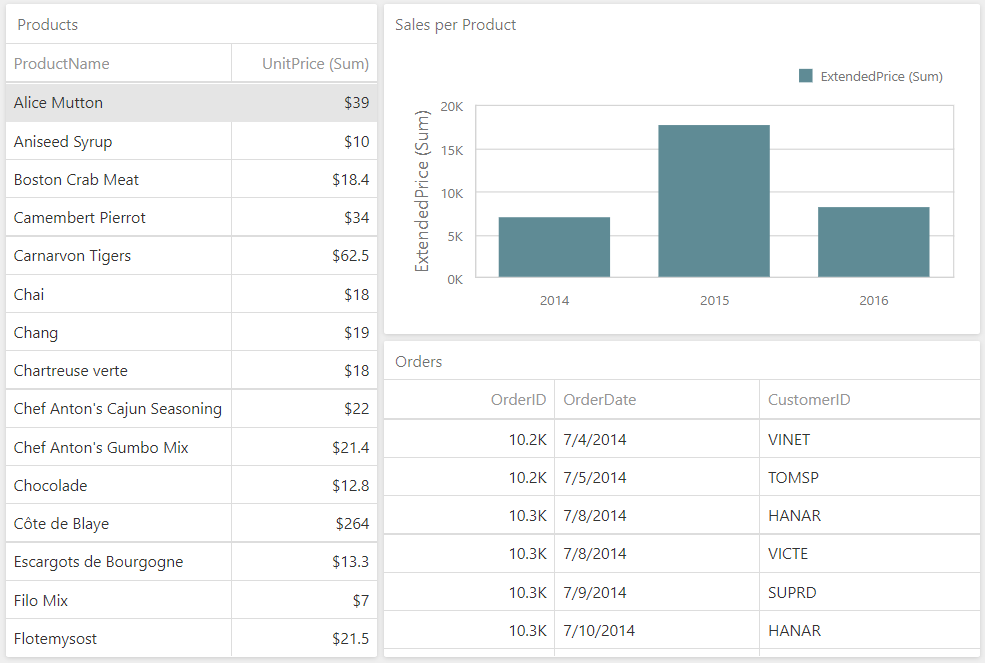
Manage an In-Memory Data Source Cache in ASP.NET MVC and ASP.NET Core
- 8 minutes to read
This article describes cache-related API members and use cases related to the data source caching mechanism in the Web Dashboard control.
The Web Dashboard control uses an in-memory data source cache to optimize the dashboard performance. An in-memory cache is a set of cache records. Each cache record consists of a cache key and a data source instance. Each data request results in the creation of a data source cache key. If there is no cache record with such a key, a new cache record is created. Creation of a cache record fires the ConfigureDataConnection or DataLoading event (depending on the data source configuration in your application). Use the DataSourceCacheKeyCreated event to access and modify the data source cache key when it is created.
Disable Caching
Set the DataSourceCacheEnabled property to false to disable data source caching. When caching is disabled, data is queried from the database each time a dashboard item requests data. ConfigureDataConnection and DataLoading events are fired every time data is requested.
The following code snippets disable the cache in the ASP.NET Core Dashboard Control and ASP.NET MVC Dashboard Extension:
DashboardConfigurator configurator = new DashboardConfigurator();
configurator.DataSourceCacheEnabled = false;
Share Cache
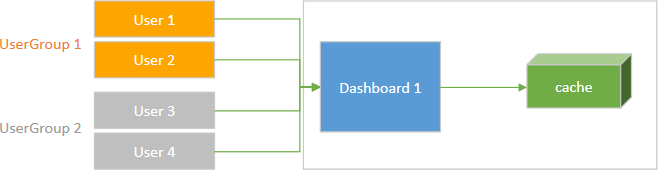
The in-memory cache is created when data is loaded for the first time. The Web Dashboard can create multiple cache records to accelerate data loading for different dashboards/data sources. The cache is shared across all users of all Web Dashboard instances.
Separate Cache for User Groups
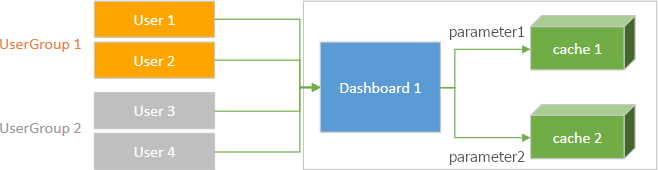
The Web Dashboard can create multiple cache records to accelerate data loading for different dashboards/data sources. Each cache record has its own unique key that implements the IDataSourceCacheKey interface. Use the CustomData field to add information about user groups to the cache key to use separate cached datasets for different users. Note that the information stored in the cache key cannot be accessed from the client side.
Caches are shared among all users:
You can manage access to different caches for different users. For this, add information about user groups to the CustomData field.
- ASP.NET Core
The following example uses the CustomData field to add information about a user to the cache key:
// Configure user-specific data caching private void DashboardConfigurator_DataSourceCacheKeyCreated(object sender, DataSourceCacheKeyCreatedEventArgs e) { var userId = contextAccessor.HttpContext.Session.GetString("CurrentUser").GetHashCode(); e.Key.CustomData.Add("UserId", userId.ToString()); }- ASP.NET MVC
The following example uses the CustomData field to add information about a user to the cache key:
// Configure user-specific data caching private static void DashboardConfigurator_DataSourceCacheKeyCreated(object sender, DataSourceCacheKeyCreatedEventArgs e) { var userId = HttpContext.Current.Session["CurrentUser"].GetHashCode(); e.Key.CustomData.Add("UserId", userId.ToString()); }
Specify the Cache Timeout on the Server
When the Web Dashboard loads data for the first time, it checks whether any cache record exists. If a cache record is older than 300 seconds, the Web Dashboard recreates it. The Web Dashboard manages this cache in the following independent ways:
- Default time interval
- The Web Dashboard clears the cache record if the time interval between two data requests exceeds 300 seconds. If the time interval between two data requests is less than 300 seconds, the Web Dashboard leaves the existing cache record unchanged and starts the timer again.
- Specified time interval
- The Web Dashboard allows you to set a time interval between two data requests, after which the cache record will be cleared. Handle the DashboardConfigurator.ConfigureDataReloadingTimeout event to change this time interval. For instance, if you set the e.DataReloadingTimeout event parameter to 100 seconds, the Web Dashboard recreates a cache record when a new request is received and the current cache record is older than 100 seconds.
Refresh the Control on the Client
When you call the client-side DashboardControl.refresh method, the control requests the latest data from the server and reloads the dashboard items. If a cache exists, the control fetches data from the cache.
Get access to the underlying DashboardControl instance and call the refresh method as follows:
function onClick() {
clientDashboardControl.refresh();
}
To refresh specific dashboard items, pass their names as a parameter. The code below refreshes Chart and Grid items:
function onClick() {
clientDashboardControl.refresh(["chartDashboardItem1", "gridDashboardItem1"]);
}
See the following topics for details on how to customize the Web Dashboard control on the client:
- Client-Side API Overview for ASP.NET Core Dashboard
- Client-Side API Overview for ASP.NET MVC Dashboard
Force the Cache Reset
Client Side
To update the data source cache on the client, call the client-side DashboardControl.reloadData method. The method call sends a callback to the server. This forces the cache reset and recreates a new one. Note that multiple users can simultaneously open the dashboard and share the same server-side cache. If one of the users calls the reloadData method, it forces the server cache to be reset and all users get new data on the next request to the server.
function reloadOnClient() {
dashboardControl1.reloadData();
}
See the following topics for details on how to customize the Web Dashboard control on the client:
- Client-Side API Overview for ASP.NET Core Dashboard
- Client-Side API Overview for ASP.NET MVC Dashboard
Server Side
Use the InvalidateCacheRecord() method to reset a cache record referenced by the current cache key. This way you can ensure that data is always requested from the server and users have access to the latest changes.
The following code snippets invalidate the cache record for the sqlDataSource1 data source:
- ASP.NET Core
configurator.DataSourceCacheKeyCreated += (sender, args) => { if (args.Key.DataSourceId == "sqlDataSource1") args.InvalidateCacheRecord(); };- ASP.NET MVC
private static void DashboardConfigurator_DataSourceCacheKeyCreated(object sender, DataSourceCacheKeyCreatedEventArgs e) { if (args.Key.DataSourceId == "sqlDataSource1") args.InvalidateCacheRecord(); };
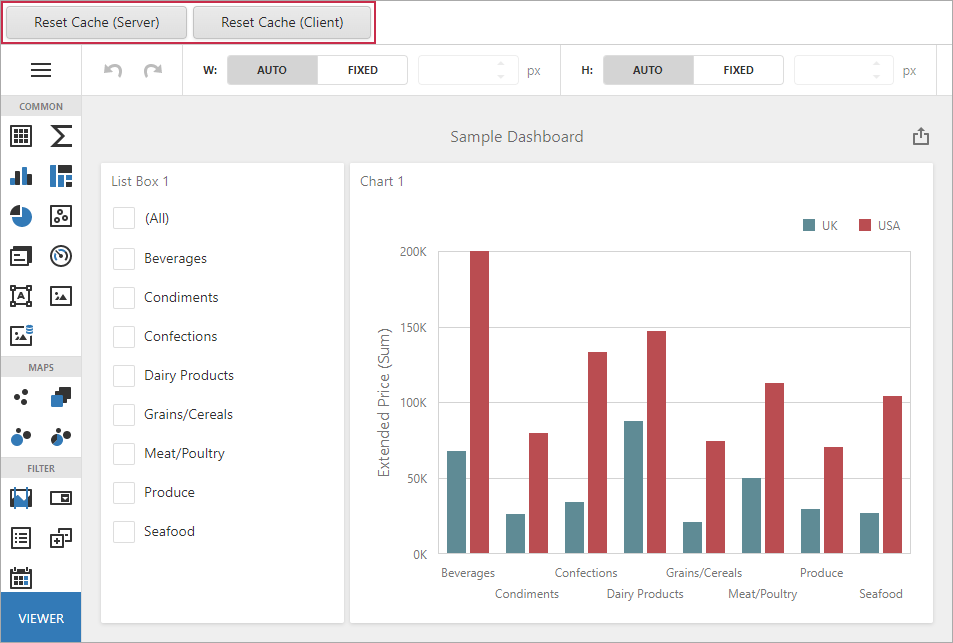
Example: How to Reset the Cache
The following example shows how you can manage the cache in the Web Dashboard control.
- Click Refresh Cache (Server) to force the cache reset on the server.
- Click Refresh Cache (Client) to force the cache reset using a client API.
Server Side
On the server-side, the Web Dashboard uses the same cache record within a session. To implement the scenario, a value identifying the session is written to the CustomData field.
ASP.NET Core
Create the cache manager that stores a unique GUID value within a Session or static variable as a parameter:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System;
namespace AspNetCoreDashboardUseDifferentCaches
{
public class CacheManager {
const string SessionKey = "UniqueCacheParam";
protected IHttpContextAccessor HttpContextAccessor { get; }
public CacheManager(IHttpContextAccessor httpContextAccessor) {
this.HttpContextAccessor = httpContextAccessor;
}
public void ResetCache() {
HttpContextAccessor?.HttpContext?.Session?.SetString(SessionKey,Guid.NewGuid().ToString());
}
public Guid UniqueCacheParam {
get {
ISession session = HttpContextAccessor?.HttpContext?.Session;
if(session == null) {
return Guid.Empty;
} else {
if(string.IsNullOrEmpty(session.GetString(SessionKey)))
ResetCache();
return Guid.Parse(session.GetString(SessionKey));
}
}
}
}
}
Add the CacheManager singleton to the application:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {
// ...
services.AddDistributedMemoryCache().AddSession();
services.TryAddSingleton<IHttpContextAccessor, HttpContextAccessor>();
services.AddSingleton<CacheManager>(serviceProvider => new CacheManager(serviceProvider.GetService<IHttpContextAccessor>()));
}
Create a controller for the Refresh action:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace AspNetCoreDashboardUseDifferentCaches {
public class HomeController: Controller {
// ...
public IActionResult Refresh([FromServices]CacheManager cacheManager) {
cacheManager.ResetCache();
return Ok();
}
}
}
Pass the parameter to the CustomData field:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {
// ...
services.AddScoped<DashboardConfigurator>((IServiceProvider serviceProvider) => {
DashboardConfigurator configurator = new DashboardConfigurator();
// ...
// Specifies a unique cache parameter.
configurator.DataSourceCacheKeyCreated += (sender, e) => {
e.Key.CustomData.Add("SessionId", serviceProvider.GetService<CacheManager>().UniqueCacheParam.ToString());
};
return configurator;
});
// ...
}
Reset the cache in your code: use the created Refresh action and call the DashboardControl.refresh method on success:
function reloadOnServer() {
$.ajax({
url: '@Url.Action("Refresh")',
success: function (data) {
dashboardControl1.refresh();
// To refresh specific dashboard items, pass their names as parameters:
// WebDashboard1.GetDashboardControl().refresh( ["chartDashboardItem1", "listBoxDashboardItem1"] );
}
})
}
ASP.NET MVC
Create the cache manager that stores a unique GUID value within a Session or static variable as a parameter:
using System;
using System.Web;
namespace MvcDashboardUseDifferentCaches
{
public class CacheManager {
public static void ResetCache() {
if(HttpContext.Current.Session != null)
HttpContext.Current.Session["UniqueCacheParam"] = Guid.NewGuid();
}
public static Guid UniqueCacheParam {
get {
if(HttpContext.Current.Session == null)
return Guid.Empty;
else {
if(HttpContext.Current.Session["UniqueCacheParam"] == null)
ResetCache();
return (Guid)HttpContext.Current.Session["UniqueCacheParam"];
}
}
}
}
}
Create a controller for the Refresh action:
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace MvcDashboardUseDifferentCaches.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller {
public ActionResult Index() {
return View();
}
public ActionResult Refresh() {
CacheManager.ResetCache();
return new EmptyResult();
}
}
}
Pass the parameter to the CustomData field:
private static void Default_DataSourceCacheKeyCreated(object sender, DataSourceCacheKeyCreatedEventArgs e) {
e.Key.CustomData.Add("SessionId", CacheManager.UniqueCacheParam.ToString());
}
Reset the cache in your code: use the created Refresh action and call the DashboardControl.refresh method on success:
function reloadOnServer() {
$.ajax({
url: '@Url.Action("Refresh")',
success: function (data) {
WebDashboard1.GetDashboardControl().refresh();
// To refresh specific dashboard items, pass their names as parameters:
// WebDashboard1.GetDashboardControl().refresh( ["chartDashboardItem1", "listBoxDashboardItem1"] );
}
})
}
Example: How to Use Parameters to Update a Specific Dashboard Item Without Refreshing the Entire Dashboard
This example shows how to use dashboard parameters to update a specific dashboard item without refreshing the entire dashboard. This technique is applicable when you need to filter data source data to update a specific dashboard item, but do not want to refresh data in all items in a dashboard because this operation causes performance delays.