Restrictions and Protection
- 6 minutes to read
This topic describes how to prevent end-users from document modification. The Rich Text Editor provides three ways of solving this task: forbid editing the entire document, restrict performing certain operations and prevent inserting unnecessary elements.
Protect the Document
You can keep anyone from making changes in a document by enabling the document protection. Call the Document.Protect method to protect a document from editing using a given password and protection type (read-only or allow comments only). The default protection type is DocumentProtectionType.ReadOnly. The Document.IsDocumentProtected property indicates whether the document is protected.
Use the Document.Unprotect method to disable protection. Note that it unlocks the document without prompting the user for a password. To prompt the user with a password, execute the UnprotectDocumentCommand command.
Note
The RichEditControl protection affects only the document modification. The RichEditControl protection protects the document only against modifications. The document is opened without prompting for a password.
Grant Permission to Users
You can allow certain users to edit the protected document. To do that, create the Range Permissions as described in the steps below.
Set the users and user group lists. By default, the users list is empty and the user group list contains predefined entries (Everyone, Administrators, Contributors, Owners, Editors and Current User). To use a custom list of users or user groups, provide a custom service implementing the IUserListService or IUserGroupListService interface and register this service with the RichEditControl.ReplaceService<T> method. The RichEditControl does not associate users with groups, so user names and group names are independent.
Note
A complete sample project is available at https://github.com/DevExpress-Examples/range-permissions-simple-example-t445222
richEditControl1.ReplaceService<IUserListService>(new MyUserListService()); richEditControl1.ReplaceService<IUserGroupListService>(new MyGroupListService()); class MyGroupListService : IUserGroupListService { List<string> userGroups = CreateUserGroups(); static List<string> CreateUserGroups() { List<string> result = new List<string>(); result.Add(@"Everyone"); result.Add(@"Administrators"); result.Add(@"Contributors"); result.Add(@"Owners"); result.Add(@"Editors"); result.Add(@"Current User"); result.Add("Skywalkers"); result.Add("Nihlus"); return result; } public IList<string> GetUserGroups() { return userGroups; } } class MyUserListService : IUserListService { List<string> users = CreateUsers(); static List<string> CreateUsers() { List<string> result = new List<string>(); result.Add("Nancy Skywalker"); result.Add("Andrew Nihlus"); result.Add("Janet Skywalker"); result.Add("Margaret"); return result; } public IList<string> GetUsers() { return users; } }The edit permission is given depending on the authentication credentials. To define the identity of the current user, use the AuthenticationOptions class properties.
Note
A complete sample project is available at https://github.com/DevExpress-Examples/range-permissions-simple-example-t445222
- Call the SubDocument.BeginUpdateRangePermissions method to access the document range permissions collection.
- Create a new RangePermission object using the RangePermissionCollection.CreateRangePermission method.
Utilize the RangePermission.UserName and/or RangePermission.Group properties to specify the specific user and/or the group of users that are eligible to edit the document.
The table below shows what properties should have the same value to make the range editable to the current user.
This property value
Should be equal to
“Everyone”
- Add the created object to the corresponding collection.
- Finalize the modification with the SubDocument.EndUpdateRangePermissions method.
Enable document protection as described above.
Note
A complete sample project is available at https://github.com/DevExpress-Examples/range-permissions-simple-example-t445222
RangePermissionCollection rangePermissions = richEditControl1.Document.BeginUpdateRangePermissions(); RangePermission permission = rangePermissions.CreateRangePermission(rangeAdmin); permission.UserName = "Nancy Skywalker"; permission.Group = "Skywalkers"; rangePermissions.Add(permission); RangePermission permission2 = rangePermissions.CreateRangePermission(rangeBody); permission2.Group = @"Everyone"; rangePermissions.Add(permission2); RangePermission permission3 = rangePermissions.CreateRangePermission(rangeSignature); permission3.Group = "Nihlus"; rangePermissions.Add(permission3); richEditControl1.Document.EndUpdateRangePermissions(rangePermissions); // Enforce protection and set password. richEditControl1.Document.Protect("123");Customize the appearance of the protected ranges in the document. At runtime, they are highlighted with a certain color and enclosed with bookmark brackets. By default, the highlighting color is selected from a predefined colors collection. This is done to specify different highlighting colors for ranges that belong to different user groups. There is no straightforward way to change these colors manually.

You can set the highlighting options to the ranges that are editable to the current user only. To do that, use the RangePermissionOptions properties. They can be accessed through the Options.RangePermissions notation.
Note
A complete sample project is available at https://github.com/DevExpress-Examples/range-permissions-simple-example-t445222
Restrict Performing Operations
Protect the document from editing, copying or printing by restricting the corresponding functions. To perform the restriction, access the desired operation using the RichEditControlOptionsBase.Behavior property and specify its behavior. Depending on the selected property value, the application menu buttons that correspond to restricted operations can be disabled or hidden. Additionally, you can prevent the showing of the context menu. To do that, use the RichEditBehaviorOptions.ShowPopupMenu property.
private void RestrictOperations()
{
richEditControl.Options.Behavior.Drag = DocumentCapability.Disabled;
richEditControl.Options.Behavior.Printing = DocumentCapability.Disabled;
richEditControl.Options.Behavior.Copy = DocumentCapability.Hidden;
}
The code execution result is illustrated in the picture below. Such buttons as Print, Quick Print and Print Preview are disabled, whereas the Copy item is hidden from the context menu.
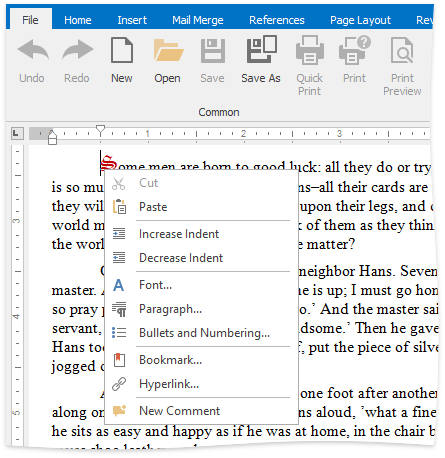
Restrict Using Document Elements
You can also forbid the formatting of characters and paragraphs or the use of certain document elements, such as pictures, tables, fields, etc.
These restrictions can be specified by the RichEditControlOptionsBase.DocumentCapabilities property, as illustrated in the following code sample.
private void RestrictFormatting()
{
richEditControl.Options.DocumentCapabilities.CharacterFormatting = DocumentCapability.Hidden;
richEditControl.Options.DocumentCapabilities.Comments = DocumentCapability.Disabled;
richEditControl.Options.DocumentCapabilities.FloatingObjects = DocumentCapability.Hidden;
}
Similar with operation restrictions, the application menu items that correlate with the forbidden actions can be hidden or disabled. If a document is loaded after certain restrictions are applied, the corresponding characteristics are set to default and the restricted objects are not created. In case of the floating objects, the existing floating pictures are converted into inline pictures, whereas the text boxes and their contents are hidden.