
{
// Create a List object containing string values.
List<string> cities = new List<string>
{
"New York",
"Rome",
"Beijing",
"Delhi"
};
List<byte[]> imageList = new List<byte[]>();
{
imageList.Add(imageBytes1);
imageList.Add(imageBytes2);
};
// Import the list into the worksheet and insert it vertically, starting with cell B1.
worksheet.Import(cities, 0, 1, true);
// Import the image list into the worksheet and insert it vertically
worksheet.Import(imageList, 0, 2, true, new DataImportOptions());
}
Import Data from a List of Custom Objects
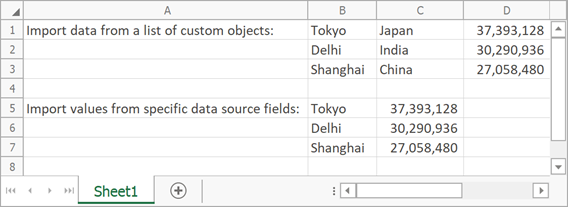
The following code imports data from a list of custom Cities class objects.
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// ...
void ImportListValues(Workbook workbook) {
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Create a list of the most populated cities.
var cities = new List<City>()
{
new City(){ Name = "Tokyo", Country= "Japan", Population = 37393128 },
new City(){ Name = "Delhi", Country= "India", Population = 30290936 },
new City(){ Name = "Shanghai", Country= "China", Population = 27058480},
};
// Insert list values into the worksheet.
// Data starts with the B1 cell.
worksheet.Import(cities, 0, 1);
// Apply the number format to the "Population" column.
worksheet["D1:D3"].NumberFormat = "_(* #,##0_);_(* (#,##0);_(* \" - \"??_);_(@_)";
// Import values from specific data source fields.
// Data starts with the B5 cell.
var importOptions = new DataSourceImportOptions()
{
PropertyNames = new string[] { "Name", "Population" }
};
worksheet.Import(cities, 4, 1, importOptions);
// Apply the number format to the "Population" column.
worksheet["C5:C7"].NumberFormat = "_(* #,##0_);_(* (#,##0);_(* \" - \"??_);_(@_)";
}
class City
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; }
public int Population { get; set; }
}
Import Data from a Data Table
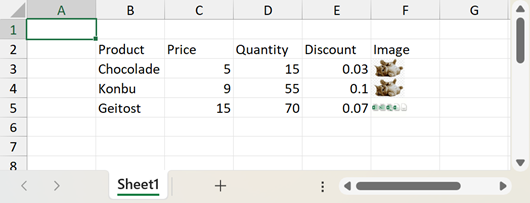
The following code imports data from a DataTable object to a worksheet:
Note that the cell data types are set automatically according to the data types of the source column. Cell formats are set automatically to the default value for the cell data type. Refer to the following topic for information on how to change this behavior: How to: Specify Number or Date Format for Cell Content
byte[] imageBytes1 = File.ReadAllBytes("images//img.png");
byte[] imageBytes2 = File.ReadAllBytes("images//x-docserver.png");
// ...
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
workbook.BeginUpdate();
try
{
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
worksheet.Clear(worksheet.GetUsedRange());
ImportDataTable(worksheet);
// ...
}
finally
{
workbook.EndUpdate();
workbook.SaveDocument("result.xlsx");
Process.Start(new ProcessStartInfo("result.xlsx") { UseShellExecute = true });
}
workbook.Dispose();
// ...
void ImportDataTable(Worksheet worksheet)
{
// Create a "Products" DataTable object with four columns.
DataTable sourceTable = new DataTable("Products");
sourceTable.Columns.Add("Product", typeof(string));
sourceTable.Columns.Add("Price", typeof(float));
sourceTable.Columns.Add("Quantity", typeof(Int32));
sourceTable.Columns.Add("Discount", typeof(float));
sourceTable.Columns.Add("Image", typeof(byte[]));
sourceTable.Rows.Add("Chocolade", 5, 15, 0.03, imageBytes1);
sourceTable.Rows.Add("Konbu", 9, 55, 0.1, imageBytes1);
sourceTable.Rows.Add("Geitost", 15, 70, 0.07, imageBytes2);
// Import data from the data table into the worksheet and insert it, starting with cell B2.
worksheet.Import(sourceTable, true, 1, 1);
}
Import Data with a Custom Converter
The following code sample uses the IDataValueConverter implementation to import data from a list. The TryConvert method override converts Boolean data to string values and base64 image data to DXImage values.
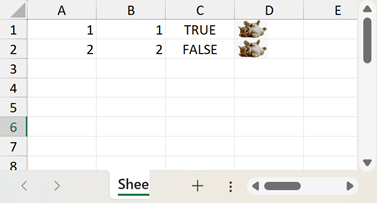
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
worksheet.Clear(worksheet.GetUsedRange());
string imageBase64 = Convert.ToBase64String(imageBytes1);
List<TestObject> list = [new TestObject(1, "1", true, imageBase64), new TestObject(2, "2", false, imageBase64)];
worksheet.Import(list, 0, 0, new DataSourceImportOptions()
{
Converter = new TestDataValueConverter(),
PropertyNames = new string[] { "IntValue", "Value", "BoolValue", "ImageBase64" }
});
workbook.SaveDocument("result.xlsx");
Process.Start(new ProcessStartInfo("result.xlsx") { UseShellExecute = true });
class TestDataValueConverter : IDataValueConverter
{
public bool TryConvert(object value, int index, out CellValue result) {
if (value is string) {
string strValue = value as string;
try
{
result = DXImage.FromBase64String(strValue);
}
catch
{
int str2int = 0;
if (Int32.TryParse(strValue, out str2int))
result = str2int;
else
result = strValue;
}
return true;
}
result = DevExpress.Spreadsheet.CellValue.TryCreateFromObject(value);
return true;
}
}
Tip
You can also use the following method to import data into a worksheet:
Bind the worksheet to a read-only data source as described in this help topic: Data Binding.
Call the WorksheetDataBindingCollection.Remove or WorksheetDataBindingCollection.Clear method to remove the binding.