Routing
- 9 minutes to read
The Map control supports the Microsoft’s Azure Route service. It provides the most optimal route, either from major roads in four directions, or calculated between two or more locations on a map.

Azure Maps Route
The AzureRouteDataProvider implements the Azure Maps Route service. Assign such an object to the InformationLayer.DataProvider property to enable the service and allow users to calculate a route on a map.
Note
To display an image on a map control, add image layers. Then you can implement routing functionality on the information layer.
Calculate a Route Between Locations
Call one of the AzureRouteDataProvider.CalculateRoute method overloads to calculate a route between the specified origin and destination, passing through the selected waypoints.
The AzureRouteOptions parameter of the AzureRouteDataProvider.CalculateRoute method overload allows you to specify route options.
The following settings are available:
- AzureRouteOptions.TravelMode
- Specifies the transportation / commute mode.
- AzureRouteOptions.MaxAlternatives
- Specifies the number of alternative routes to be calculated.
- AzureRouteOptions.AvoidTypes
- Specifies items that
AzureRouteDataProvidershould try to avoid when calculating the route. - AzureRouteOptions.CustomParameters
- Specifies additional route definitions.
The following example calculates a car-optimized route through the specified waypoints:
using DevExpress.XtraMap;
// ...
const string key = "your key";
// ...
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) {
MapControl map = new MapControl();
// Specify the map position on the form.
map.Dock = DockStyle.Fill;
// Create a layer.
ImageLayer image = new ImageLayer();
image.DataProvider = new AzureMapDataProvider(){
AzureKey = key,
};
AzureRouteDataProvider routeProvider = new AzureRouteDataProvider();
routeProvider.AzureKey = key;
// Create three waypoints and add them to the route waypoints list.
List<RouteWaypoint> waypoints = new List<RouteWaypoint>();
waypoints.Add(new RouteWaypoint("NY", new GeoPoint(41.145556, -73.995)));
waypoints.Add(new RouteWaypoint("Oklahoma", new GeoPoint(36.131389, -95.937222)));
waypoints.Add(new RouteWaypoint("Las Vegas", new GeoPoint(36.175, -115.136389)));
// Call the AzureRouteDataProvider.CalculateRoute method.
azureRoute.CalculateRoute(waypoints, new AzureRouteOptions() {
TravelMode = AzureTravelMode.Car,
AvoidTypes = AzureRouteAvoidType.AlreadyUsedRoads
});
InformationLayer route = new InformationLayer();
route.DataProvider = routeProvider;
map.Layers.AddRange(new LayerBase[] { image, route});
this.Controls.Add(map);
}
Calculate Routes between GeoPoints Specified on a Map Surface
The following example calculates a route based on two or more RouteWaypoint objects.
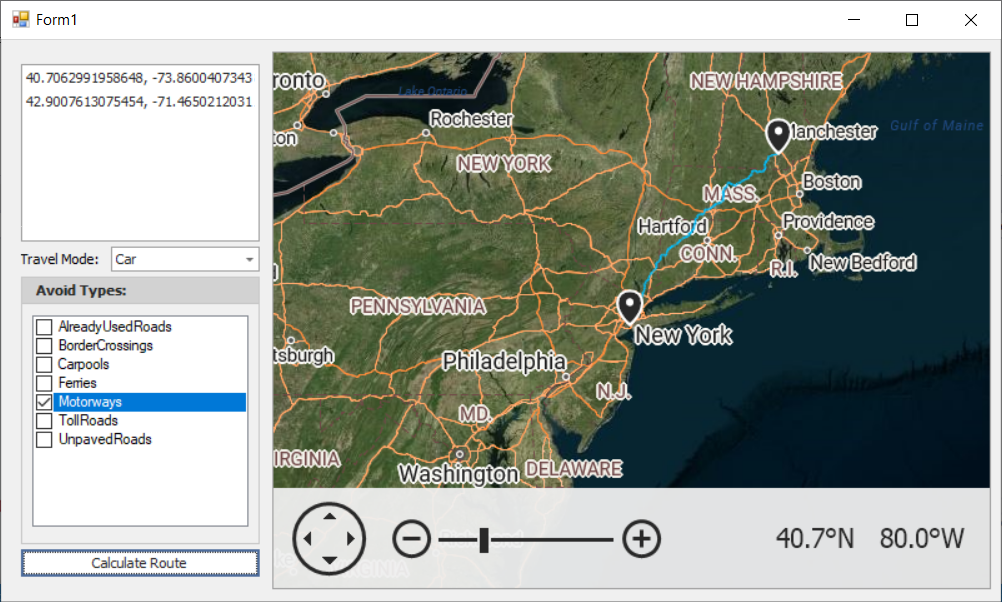
Right-click on a map surface to specify waypoints: origin, destination, and points between. ListBox entries display geographical points (GeoPoint.Longitude and GeoPoint.Latitude). The “Calculate Route” button initiates the routing request by obtaining the waypoint information and passing it to the CalculateRoute method. The ComboBoxEdit and CheckedListBox editors specify route options (AzureRouteOptions.AvoidTypes and AzureRouteOptions.TravelMode properties).
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using DevExpress.XtraMap;
namespace AzureRouting {
public partial class Form1 : Form {
const string azureKey = "your key";
ObservableCollection<GeoPoint> geoPoints = new ObservableCollection<GeoPoint>();
MapItemStorage itemData;
InformationLayer routeInfoLayer;
AzureRouteDataProvider azureRoute;
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
mapControl.Layers.AddRange(
new LayerBase[] {
new ImageLayer() {
DataProvider = new AzureMapDataProvider() {
AzureKey = azureKey,
Tileset = AzureTileset.Imagery,
},
},
new ImageLayer() {
DataProvider = new AzureMapDataProvider() {
AzureKey = azureKey,
Tileset = AzureTileset.BaseHybridRoad,
},
},
routeInfoLayer = new InformationLayer() {
DataProvider = azureRoute = new AzureRouteDataProvider() {
AzureKey = azureKey,
},
},
new VectorItemsLayer() {
Data = itemData = new MapItemStorage(),
}
}
);
routeInfoLayer.ItemStyle.StrokeWidth = 2;
routeInfoLayer.ItemStyle.Stroke = Color.DeepSkyBlue;
routeInfoLayer.Error += RouteInfoLayer_Error;
waypointsListBoxControl.DataSource = geoPoints;
mapControl.Zoom(6);
mapControl.SetCenterPoint(new GeoPoint(40.714627, -74.002863), false);
mapControl.EnableRotation = false;
}
private void RouteInfoLayer_Error(object sender, MapErrorEventArgs e) {
throw new System.NotImplementedException();
}
private void mapControl_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) {
MouseEventArgs mouseEventArgs = (MouseEventArgs)e;
if(mouseEventArgs.Button == MouseButtons.Right) {
GeoPoint mousePoint = mapControl.ScreenPointToCoordPoint(mouseEventArgs.Location) as GeoPoint;
geoPoints.Add(mousePoint);
itemData.Items.Add(new MapPushpin() {
Location = mousePoint,
});
}
}
private void calculateRouteButton_Click(object sender, System.EventArgs e) {
if (geoPoints.Count <= 1) {
MessageBox.Show("Specify at least two Waypoints to calculate a route.");
return;
}
azureRoute.CalculateRoute(geoPoints.Select(point => new RouteWaypoint("", point)).ToList(), new AzureRouteOptions() {
TravelMode = GetTravelMode(),
AvoidTypes = GetAvoidTypes()
});
geoPoints.Clear();
itemData.Items.Clear();
}
AzureTravelMode GetTravelMode() {
return (AzureTravelMode)Enum.Parse(typeof(AzureTravelMode), (string)travelModeComboBox.SelectedItem);
}
AzureRouteAvoidType GetAvoidTypes() {
var avoidTypes = AzureRouteAvoidType.None;
foreach (string item in avoidTypesCheckedListBox.CheckedItems) {
var avoidType = (AzureRouteAvoidType)Enum.Parse(typeof(AzureRouteAvoidType), item);
avoidTypes |= avoidType;
}
return avoidTypes;
}
}
}
Obtain Routing Result
The following example displays detailed information about the calculated route:
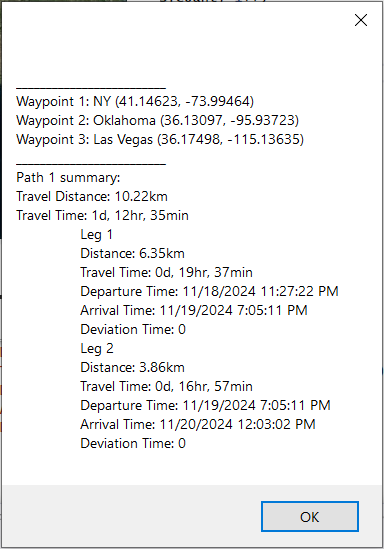
The button click initiates the routing request. The CalculateRoute method is called in the button click event handler.
The RouteCalculated event is handled to process the request result. e.CalculationResult gets the AzureRouteCalculationResult object that contains the result of the route calculation and allows you to obtain the following information:
- An AzureRouteCalculationResult.IntermediatePoints collection. You can obtain the Description and Location of each
RouteWaypointin the list. - An AzureRouteCalculationResult.RouteResults collection. You can obtain summary information about the route, its legs and sections. For example, TravelLengthMeters, TravelTimeSeconds Arrival and Departure time.
using DevExpress.XtraMap;
using System.Text;
// ...
const string key = "your key";
// ...
routeProvider = new AzureRouteDataProvider { AzureKey = key };
routeProvider.RouteCalculated += OnRouteCalculated;
// ...
private void OnCalculateRoutesClick(object sender, EventArgs e) {
List<RouteWaypoint> waypoints = new List<RouteWaypoint>();
waypoints.Add(new RouteWaypoint("NY", new GeoPoint(41.145556, -73.995)));
waypoints.Add(new RouteWaypoint("Oklahoma", new GeoPoint(36.131389, -95.937222)));
waypoints.Add(new RouteWaypoint("Las Vegas", new GeoPoint(36.175, -115.136389)));
routeProvider.CalculateRoute(waypoints, new AzureRouteOptions() {
TravelMode = AzureTravelMode.Car
});
}
private void OnRouteCalculated(object sender, AzureRouteCalculatedEventArgs e) {
AzureRouteCalculationResult result = e.CalculationResult;
if ((result.RouteResults == null) ||
(result.ResultCode == RequestResultCode.BadRequest)) {
MessageBox.Show("The Azure Route service does not work for this location.");
return;
}
StringBuilder resultList = new StringBuilder("");
if (result.IntermediatePoints != null) {
resultList.Append(String.Format("_________________________\n"));
for (int i = 0; i < e.CalculationResult.IntermediatePoints.Count; i++)
resultList.Append(
String.Format("Waypoint {0}: {1} ({2})\n",
i + 1,
e.CalculationResult.IntermediatePoints[i].Description,
e.CalculationResult.IntermediatePoints[i].Location)
);
}
if (result.RouteResults != null) {
for (int rnum = 0; rnum < e.CalculationResult.RouteResults.Count; rnum++) {
var routeSummary = e.CalculationResult.RouteResults[rnum].Summary;
resultList.AppendLine("_________________________");
resultList.AppendLine($"Path {rnum + 1} summary:");
resultList.AppendLine($"Travel Distance: {GetDistanceString(routeSummary)}");
resultList.AppendLine($"Travel Time: {GetTravelTimeString(routeSummary)}");
if (e.CalculationResult.RouteResults[rnum].Legs != null){
int legNum = 1;
foreach (AzureRouteLeg leg in e.CalculationResult.RouteResults[rnum].Legs){
resultList.AppendLine($"\tLeg {legNum++}");
resultList.AppendLine($"\tDistance: {GetDistanceString(leg.Summary)}");
resultList.AppendLine($"\tTravel Time: {GetTravelTimeString(leg.Summary)}");
resultList.AppendLine($"\tDeparture Time: {leg.Summary.Departure}");
resultList.AppendLine($"\tArrival Time: {leg.Summary.Arrival}");
resultList.AppendLine($"\tDeviation Time: {leg.Summary.DeviationTime}");
}
}
}
}
MessageBox.Show(resultList.ToString());
}
static string GetTravelTimeString(AzureRouteSummary summary) {
var timeSpan = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(summary.TravelTimeSeconds);
return $"{timeSpan.Days}d, {timeSpan.Hours}hr, {timeSpan.Minutes}min";
}
static string GetDistanceString(AzureRouteSummary summary) {
return String.Format("{0:0.00}km", (double)summary.TravelLengthMeters / 1000);
}
Examples
The following examples demonstrate how to use the routing feature in the map control:
- How to: Calculate a Route by Addresses
- How to: Implement a Custom Route Provider
- How to: Use the Azure Maps Route Service to Calculate Routes between GeoPoints on a Map Surface