GridControl Class
Displays data from a data source in various formats (Views): Tabular, Banded Tabular, Cards, Windows UI-inspired Tiles and MS Windows Explorer-inspired UI.
Namespace: DevExpress.XtraGrid
Assembly: DevExpress.XtraGrid.v20.2.dll
NuGet Package: DevExpress.Win.Grid
Declaration
public class GridControl :
EditorContainer,
IScrollBarAnnotationsOwner<ScrollAnnotationKind>,
IScrollBarOwner,
IPrintableEx,
IPrintable,
IBasePrintable,
IPrintHeaderFooter,
INavigatableControl,
IToolTipControlClient,
IDXManagerPopupMenu,
IViewController,
IFilteredComponent,
IFilteredComponentBase,
IBoundControl,
ISupportXtraSerializer,
IGestureClient,
IGuideDescription,
ISearchControlColumnsClient,
ISearchControlClient,
ILogicalOwner,
ISupportFilterCriteriaDisplayStyleRemarks
The Data Grid is a container of Views, which display data from a bound list/table/collection in a specific format. If you bind the grid to a simple list/table/collection, a single View is required to present this data. To choose the data presentation format, set the GridControl.MainView property to any of the following objects:
- GridView - Displays data in a tabular form.
- BandedGridView - Displays data in a tabular form and organizes columns into bands.
- AdvBandedGridView - Displays data in a tabular form and organizes columns into bands. Supports complex data cell arrangements.
- CardView - Displays data records as cards, arranged down and then across. Card fields are always arranged in a single column.
- LayoutView - Displays records as cards in one or more columns, in one or more rows, in an ellipse (carousel mode), or as a single card at a time. Supports complex card field layouts, built-in groups, tabbed groups, and labels.
- TileView - Displays records as read-only tiles, using one of the following layout modes: default (standard table layout), list (tiles have no space between them), and Kanban. This View includes the Tile Template feature, which helps you arrange fields relative to other fields, specify absolute or relative field display bounds, etc.
- WinExplorerView - Displays records using one of seven styles supported by MS Windows Explorer - Small, Medium, Large, Extra Large, List, Tiles and Content.
If you bind the grid to a table with master-detail relationships, the View you assign to the GridControl.MainView property presents data from the master table, while the detail Views, which you can specify with the GridControl.LevelTree collection, present data from the child tables.
The following are main properties the Data Grid provides:
- GridControl.DataSource and GridControl.DataMember - Use these properties to bind the control to a data source.
- GridControl.MainView - Allows you to specify the View to present the top-level list/table/collection in the bound data source.
- GridControl.LevelTree - Allows you to associate master-detail relationships with Views.
- GridControl.Views - The collection of currently existing Views (main and detail Views) that are currently displayed onscreen.
- GridControl.UseEmbeddedNavigator - Allows you to enable the embedded record navigator.
See the following topics to learn more:
Example
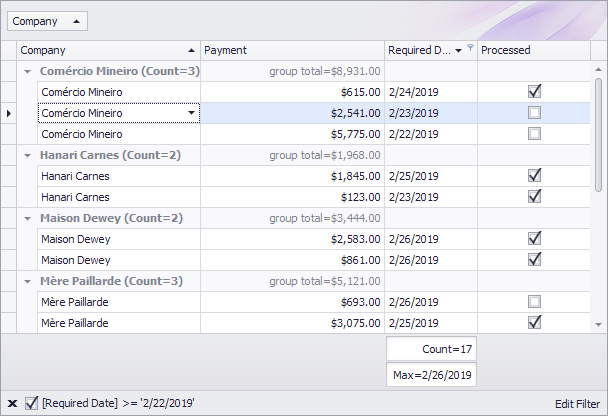
The following example creates a GridControl at runtime and shows how to perform basic customization tasks:
- Bind the grid to a data source
- Access the View that presents the underlying data
- Access columns
- Assign an in-place editor (a combobox) to a column
- Sort and group data
- Calculate total and group summaries
- Create a filter
- Hide columns and calculate column “best” widths
- Expand group rows
- Focus a specific cell
- Specify DataAnnotation attributes (column display names and data formats) at the data source level
using DevExpress.Data;
using DevExpress.XtraEditors.Repository;
using DevExpress.XtraGrid;
using DevExpress.XtraGrid.Columns;
using DevExpress.XtraGrid.Views.Grid;
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 {
public partial class Form1 : Form {
public Form1() {
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) {
GridControl gridControl1 = new GridControl();
gridControl1.Parent = this;
gridControl1.Dock = DockStyle.Fill;
gridControl1.DataSource = DataHelper.GetData(30);
// The grid automatically creates columns for the public fields found in the data source.
// Calling the gridView1.PopulateColumns method is not required unless the gridView1.OptionsBehavior.AutoPopulateColumns is disabled
// The grid automatically creates a GridView that presents the underlying data as a two-dimensional table.
GridView gridView1 = gridControl1.MainView as GridView;
// Obtain created columns.
GridColumn colCompany = gridView1.Columns["CompanyName"];
GridColumn colID = gridView1.Columns["ID"];
GridColumn colDate = gridView1.Columns["RequiredDate"];
GridColumn colPayment = gridView1.Columns["Value"];
GridColumn colProcessed = gridView1.Columns["Processed"];
// The Company column uses a ComboBox in-place editor that shows a list of available companies.
RepositoryItemComboBox riComboBox = new RepositoryItemComboBox();
riComboBox.Items.AddRange(DataHelper.companies);
gridControl1.RepositoryItems.Add(riComboBox);
colCompany.ColumnEdit = riComboBox;
// Hide a column.
colID.Visible = false;
//Group and sort data.
colCompany.GroupIndex = 0;
colDate.SortIndex = 0;
colDate.SortOrder = DevExpress.Data.ColumnSortOrder.Descending;
//Show group columns in the table.
gridView1.OptionsView.ShowGroupedColumns = true;
// Expand group rows.
gridView1.ExpandAllGroups();
// Apply a filter.
gridView1.ActiveFilterString = "[RequiredDate]>= #" + DateTime.Today.ToString() + "#";
//Calculate two total summaries.
colDate.Summary.Add(SummaryItemType.Count, colDate.FieldName, "Count={0}");
colDate.Summary.Add(SummaryItemType.Max, colDate.FieldName, "Max={0:d}");
gridView1.OptionsView.ShowFooter = true;
//Calculate group summaries.
GridGroupSummaryItem item = new GridGroupSummaryItem();
item.FieldName = colCompany.FieldName;
item.SummaryType = DevExpress.Data.SummaryItemType.Count;
gridView1.GroupSummary.Add(item);
GridGroupSummaryItem item1 = new GridGroupSummaryItem();
item1.FieldName = colPayment.FieldName;
item1.SummaryType = SummaryItemType.Sum;
item1.DisplayFormat = "group total={0:c2}";
item1.ShowInGroupColumnFooter = colPayment;
gridView1.GroupSummary.Add(item1);
// Forcibly move group footer summaries to positions in group rows under corresponding column headers.
gridView1.OptionsBehavior.AlignGroupSummaryInGroupRow = DevExpress.Utils.DefaultBoolean.True;
// Focus a specific cell.
gridView1.FocusedRowHandle = 1;
gridView1.FocusedColumn = colCompany;
// Optimize column widths.
colDate.BestFit();
colProcessed.BestFit();
}
}
public class Record : INotifyPropertyChanged {
public Record() {
}
int id;
public int ID {
get { return id; }
set {
if (id != value) {
id = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
string text;
[DisplayName("Company")]
public string CompanyName {
get { return text; }
set {
if (text != value) {
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(value))
throw new Exception();
text = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
Nullable<decimal> val;
[DataType(DataType.Currency)]
[DisplayName("Payment")]
public Nullable<decimal> Value {
get { return val; }
set {
if (val != value) {
val = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
DateTime dt;
[DisplayFormat(DataFormatString = "d")]
public DateTime RequiredDate {
get { return dt; }
set {
if (dt != value) {
dt = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
bool state;
public bool Processed {
get { return state; }
set {
if (state != value) {
state = value;
OnPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
public override string ToString() {
return string.Format("ID = {0}, Text = {1}", ID, CompanyName);
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = "") {
if (PropertyChanged != null)
PropertyChanged(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
public class DataHelper {
public static string[] companies = new string[] { "Hanari Carnes", "Que Delícia", "Romero y tomillo", "Mère Paillarde",
"Comércio Mineiro", "Reggiani Caseifici", "Maison Dewey" };
public static BindingList<Record> GetData(int count) {
BindingList<Record> records = new BindingList<Record>();
Random rnd = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
int n = rnd.Next(10);
records.Add(new Record() {
ID = i + 100,
CompanyName = companies[i % companies.Length],
RequiredDate = DateTime.Today.AddDays(n - 5),
Value = i % 2 == 0 ? (i + 1) * 123 : i * 231,
Processed = i % 2 == 0,
});
};
return records;
}
}
}