How to: Use the Entity Framework 6 Code First in XAF
- 8 minutes to read
This topic demonstrates how to create a simple XAF application with a business model in a DbContext context.
Note
The Solution Wizard generates the code shown in this help topic when you create an application. Follow this article if you want to implement the demonstrated functionality in an existing XAF solution.
- A more complex example is provided in the EFDemoCodeFirst application that is shipped with XAF.
- ASP.NET Core Blazor applications do not support the EF 6 business model. You can use EF Core instead. For more information, refer to the following help topic: How to: Initialize Business Objects with Default Property Values in Entity Framework Core.
Tip
A complete sample project is available in the DevExpress Code Examples database at https://supportcenter.devexpress.com/ticket/details/e4375/obsolete-how-to-use-the-entity-framework-6-code-first-in-xaf.
1. Create an XAF Application
Create a new XAF solution called MySolution using the DevExpress v21.2 XAF Template Gallery. Select Entity Framework 6 at the Choose ORM step and click Finish.
2. Add the Entity Data Model and Context
In this topic, we will not describe entities and context implementation in detail, as it is already described in MSDN (see Code First to a New Database). Here, we assume that you are already familiar with creating an EF data model in code.
In the module project, implement the following Employee and Task classes.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; using DevExpress.Persistent.Base; // ... [DefaultClassOptions, ImageName("BO_Employee")] public class Employee : INotifyPropertyChanged { private int id; [Browsable(false)] public int Id { get { return id; } protected set { if (id != value) { id = value; OnPropertyChanged(); } } } private string firstName; public string FirstName { get { return firstName; } set { if (firstName != value) { firstName = value; OnPropertyChanged(); } } } private string lastName; public string LastName { get { return lastName; } set { if (lastName != value) { lastName = value; OnPropertyChanged(); } } } private DateTime? birthday; public DateTime? Birthday { get { return birthday; } set { if (birthday != value) { birthday = value; OnPropertyChanged(); } } } private List<Task> tasks; public virtual List<Task> Tasks { get { return tasks; } set { if (tasks != value) { tasks = value; OnPropertyChanged(); } } } #region INotifyPropertyChanged members public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null) { PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName)); } #endregion }The INotifyPropertyChanged interface allows you to receive notifications from business classes when their property values are changed.
In this code, you see the use of Data Annotations that influences UI generation - DefaultClassOptionsAttribute, ImageNameAttribute and FieldSizeAttribute, as well as the standard .NET Browsable attribute. As a result, the Employee and Task navigation items will be created, icons from the built-in image library will be used, the multiline editor will be displayed for the Task.Description property, and the service Id properties will be invisible in UI.
Note
You can use EF Power Tools to reverse engineer an existing database instead of writing code manually.
Implement the following DbContext descendant.
Note that the MyDBContext class should implement a constructor that takes the connectionString string parameter. This constructor will be called by the EFObjectSpaceProvider Object Space Provider internally.
3. Use the Entity Framework 6 Object Space Provider
To use the EFObjectSpace instances to access data in your application, modify the default implementation of the CreateDefaultObjectSpaceProvider method located in WinApplication.cs (WinApplication.vb) and WebApplication.cs (WebApplication.vb) files. For details on this code, refer to the Use the Entity Framework 6 Data Model topic.
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.DC;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.EF;
// ...
protected override void CreateDefaultObjectSpaceProvider(CreateCustomObjectSpaceProviderEventArgs args) {
args.ObjectSpaceProvider = new EFObjectSpaceProvider(typeof(MyDbContext), args.ConnectionString);
}
4. Specify the Connection String to the Database
To connect the database that was generated for your data model, specify the XafApplication.ConnectionString property in code or use the corresponding option in the App.config and Web.config files located in the WinForms and ASP.NET Web Forms application projects. Refer to the Connect an XAF Application to a Database Provider topic for details.
5. Run the Application
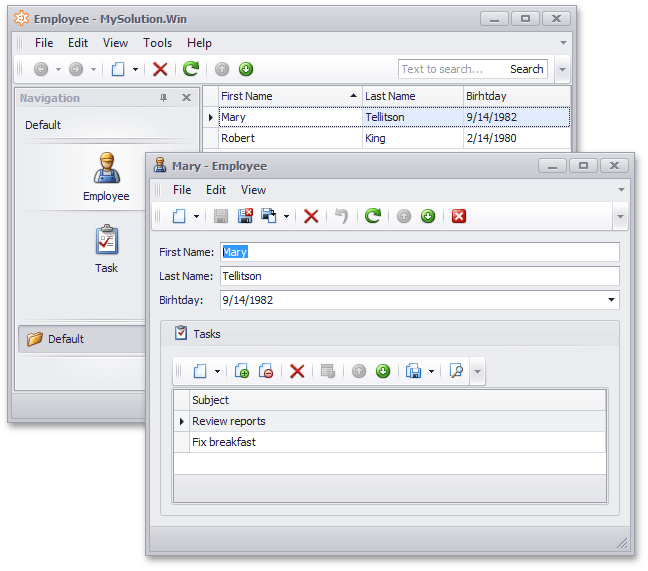
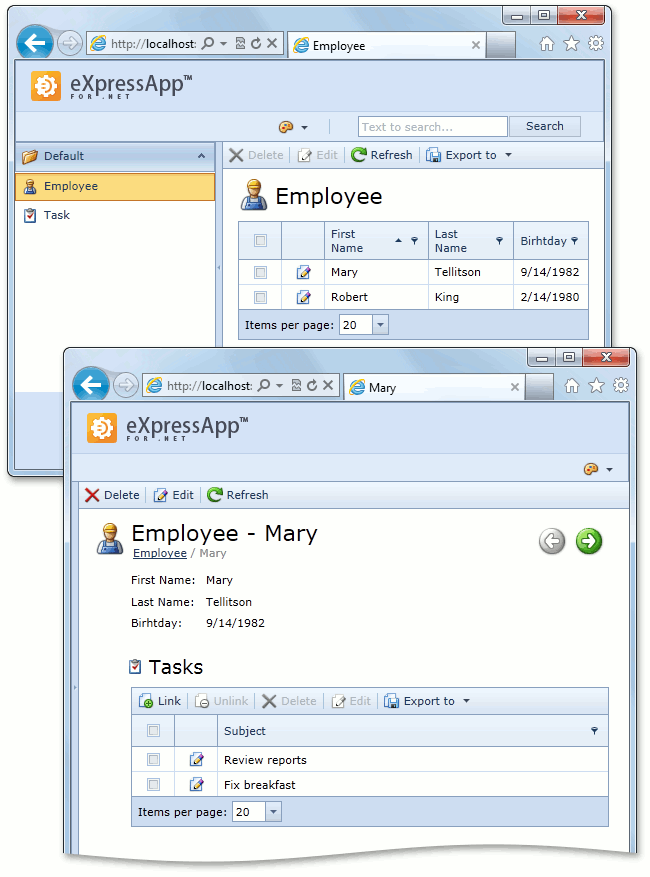
Now you can run both the Windows Forms and ASP.NET Web Forms applications. You will see that a UI is automatically generated for your data model.
Windows Forms:
ASP.NET Web Forms:
Note
To learn how to fill the database with predefined data, refer to the How to: Supply Initial Data for the Entity Framework 6 Data Model topic.