Worksheet Interface
Namespace: DevExpress.Spreadsheet
Assembly: DevExpress.Spreadsheet.v19.1.Core.dll
Declaration
Related API Members
The following members return Worksheet objects:
Remarks
A worksheet is a single page within a document. It is divided into rows and columns and is used to store and edit spreadsheet data. Use one of the following properties to access a collection of worksheets in a workbook:
-
Returns the worksheet collection for a non-visual Workbook.
-
Returns the worksheet collection for the Spreadsheet control’s document.
Worksheet Content
The following table lists properties used to access and manage different worksheet elements:
| Property | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Worksheet.Rows | Returns the collection of worksheet rows. | Access a Row or Column |
| Worksheet.Columns | Returns the collection of worksheet columns. | Access a Row or Column |
| Worksheet.Cells | Returns the cell collection. | Access a Cell in a Worksheet |
| Worksheet.Range | Provides access to a cell range. | Access a Cell Range in a Worksheet |
| Worksheet.Charts | Provides access to the collection of all charts in a worksheet. | Create a Chart |
| Worksheet.Pictures | Returns the picture collection. | Insert a Picture |
| Worksheet.Shapes | Returns all drawing objects embedded in a worksheet: shapes, pictures, and charts. | Create a Shape |
| Worksheet.Comments | Returns the collection of comments attached to worksheet cells. | Add a Comment To a Cell |
| Worksheet.Hyperlinks | Returns the hyperlink collection. | Add a Hyperlink to a Cell |
| Worksheet.Tables | Provides access to the collection of worksheet tables. | Create a Table |
| Worksheet.PivotTables | Provides access to the collection of pivot tables. | Create a Pivot Table |
| Worksheet.DefinedNames | Provides access to worksheet-level defined names. | Create a Defined Name |
Access a Worksheet
Use the WorksheetCollection.Item property to access a worksheet in a workbook.
Obtain the worksheet at the specified index
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
// ...
// Access the worksheet collection.
WorksheetCollection worksheets = workbook.Worksheets;
// Access the first worksheet.
Worksheet worksheet1 = workbook.Worksheets[0];
A worksheet index is zero-based. It specifies the worksheet position within a collection.
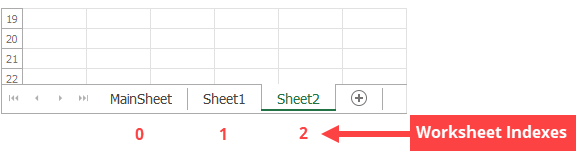
Obtain the worksheet with a given name
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
// ...
// Access the worksheet collection.
WorksheetCollection worksheets = workbook.Worksheets;
// Access the worksheet with the specified name.
Worksheet worksheet2 = workbook.Worksheets["MainSheet"];
A worksheet name is unique within the collection and is shown on a worksheet tab.
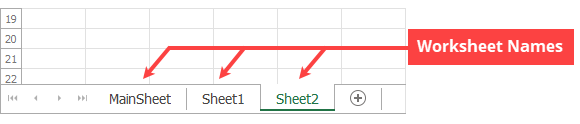
Add a New Worksheet
Use the WorksheetCollection.Add method to add a worksheet to the end of the worksheet collection.
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
// ...
// Add a worksheet with the default name.
// Default names are "Sheet1", "Sheet2", ..., "SheetN".
workbook.Worksheets.Add();
// Add new worksheets with the specified names.
workbook.Worksheets.Add().Name = "TestSheet1";
workbook.Worksheets.Add("TestSheet2");

The WorksheetCollection.Insert method allows you to insert a worksheet at the specified position in the collection.
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
// ...
// Insert a worksheet at the second position in the workbook.
workbook.Worksheets.Insert(1, "TestSheet3");
// Insert a worksheet with the default name at the fourth position in the workbook.
workbook.Worksheets.Insert(3);
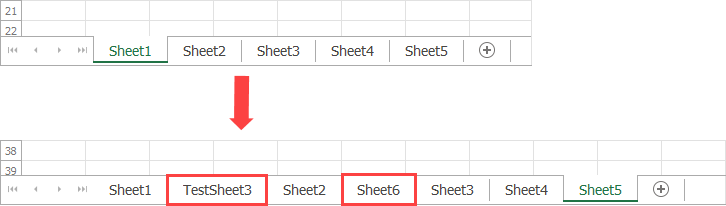
Rename a Worksheet
Use the Worksheet.Name property to change the worksheet name.
Set an Active Worksheet
Use the WorksheetCollection.ActiveWorksheet property to specify the active worksheet in a workbook.
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
// ...
// Set "Sheet2" as the active worksheet.
workbook.Worksheets.ActiveWorksheet = workbook.Worksheets["Sheet2"];
Change a Worksheet’s Appearance
Use the Worksheet.ActiveView property to access display settings for a worksheet.
Hide worksheet elements
WorksheetView.ShowGridlines - shows or hides gridlines.
WorksheetView.ShowHeadings - shows or hides row and column headings.
// Hide gridlines on the first worksheet.
workbook.Worksheets[0].ActiveView.ShowGridlines = false;
// Hide row and column headings on the first worksheet.
workbook.Worksheets[0].ActiveView.ShowHeadings = false;
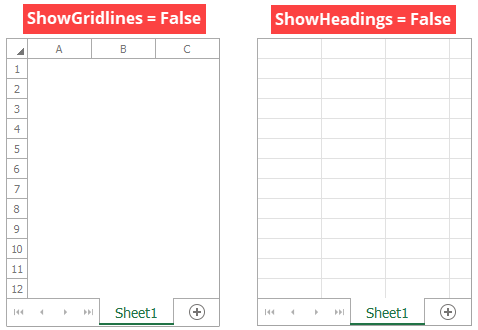
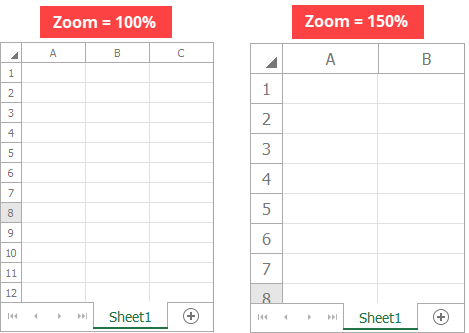
Change the zoom level
Use the WorksheetView.Zoom property to change the worksheet zoom percentage.
Specify the tab color
Use the WorksheetView.TabColor property to change the color of a worksheet tab.
// Change the tab color for the first worksheet.
workbook.Worksheets[0].ActiveView.TabColor = Color.LightSkyBlue;
Copy a Worksheet
Use the Worksheet.CopyFrom method to copy data from the specified worksheet to the current Worksheet instance.
Copy a worksheet within a workbook
// Add a new worksheet to the workbook.
workbook.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1_Copy");
// Copy all information from "Sheet1"
// to the newly created worksheet.
workbook.Worksheets["Sheet1_Copy"].CopyFrom(workbook.Worksheets["Sheet1"]);
Copy a worksheet between workbooks
Important
You need an active license for the DevExpress Office File API Subscription or DevExpress Universal Subscription to use this example in production code.
// Create a source workbook.
Workbook sourceWorkbook = new Workbook();
// Create a destination workbook.
Workbook destWorkbook = new Workbook();
// Add data to the first worksheet of the source workbook.
sourceWorkbook.Worksheets[0].Cells["A1"].Value = "A worksheet to copy";
sourceWorkbook.Worksheets[0].Cells["A1"].Font.Color = Color.ForestGreen;
// Copy the first worksheet of the source workbook
// to the destination workbook.
destWorkbook.Worksheets[0].CopyFrom(sourceWorkbook.Worksheets[0]);
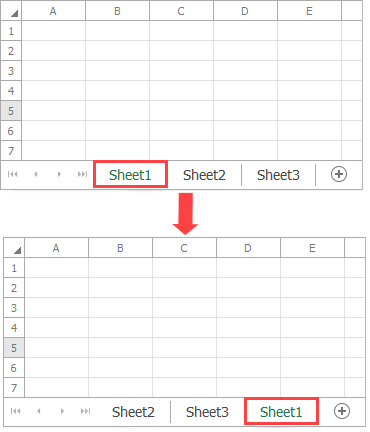
Move a Worksheet
Use the following methods to move a worksheet to another location in a workbook:
Worksheet.Move - moves a worksheet to a specific position in the document;
Worksheet.MoveAfter - positions a worksheet after the specified worksheet;
Worksheet.MoveBefore - positions a worksheet before the specified worksheet;
Worksheet.MoveToBeginning - moves a worksheet to the first position in the workbook;
Worksheet.MoveToEnd - moves a worksheet to the last position in the workbook.
// Move the first worksheet to the last position in the document.
workbook.Worksheets[0].MoveToEnd();
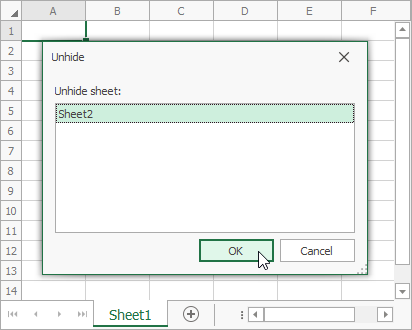
Hide a Worksheet
Use the Worksheet.Visible or Worksheet.VisibilityType property to control the visibility of a worksheet.
// Hide the "Sheet2" worksheet.
// End users can unhide this worksheet from the user interface.
workbook.Worksheets["Sheet2"].Visible = false;
// Mark the "Sheet3" worksheet as "very hidden".
// End users cannot unhide this worksheet from the user interface.
workbook.Worksheets["Sheet3"].VisibilityType = WorksheetVisibilityType.VeryHidden;
Note
A workbook must contain at least one visible worksheet.
Delete a Worksheet
Use the following methods to delete a worksheet:
WorksheetCollection.Remove - removes a specific worksheet from the collection.
WorksheetCollection.RemoveAt - removes the worksheet with the specified index from the collection.
Note
A workbook must contain at least one visible worksheet.
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
// ...
// Delete the first worksheet from the workbook.
workbook.Worksheets.RemoveAt(0);
// Delete the "Sheet2" worksheet from the workbook.
workbook.Worksheets.Remove(workbook.Worksheets["Sheet2"]);

Print a Worksheet
Use the Worksheet.Print method to print a worksheet.
// Send the active worksheet to the default printer.
workbook.Worksheets.ActiveWorksheet.Print();
Specify printer settings
To select a printer and specify printer settings, create a PrinterSettings class instance and pass it to the Worksheet.Print method.
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
using System.Drawing.Printing;
// ...
// Create an object that contains printer settings.
PrinterSettings printerSettings = new PrinterSettings();
// Specify that the first two pages should be printed.
printerSettings.PrintRange = PrintRange.SomePages;
printerSettings.FromPage = 1;
printerSettings.ToPage = 2;
// Set the number of copies to print.
printerSettings.Copies = 2;
// Print the active worksheet.
workbook.Worksheets.ActiveWorksheet.Print(printerSettings);
Print multiple worksheets
The Workbook.Print method allows you to print multiple worksheets at once.
Important
You require a license to the DevExpress Office File API or DevExpress Universal Subscription to use this method in production code.
using DevExpress.Spreadsheet;
using System.Drawing.Printing;
// ...
// Create a new Workbook object.
Workbook workbook = new Workbook();
// Load a document from a file.
workbook.LoadDocument("Document.xlsx");
// Create an object that contains printer settings.
PrinterSettings printerSettings = new PrinterSettings();
// Define the printer to use.
printerSettings.PrinterName = "Microsoft Print to PDF";
printerSettings.PrintToFile = true;
printerSettings.PrintFileName = "PrintedDocument.pdf";
// Print specific worksheets in the document.
workbook.Print(printerSettings, "Sheet1", "Sheet2");
Define page options
Use the Worksheet.ActiveView property to access and specify general page options.
WorksheetView.Orientation - sets the page orientation.
WorksheetView.Margins - defines page margins.
// Set the measurement unit to inches. workbook.Unit = DevExpress.Office.DocumentUnit.Inch; // Access page margins. Margins pageMargins = workbook.Worksheets[0].ActiveView.Margins; // Specify page margins. pageMargins.Left = 1; pageMargins.Top = 1.5F; pageMargins.Right = 1; pageMargins.Bottom = 0.8F; // Specify header and footer margins. pageMargins.Header = 1; pageMargins.Footer = 0.4F;WorksheetView.PaperKind - specifies paper size.
Specify print options
The Worksheet.PrintOptions property allows you to access and configure print options, as shown in the following example:
// Access an object that contains print options.
WorksheetPrintOptions printOptions = worksheet.PrintOptions;
// Do not print gridlines.
printOptions.PrintGridlines = false;
// Scale the worksheet to fit within the width of one page.
printOptions.FitToPage = true;
printOptions.FitToWidth = 1;
// Print in black and white.
printOptions.BlackAndWhite = true;
// Print a dash instead of the cell error message.
printOptions.ErrorsPrintMode = ErrorsPrintMode.Dash;
Protect a Worksheet
Use the Worksheet.Protect method to protect a worksheet. The WorksheetProtectionPermissions enumeration members allow you to specify actions that users can execute on the protected worksheet.
When protection is applied, worksheet cells become read-only. To allow users to edit a specific cell, set its Protection.Locked attribute to false.
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Protect the worksheet.
// End users are only allowed to select worksheet cells.
if (!worksheet.IsProtected)
worksheet.Protect("password", WorksheetProtectionPermissions.Default);
Note
If a worksheet is already protected, the Protect method throws an exception. Check the Worksheet.IsProtected value before the method call.
Unprotect a worksheet
Use the Worksheet.Unprotect method to remove worksheet protection.
Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[0];
// Unprotect the worksheet.
if (worksheet.IsProtected) {
worksheet.Unprotect("password");
}
Scroll a Worksheet
Use the Worksheet.ScrollTo method to scroll a worksheet to the specified column and row.
// Scroll the worksheet to the "C3" cell.
workbook.Worksheets[0].ScrollTo(worksheet("C3"));
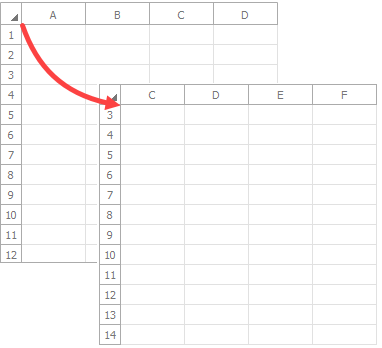
Call the Worksheet.ScrollToColumn method to scroll a worksheet to a specific column.
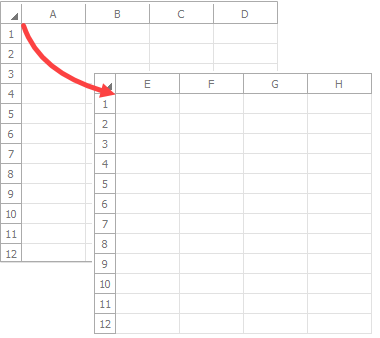
Call the Worksheet.ScrollToRow method to scroll a worksheet to a specific row.
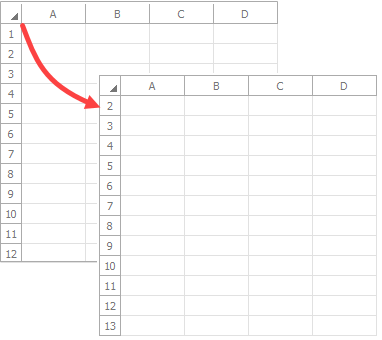
Note
If you scroll to a hidden column, the worksheet is scrolled to the first visible column to the right of the specified column.
If you scroll to a hidden row, the worksheet is scrolled to the first visible row below the specified row.