Customize Standard Authentication Behavior and Supply Additional Logon Parameters (.NET Applications)
- 10 minutes to read
When an XAF application uses the AuthenticationStandard authentication, the default login form displays User Name and Password editors. This topic explains how to customize this form and show Company and Application User lookup editors instead of User Name.

Define a Data Model for Custom Parameters
Add a
Companyclass to your project. This class should contain company names and a list ofApplicationUserobjects as a part of a one-to-many relationship.using DevExpress.Persistent.Base; using DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF; using EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.BusinessObjects; using System.Collections.ObjectModel; namespace EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.BusinessObjects; [DefaultClassOptions] public class Company : BaseObject { public virtual string Name { get; set; } public virtual IList<ApplicationUser> ApplicationUsers { get; set; } = new ObservableCollection<ApplicationUser>(); }Add the second part of this relationship to the
ApplicationUserclass generated by the Template Kit.public class ApplicationUser : PermissionPolicyUser, ISecurityUserWithLoginInfo, ISecurityUserLockout { // ... public virtual Company Company { get; set; } // ... }Add the
Companyclass to your application’sDbContext.public class EFCoreCustomLogonAllEFCoreDbContext : DbContext { // ... public DbSet<Company> Companies { get; set; } // ... }
Add Custom Parameters to the Login Window
The default login form uses an AuthenticationStandardLogonParameters Detail View that includes UserName and Password fields. To add custom fields, create a CustomLogonParameters class in your application’s module project (MySolution.Module).
using DevExpress.ExpressApp;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.ConditionalAppearance;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.DC;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security;
using DevExpress.Persistent.Base;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Runtime.Serialization;
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
namespace EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.Authentication;
[DataContract]
[DomainComponent]
[DisplayName("Log In")]
[Appearance("CompanyIsNull", TargetItems = $"{nameof(Password)}, {nameof(ApplicationUser)}", Criteria = "IsNull([Company])", Enabled = false)]
public class CustomLogonParameters : IAuthenticationStandardLogonParameters, ISupportClearPassword, INotifyPropertyChanged, IObjectSpaceLink {
private CompanyDTO? company;
private ApplicationUserDTO? applicationUser;
private string? password;
private IReadOnlyList<CompanyDTO>? _companies = null;
private IObjectSpace? objectSpace;
private ILogonDataProvider? logonDataProvider;
[Browsable(false)]
public string? UserName { get; set; }
[JsonIgnore]
[ImmediatePostData]
[DataSourceProperty("Companies", DataSourcePropertyIsNullMode.SelectAll)]
[IgnoreDataMember]
public CompanyDTO? Company {
get { return company; }
set {
if(value == company) return;
company = value;
if(company == null || ApplicationUser?.CompanyID != company.ID) {
ApplicationUser = null;
}
OnPropertyChanged(nameof(CompanyDTO));
}
}
[Browsable(false)] // hide from UI
[JsonIgnore]
[IgnoreDataMember]
public IReadOnlyList<CompanyDTO>? Companies {
get {
if(_companies == null) {
if(logonDataProvider != null) {
_companies = logonDataProvider.GetCompanies().AsReadOnly();
} else {
_companies = Array.Empty<CompanyDTO>();
}
}
return _companies;
}
}
[JsonIgnore]
[DataSourceProperty($"{nameof(Company)}.{nameof(Company.ApplicationUsers)}"), ImmediatePostData]
[System.Runtime.Serialization.IgnoreDataMember]
public ApplicationUserDTO? ApplicationUser {
get { return applicationUser; }
set {
if(value == applicationUser)
return;
applicationUser = value;
UserName = applicationUser?.UserName;
OnPropertyChanged(nameof(ApplicationUser));
}
}
[PasswordPropertyText(true)]
[DataMember]
public string? Password {
get { return password; }
set {
if(password == value)
return;
password = value;
OnPropertyChanged(nameof(Password));
}
}
IObjectSpace? IObjectSpaceLink.ObjectSpace {
get => objectSpace;
set {
objectSpace = value;
if(objectSpace != null) {
logonDataProvider = objectSpace.ServiceProvider.GetService<ILogonDataProvider>();
}
ApplicationUser = null;
Company = null;
_companies = null;
}
}
private void OnPropertyChanged(string propertyName) {
if(PropertyChanged != null) {
PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
void ISupportClearPassword.ClearPassword() {
password = null;
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler? PropertyChanged;
}
Note the following implementation details:
- The
CustomLogonParametersclass must implement theISupportClearPasswordandIAuthenticationStandardLogonParametersinterfaces. - (Blazor specific) Properties with data types that cannot be serialized to JSON must be marked with JsonIgnoreAttribute.
- (Blazor specific) To keep the cookie compact, assign
nullto unnecessary properties after login in theISupportClearPassword.ClearPasswordmethod. - (WinForms specific) Properties should be marked with the correct attributes based on whether they need to be serialized and transferred between the client and server after login:
- DataMemberAttribute - a property is serializable and must be passed between the client and server.
- IgnoreDataMemberAttribute - a property is not serializable or should not be passed between the client and server.
- (WinForms specific) If nullable reference types are enabled for the project, all properties in the
CustomLogonParametersclass should be marked as nullable.
Implement Data Transfer Objects (DTO)
To access lists of companies and application users in login form (before authentication), implement
CompanyDTOandApplicationUserDTOdata transfer objects.using DevExpress.ExpressApp.DC; using DevExpress.Persistent.Base; namespace EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.Authentication; [DomainComponent] public class CompanyDTO { IList<ApplicationUserDTO>? users; public virtual string? Name { get; set; } [DevExpress.ExpressApp.Data.Key] [VisibleInListView(false), VisibleInDetailView(false), VisibleInLookupListView(false)] public virtual Guid ID { get; set; } public IList<ApplicationUserDTO>? ApplicationUsers { get { if(users == null && LogonDataProvider != null) { users = LogonDataProvider.GetCompanyUsers(ID); } return users; } } public ILogonDataProvider? LogonDataProvider { get; set; } }Implement the
AuthenticationDataControllerwithGetCompaniesandGetApplicationUsersmethods to supply data for the logon form. This data is consumed by theCustomLogonParametersclass, which operates in Middle Tier and standard Blazor applications.using DevExpress.ExpressApp; using EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.Authentication; using EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.BusinessObjects; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; namespace EFCoreCustomLogonAll.MiddleTier.Authentication { public class AuthenticationDataController : ControllerBase, IDisposable { IObjectSpace nonSecuredObjectSpace; private readonly INonSecuredObjectSpaceFactory? nonSecuredObjectSpaceFactory; public AuthenticationDataController(INonSecuredObjectSpaceFactory nonSecuredObjectSpaceFactory) { this.nonSecuredObjectSpaceFactory = nonSecuredObjectSpaceFactory; } [HttpGet("/GetCompanies")] public ActionResult GetCompanies() { List<CompanyDTO> companies = new List<CompanyDTO>(); foreach(var company in GetNonSecuredObjectSpace().GetObjects<Company>()) { companies.Add(new CompanyDTO() { ID = company.ID, Name = company.Name }); } return Ok(companies); } [HttpGet("/GetApplicationUsers({companyKey})")] public ActionResult GetApplicationUsers(string companyKey) { var users = new List<ApplicationUserDTO>(); Guid guid = new Guid(companyKey); foreach(var user in GetNonSecuredObjectSpace().GetObjectsQuery<ApplicationUser>().Where(user => user.Company != null && user.Company.ID == guid)) { users.Add(new ApplicationUserDTO() { ID = user.ID, UserName = user.UserName }); } return Ok(users); } private IObjectSpace GetNonSecuredObjectSpace() { if(nonSecuredObjectSpace == null) { nonSecuredObjectSpace = nonSecuredObjectSpaceFactory.CreateNonSecuredObjectSpace<Company>(); } return nonSecuredObjectSpace; } public void Dispose() { if(nonSecuredObjectSpace != null) { nonSecuredObjectSpace.Dispose(); nonSecuredObjectSpace = null; } } } }Create the
ILogonDataProviderservice that contains abstract data retrieval logic.namespace EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.Authentication; public interface ILogonDataProvider { IList<CompanyDTO> GetCompanies(); IList<ApplicationUserDTO> GetCompanyUsers(Guid companyID); }Implement this interface in platform-specific classes:
MiddleTierClientLogonDataProviderorBlazorLogonDataProvider.using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.ClientServer; using System.Collections.ObjectModel; using System.Net.Http.Json; using System.Text.Json; namespace EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.Authentication; public class MiddleTierClientLogonDataProvider : ILogonDataProvider { readonly WebApiSecuredDataServerClientBase dataServerClient; public MiddleTierClientLogonDataProvider(WebApiSecuredDataServerClientBase dataServerClient) { this.dataServerClient = dataServerClient; var t = dataServerClient.HttpClient; } public IList<CompanyDTO> GetCompanies() { var companies = GetAllAsync<CompanyDTO>(dataServerClient.HttpClient, "GetCompanies").GetAwaiter().GetResult(); foreach(var company in companies) { company.LogonDataProvider = this; } return new ReadOnlyCollection<CompanyDTO>(companies); } public IList<ApplicationUserDTO> GetCompanyUsers(Guid companyID) { var result = GetAllAsync<ApplicationUserDTO>(dataServerClient.HttpClient, $"GetApplicationUsers({companyID})").GetAwaiter().GetResult(); return new ReadOnlyCollection<ApplicationUserDTO>(result); } async Task<T[]> GetAllAsync<T>(HttpClient httpClient, string requestUri) { var json = await RequestAsync(httpClient, new HttpRequestMessage(HttpMethod.Get, requestUri)); return json.GetProperty("$values").Deserialize<T[]>() ?? throw new NullReferenceException(); } async Task<JsonElement> RequestAsync(HttpClient httpClient, HttpRequestMessage request, bool preventAuthorization = false) { request.Headers.Add("Accept", "application/json"); using var httpResponse = Send(httpClient, request, preventAuthorization); if(httpResponse.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound) { throw new HttpRequestException($"{request.Method} request has no JSON! Code {(int)httpResponse.StatusCode}, '{httpResponse.ReasonPhrase}'"); } if(httpResponse.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NoContent) { return new JsonElement(); } else { return await httpResponse.Content.ReadFromJsonAsync<JsonElement>(); } } HttpResponseMessage Send(HttpClient httpClient, HttpRequestMessage request, bool preventAuthorization = false) { var httpResponse = httpClient.SendAsync(request).GetAwaiter().GetResult(); if(!httpResponse.IsSuccessStatusCode) { using(var stream = httpResponse.Content.ReadAsStream()) { using(StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(stream)) { throw new HttpRequestException(httpResponse.ReasonPhrase + Environment.NewLine + reader.ReadToEnd(), null, httpResponse.StatusCode); } } } return httpResponse; } }Register platform-specific providers as services:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { // ... services.AddScoped<ILogonDataProvider, BlazorLogonDataProvider>();public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { // ... services.AddScoped<ILogonDataProvider, MiddleTierClientLogonDataProvider>();public static WinApplication BuildApplication() { // ... var builder = WinApplication.CreateBuilder(); // ... builder.Services.AddScoped<ILogonDataProvider, MiddleTierClientLogonDataProvider>();
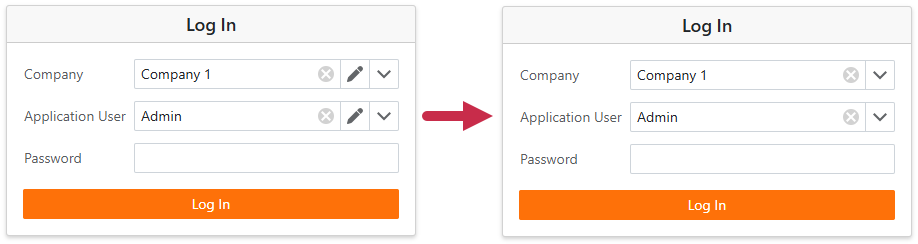
Customize Blazor Lookup Editors
A Blazor lookup editor displays the Edit button. Create a controller and call the CustomizeViewItemControl method to hide the button from the Company and Application User lookup editors.
using DevExpress.ExpressApp;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Blazor.Editors;
using EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.Authentication;
namespace EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Blazor.Server.Authentication {
// https://supportcenter.devexpress.com/ticket/details/t1164456/blazor-lookup-list-view-s-allowedit-property-does-not-affect-visibility-of
public class CustomLogonParameterLookupActionVisibilityController : ObjectViewController<DetailView, CustomLogonParameters> {
protected override void OnActivated() {
base.OnActivated();
View.CustomizeViewItemControl<LookupPropertyEditor>(this, e => {
e.HideEditButton();
});
}
}
}
Pass Custom Classes to the Security System
In the application’s Startup.cs files, set the provider’s LogonParametersType option to CustomLogonParameters in the AddPasswordAuthentication method call.
Files: MySolution.Blazor.Server\Startup.cs, MySolution.MiddleTier\Startup.cs
builder.Security
// ...
.UseIntegratedMode(options => {
// ...
})
.AddPasswordAuthentication(options => {
options.IsSupportChangePassword = true;
options.LogonParametersType = typeof(CustomLogonParameters);
});
Add Demo Data
Override the ModuleUpdater.UpdateDatabaseAfterUpdateSchema method to create companies, application users, and security roles.
using DevExpress.ExpressApp;
using DevExpress.Data.Filtering;
using DevExpress.Persistent.Base;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Updating;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.SystemModule;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.EF;
using DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF;
using DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.PermissionPolicy;
using EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.BusinessObjects;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.DatabaseUpdate;
// For more typical usage scenarios, be sure to check out https://docs.devexpress.com/eXpressAppFramework/DevExpress.ExpressApp.Updating.ModuleUpdater
public class Updater : ModuleUpdater {
public Updater(IObjectSpace objectSpace, Version currentDBVersion) :
base(objectSpace, currentDBVersion) {
}
public override void UpdateDatabaseAfterUpdateSchema() {
base.UpdateDatabaseAfterUpdateSchema();
// ...
var defaultRole = CreateDefaultRole();
var adminRole = CreateAdminRole();
ObjectSpace.CommitChanges(); //This line persists created object(s).
UserManager userManager = ObjectSpace.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<UserManager>();
ApplicationUser userAdmin = userManager.FindUserByName<ApplicationUser>(ObjectSpace, "Admin");
// If a user named 'Admin' doesn't exist in the database, create this user.
if(userAdmin == null) {
// Set a password if the standard authentication type is used.
string EmptyPassword = "";
userAdmin = userManager.CreateUser<ApplicationUser>(ObjectSpace, "Admin", EmptyPassword, (user) => {
// Add the Administrators role to the user.
user.Roles.Add(adminRole);
}).User;
}
if(ObjectSpace.FindObject<Company>(null) == null) {
Company company1 = ObjectSpace.CreateObject<Company>();
company1.Name = "Company 1";
company1.ApplicationUsers.Add(userAdmin);
ApplicationUser user1 = userManager.CreateUser<ApplicationUser>(ObjectSpace, "Sam", "", (user) => {
user.Roles.Add(defaultRole);
}).User;
ApplicationUser user2 = userManager.CreateUser<ApplicationUser>(ObjectSpace, "John", "", (user) => {
user.Roles.Add(defaultRole);
}).User;
Company company2 = ObjectSpace.CreateObject<Company>();
company2.Name = "Company 2";
company2.ApplicationUsers.Add(user1);
company2.ApplicationUsers.Add(user2);
}
ObjectSpace.CommitChanges(); //This line persists created object(s).
// ...
}
// ...
}
Middle-Tier-Specific Steps
Complete the following steps to configure an application with Middle-Tier security to work with custom login parameters.
Register the CustomLogonParameters Class in Client Applications
The CustomLogonParameters type must be explicitly registered in the client application as a known login parameter type. Call the AddKnownType(Type) method in the following files: MySolution.Blazor.Server/Program.cs (for Blazor) and MySolution.Win/Program.cs (for WinForms).
public static int Main(string[] args) {
// ...
WebApiDataServerHelper.AddKnownType(typeof(CustomLogonParameters));
// ...
}
Implement AuthenticationController and JwtTokenProviderService Classes
Implement the following classes in Middle Tier server application:
The
AuthenticationControllerclass specifies the type for deserializing incoming JSON.using DevExpress.ExpressApp; using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security; using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security.Authentication.ClientServer; using EFCoreCustomLogonAll.Module.Authentication; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; namespace EFCoreCustomLogonAll.WebApi.JWT; [ApiController] [Route("api/[controller]")] // This is a JWT authentication service sample. public class AuthenticationController : ControllerBase { readonly IAuthenticationTokenProvider tokenProvider; public AuthenticationController(IAuthenticationTokenProvider tokenProvider) { this.tokenProvider = tokenProvider; } [HttpPost("Authenticate")] public IActionResult Authenticate( [FromBody] CustomLogonParameters logonParameters ) { try { return Ok(tokenProvider.Authenticate(logonParameters)); } catch(AuthenticationException ex) { return Unauthorized(ex.GetJson()); } } }- The
JwtTokenProviderServiceclass allows you to customize logic that makes authentication decisions against the custom set of login parameters specified by a user.
Add the following code to the OnCustomAuthenticate event handler in Startup.cs files of Blazor and WinForms Middle Tier clients:
builder.Security
// ...
.UseMiddleTierMode(options => {
// ...
options.Events.OnCustomAuthenticate = (sender, security, args) => {
args.Handled = true;
HttpResponseMessage msg = args.HttpClient.PostAsJsonAsync("api/Authentication/Authenticate", (CustomLogonParameters)args.LogonParameters).GetAwaiter().GetResult();
string token = (string)msg.Content.ReadFromJsonAsync(typeof(string)).GetAwaiter().GetResult();
if(msg.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized) {
XafExceptions.Authentication.ThrowAuthenticationFailedFromResponse(token);
}
msg.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
args.HttpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("bearer", token);
};
Run the Application
Run the application to see custom parameters (Company and Application User lookup editors) in the login window.
Note
- When first running a Blazor application, it does not create a database or populate lookup editors. To create a database, either log in with an empty username or start the Middle Tier server.
- If using Middle Tier security, start the Middle Tier server before launching the Blazor or Win Forms client.
